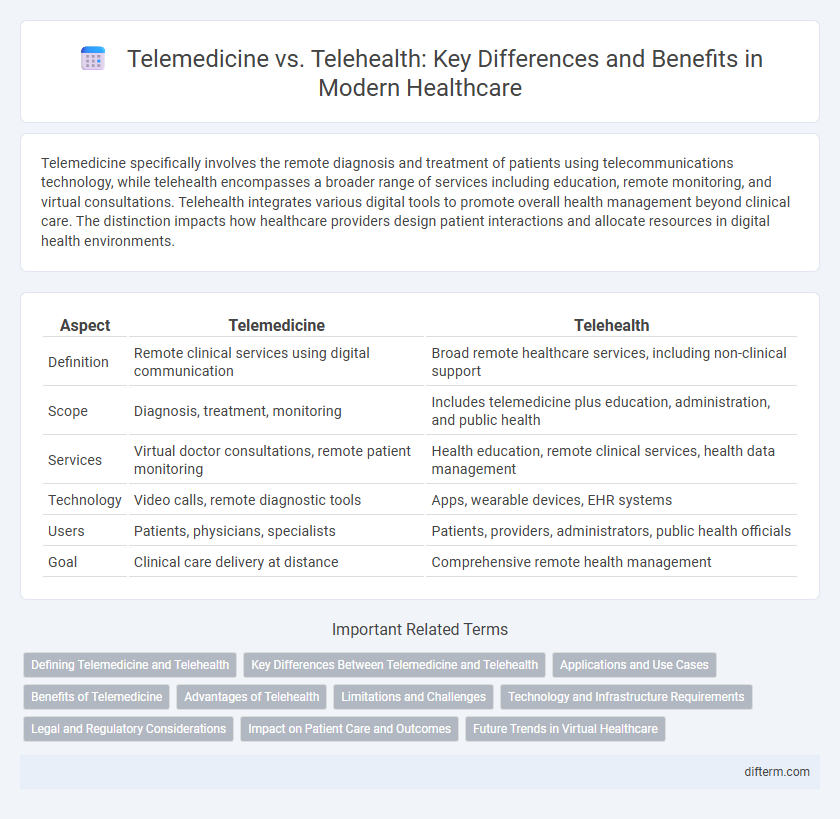
Telemedicine specifically involves the remote diagnosis and treatment of patients using telecommunications technology, while telehealth encompasses a broader range of services including education, remote monitoring, and virtual consultations. Telehealth integrates various digital tools to promote overall health management beyond clinical care. The distinction impacts how healthcare providers design patient interactions and allocate resources in digital health environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Telemedicine | Telehealth |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Remote clinical services using digital communication | Broad remote healthcare services, including non-clinical support |
| Scope | Diagnosis, treatment, monitoring | Includes telemedicine plus education, administration, and public health |
| Services | Virtual doctor consultations, remote patient monitoring | Health education, remote clinical services, health data management |
| Technology | Video calls, remote diagnostic tools | Apps, wearable devices, EHR systems |
| Users | Patients, physicians, specialists | Patients, providers, administrators, public health officials |
| Goal | Clinical care delivery at distance | Comprehensive remote health management |
Defining Telemedicine and Telehealth
Telemedicine refers specifically to the remote diagnosis and treatment of patients through digital communication technologies, focusing primarily on clinical services. Telehealth encompasses a broader scope, including non-clinical services such as health education, administrative meetings, and remote monitoring alongside telemedicine functionalities. Both leverage tools like video consultations, mobile health apps, and wearable devices, but telehealth integrates a wider range of health-related services beyond direct medical care.
Key Differences Between Telemedicine and Telehealth
Telemedicine specifically refers to the delivery of clinical services remotely using telecommunications technology, focusing primarily on diagnosis and treatment by healthcare professionals. Telehealth encompasses a broader scope, including non-clinical services such as patient education, health monitoring, and administrative meetings alongside telemedicine. The main difference lies in telemedicine's clinical contact emphasis, while telehealth integrates both clinical and non-clinical healthcare support through digital platforms.
Applications and Use Cases
Telemedicine primarily focuses on remote clinical services such as diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care using video conferencing and digital monitoring tools. Telehealth encompasses a broader range of applications, including health education, remote patient monitoring, mental health counseling, and chronic disease management. Both telemedicine and telehealth expand healthcare access in rural areas, improve patient outcomes, and reduce hospital readmissions through continuous remote support.
Benefits of Telemedicine
Telemedicine enhances healthcare access by allowing remote diagnosis and treatment, reducing the need for in-person visits and travel time. It supports chronic disease management through continuous monitoring and timely interventions, improving patient outcomes. Cost savings arise from decreased hospital admissions and efficient use of healthcare resources, benefiting both patients and providers.
Advantages of Telehealth
Telehealth expands access to comprehensive healthcare services by integrating remote clinical care, patient education, and health monitoring, surpassing telemedicine's focus on virtual doctor visits. It enhances patient engagement and chronic disease management through real-time data sharing and interactive tools, promoting proactive health maintenance. Cost savings and improved health outcomes are evident as telehealth reduces hospital readmissions and facilitates timely interventions across diverse populations.
Limitations and Challenges
Telemedicine faces limitations such as restricted physical examinations and reliance on stable internet connectivity, which can impact diagnostic accuracy and patient engagement. Telehealth encounters challenges including data privacy concerns, regulatory variability across regions, and disparities in technology access among underserved populations. Both modalities require robust cybersecurity measures, enhanced provider training, and infrastructure investment to address these barriers effectively.
Technology and Infrastructure Requirements
Telemedicine requires advanced video conferencing technology and secure data transmission infrastructure to enable real-time patient consultations and remote diagnostics. Telehealth encompasses a broader range of digital health services, including remote patient monitoring devices, mobile health apps, and electronic health record integration, demanding extensive interoperability and scalable network capabilities. Both rely heavily on robust broadband connectivity, cybersecurity measures, and compliant cloud storage solutions to ensure data privacy and continuous service delivery.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Telemedicine and telehealth are governed by distinct legal and regulatory frameworks that impact licensure, patient privacy, and reimbursement policies. Telemedicine specifically requires compliance with state medical board regulations and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to ensure secure patient data transmission and service delivery. Telehealth encompasses a broader range of services, often subject to varying telecommunication laws and changing federal guidelines, demanding continuous monitoring of jurisdictional requirements to maintain compliance.
Impact on Patient Care and Outcomes
Telemedicine enhances patient care by enabling remote diagnosis and treatment, reducing travel barriers and allowing timely medical interventions, which directly improve health outcomes. Telehealth broadens this impact by incorporating education, monitoring, and support services, fostering ongoing patient engagement and chronic disease management. Both approaches leverage technology to increase access, convenience, and efficiency, ultimately resulting in higher patient satisfaction and better clinical results.
Future Trends in Virtual Healthcare
Telemedicine and telehealth are evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in AI-powered diagnostics, wearable health devices, and real-time remote patient monitoring systems. Future trends emphasize integrated virtual care platforms that combine telemedicine consultations with telehealth preventive services to enhance patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. Interoperability of electronic health records (EHR) and expanded broadband access will further accelerate the adoption of comprehensive virtual healthcare solutions worldwide.
Telemedicine vs Telehealth Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com