Telehealth encompasses a broad range of remote healthcare services, including education, monitoring, and consultations, while telemedicine specifically refers to clinical services delivered via technology to diagnose and treat patients. Both improve access to care, but telehealth offers a more comprehensive approach by integrating non-clinical services such as patient education and health administration. Understanding the distinction enhances the effective deployment of digital health solutions for improved patient outcomes.
Table of Comparison
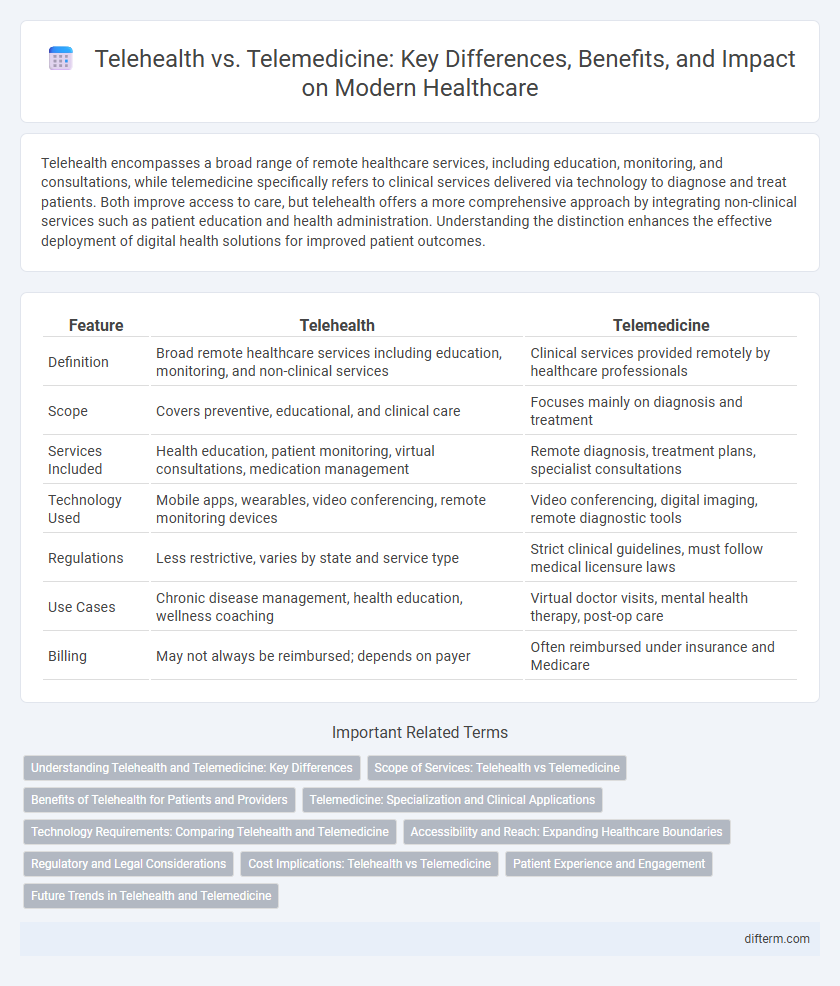
| Feature | Telehealth | Telemedicine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broad remote healthcare services including education, monitoring, and non-clinical services | Clinical services provided remotely by healthcare professionals |
| Scope | Covers preventive, educational, and clinical care | Focuses mainly on diagnosis and treatment |
| Services Included | Health education, patient monitoring, virtual consultations, medication management | Remote diagnosis, treatment plans, specialist consultations |
| Technology Used | Mobile apps, wearables, video conferencing, remote monitoring devices | Video conferencing, digital imaging, remote diagnostic tools |
| Regulations | Less restrictive, varies by state and service type | Strict clinical guidelines, must follow medical licensure laws |
| Use Cases | Chronic disease management, health education, wellness coaching | Virtual doctor visits, mental health therapy, post-op care |
| Billing | May not always be reimbursed; depends on payer | Often reimbursed under insurance and Medicare |
Understanding Telehealth and Telemedicine: Key Differences
Telehealth encompasses a broad range of digital healthcare services, including remote patient monitoring, health education, and virtual consultations, while telemedicine specifically refers to the delivery of clinical services via video calls or phone. Telehealth integrates multidisciplinary care and non-clinical support, expanding access beyond direct physician interactions characteristic of telemedicine. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimizing healthcare delivery, improving patient outcomes, and guiding regulatory and reimbursement policies.
Scope of Services: Telehealth vs Telemedicine
Telehealth encompasses a broad range of remote healthcare services, including preventive care, health education, and chronic disease management, while telemedicine specifically refers to the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions via virtual consultations. Telehealth integrates non-clinical services such as patient monitoring and administrative meetings, contrasting with telemedicine's focus on clinical interactions between patients and healthcare providers. Both modalities utilize digital communication tools, but telehealth's scope extends beyond the clinical boundaries of telemedicine to support overall health and wellness.
Benefits of Telehealth for Patients and Providers
Telehealth expands access to healthcare services by enabling remote consultations, reducing travel time, and increasing appointment availability for patients. It enhances patient engagement through real-time monitoring and personalized care, leading to improved health outcomes. Providers benefit from streamlined workflows, reduced overhead costs, and greater flexibility, which collectively improve the efficiency and quality of care delivery.
Telemedicine: Specialization and Clinical Applications
Telemedicine encompasses specialized clinical applications that enable healthcare providers to diagnose, treat, and monitor patients remotely using advanced technology. It supports diverse medical fields such as cardiology, dermatology, and psychiatry by offering real-time consultations, remote patient monitoring, and electronic health record integration. These capabilities improve patient access to specialized care, enhance treatment precision, and facilitate continuous clinical management outside traditional healthcare settings.
Technology Requirements: Comparing Telehealth and Telemedicine
Telehealth platforms require a broader range of technology, including smartphones, tablets, and remote monitoring devices to facilitate diverse health services beyond clinical visits. Telemedicine specifically relies on high-quality video conferencing software, secure electronic health records (EHR) integration, and compliant data encryption to conduct remote clinical diagnostics and treatment effectively. Both modalities depend on reliable internet connectivity and advanced cybersecurity measures to ensure patient privacy and seamless communication.
Accessibility and Reach: Expanding Healthcare Boundaries
Telehealth expands healthcare access by encompassing a wide range of services like remote patient monitoring, health education, and virtual consultations, reaching underserved populations beyond traditional clinical settings. Telemedicine specifically focuses on clinical services via telecommunications technology, enabling direct diagnosis and treatment across geographic barriers. Together, they break down accessibility barriers, improve healthcare delivery in rural and remote areas, and extend specialist reach to patients with limited mobility.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Telehealth and telemedicine both face evolving regulatory frameworks that govern patient privacy, data security, and licensure requirements across different jurisdictions. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establishes strict standards for protecting electronic health information, impacting telehealth platforms and telemedicine consultations. Legal considerations also include state-specific medical licensing laws and reimbursement policies, which vary widely and influence the delivery of remote healthcare services.
Cost Implications: Telehealth vs Telemedicine
Telehealth services generally offer broader cost-saving benefits by integrating remote patient monitoring, virtual visits, and health education, reducing administrative overhead and travel expenses. Telemedicine, while a subset focused on clinical services, provides direct cost reductions through fewer in-person office visits and streamlined chronic disease management. Healthcare systems adopting telehealth report significant decreases in overall care delivery costs, enhancing patient access and financial efficiency.
Patient Experience and Engagement
Telehealth expands patient experience by incorporating remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and continuous health education, enhancing engagement beyond traditional clinical visits. Telemedicine specifically targets clinical diagnosis and treatment through video calls or digital transmission of medical data, improving accessibility and convenience for patients. Both approaches leverage technology to foster proactive patient involvement, but telehealth offers a broader platform for sustained health management and personalized care.
Future Trends in Telehealth and Telemedicine
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven diagnostics and 5G connectivity are poised to enhance the scalability and accuracy of telehealth and telemedicine services. Integration of wearable devices and remote patient monitoring systems will provide real-time health data, improving personalized care and chronic disease management. Expansion of virtual reality applications is expected to transform tele-rehabilitation and mental health treatments, driving the next wave of innovation in digital healthcare.
Telehealth vs Telemedicine Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com