Psoriasis and eczema are chronic skin conditions that cause redness, itching, and inflammation but differ in their underlying causes and symptoms. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by thick, scaly patches of skin, often appearing on the elbows, knees, and scalp, while eczema typically results from allergic reactions or irritants, causing dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Effective management depends on accurate diagnosis and tailored treatments such as topical steroids, moisturizers, and lifestyle adjustments to reduce flare-ups.
Table of Comparison
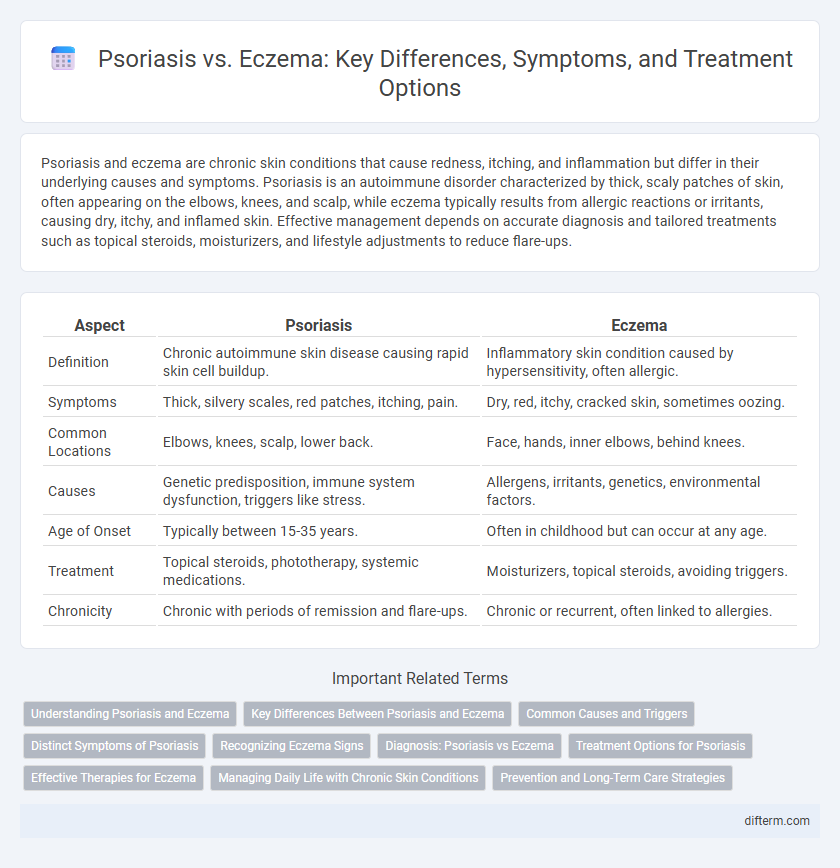
| Aspect | Psoriasis | Eczema |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic autoimmune skin disease causing rapid skin cell buildup. | Inflammatory skin condition caused by hypersensitivity, often allergic. |
| Symptoms | Thick, silvery scales, red patches, itching, pain. | Dry, red, itchy, cracked skin, sometimes oozing. |
| Common Locations | Elbows, knees, scalp, lower back. | Face, hands, inner elbows, behind knees. |
| Causes | Genetic predisposition, immune system dysfunction, triggers like stress. | Allergens, irritants, genetics, environmental factors. |
| Age of Onset | Typically between 15-35 years. | Often in childhood but can occur at any age. |
| Treatment | Topical steroids, phototherapy, systemic medications. | Moisturizers, topical steroids, avoiding triggers. |
| Chronicity | Chronic with periods of remission and flare-ups. | Chronic or recurrent, often linked to allergies. |
Understanding Psoriasis and Eczema
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by rapid skin cell turnover resulting in thick, red, scaly patches often found on the scalp, elbows, and knees. Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, involves inflammation and a defective skin barrier leading to itchy, dry, and cracked skin commonly appearing on the hands, face, and behind the knees. Both conditions share symptoms like redness and itching but differ fundamentally in cause, presentation, and treatment approaches.
Key Differences Between Psoriasis and Eczema
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, causing thick, silvery scales and red patches, while eczema (atopic dermatitis) results from a compromised skin barrier leading to itchy, inflamed, and dry skin. Psoriasis often affects the scalp, elbows, and knees and may be linked to systemic conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, whereas eczema primarily targets flexural areas like the inside of elbows and behind the knees and is frequently associated with allergies and asthma. Treatment options differ significantly; psoriasis typically requires immunosuppressants or biologics, while eczema management focuses on moisturizers, corticosteroids, and avoiding irritants.
Common Causes and Triggers
Psoriasis and eczema both result from immune system dysfunction, with genetic predisposition playing a significant role in their development. Common triggers for psoriasis include stress, infections, cold weather, and certain medications, while eczema flare-ups are often caused by allergens, irritants like soaps, heat, and sweat. Both conditions share environmental factors such as dry skin and seasonal changes that exacerbate symptoms.
Distinct Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is characterized by thick, red patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales, commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Unlike eczema, psoriasis lesions are well-defined with a sharp border and may cause itching, burning, or soreness. The presence of nail changes such as pitting, discoloration, and separation from the nail bed is a distinct symptom often associated with psoriasis but not eczema.
Recognizing Eczema Signs
Eczema is characterized by red, inflamed, and itchy skin, often appearing as dry, scaly patches that may ooze or crust over. Unlike psoriasis, which typically forms thick, silvery scales, eczema lesions tend to be more irregular and are commonly found on the face, inside the elbows, and behind the knees. Early recognition of eczema signs, such as persistent itching and skin sensitivity, is essential for effective management and preventing flare-ups.
Diagnosis: Psoriasis vs Eczema
Psoriasis diagnosis often involves identifying thick, scaly plaques with a silvery appearance, while eczema is characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin patches. Dermatologists use clinical examination and patient history, sometimes supplemented with skin biopsies, to differentiate between these chronic inflammatory skin conditions. Accurate diagnosis is crucial as psoriasis typically presents with well-defined lesions and may affect nails and joints, whereas eczema tends to have poorly defined borders and is commonly linked to allergic reactions or irritants.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Psoriasis treatment options primarily include topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and phototherapy to reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth. Systemic treatments such as biologics or oral medications like methotrexate target immune system dysfunction in moderate to severe psoriasis cases. Emerging therapies focus on interleukin inhibitors, offering targeted relief and improved outcomes compared to traditional treatments.
Effective Therapies for Eczema
Effective therapies for eczema include topical corticosteroids, which reduce inflammation and itching, and calcineurin inhibitors that modulate immune response without thinning the skin. Moisturizers with ceramides help restore the skin barrier, preventing dryness and flare-ups, while antihistamines can alleviate severe itching. Phototherapy using UVB light is also a proven treatment for chronic eczema, improving skin condition in resistant cases.
Managing Daily Life with Chronic Skin Conditions
Managing daily life with psoriasis and eczema requires consistent skincare routines tailored to reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups. Moisturizing multiple times a day, avoiding known irritants, and using prescribed topical treatments help maintain skin barrier function and alleviate symptoms. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques and regular dermatologist consultations further support long-term control and improve quality of life.
Prevention and Long-Term Care Strategies
Effective prevention of psoriasis and eczema involves maintaining proper skin hydration with moisturizers containing ceramides and avoiding known irritants such as harsh soaps and allergens. Long-term care strategies include consistent use of prescribed topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors to reduce inflammation, along with regular dermatologist consultations to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment plans. Incorporating stress management techniques and a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory nutrients can also minimize flare-ups and improve overall skin health.
Psoriasis vs Eczema Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com