Nutrigenomics explores how diet influences gene expression and impacts overall health, while nutrigenetics examines how individual genetic variations affect nutrient metabolism and dietary response. Both fields contribute to personalized nutrition strategies aimed at optimizing health outcomes and preventing chronic diseases. Understanding the interplay between genes and nutrients enables tailored dietary recommendations that enhance wellness and reduce disease risk.
Table of Comparison
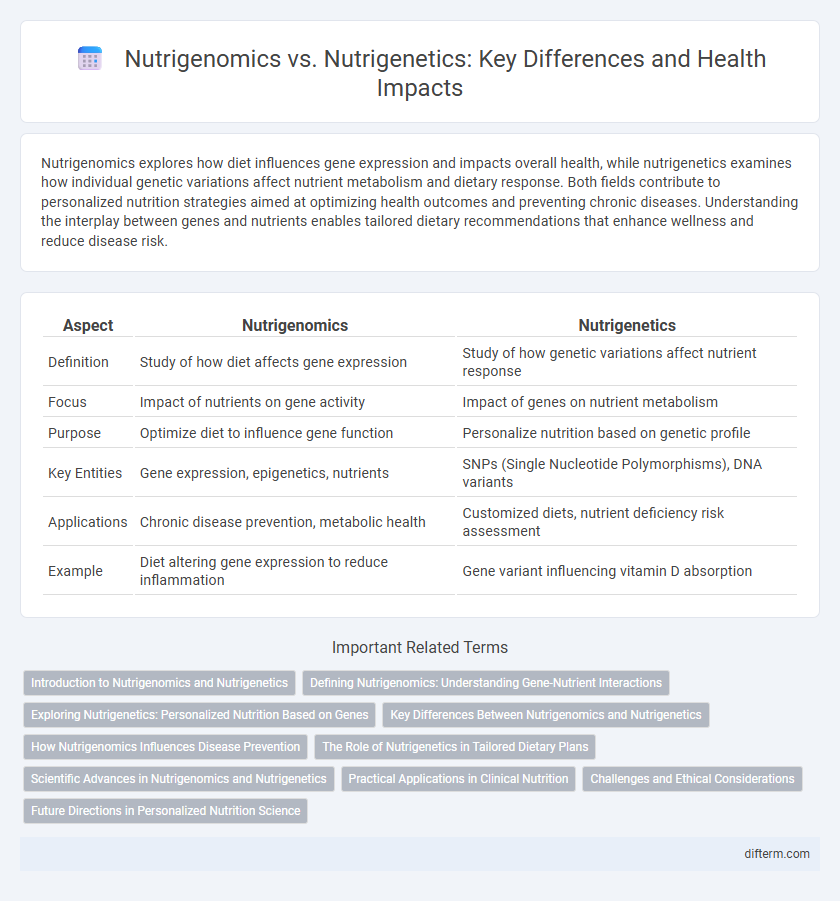
| Aspect | Nutrigenomics | Nutrigenetics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of how diet affects gene expression | Study of how genetic variations affect nutrient response |
| Focus | Impact of nutrients on gene activity | Impact of genes on nutrient metabolism |
| Purpose | Optimize diet to influence gene function | Personalize nutrition based on genetic profile |
| Key Entities | Gene expression, epigenetics, nutrients | SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms), DNA variants |
| Applications | Chronic disease prevention, metabolic health | Customized diets, nutrient deficiency risk assessment |
| Example | Diet altering gene expression to reduce inflammation | Gene variant influencing vitamin D absorption |
Introduction to Nutrigenomics and Nutrigenetics
Nutrigenomics explores how nutrients and diet influence gene expression, aiming to understand the interaction between nutrition and genetic makeup to optimize health outcomes. Nutrigenetics examines how individual genetic variations affect the body's response to specific nutrients and dietary components, providing insights for personalized nutrition plans. Both fields contribute to precision medicine by tailoring dietary recommendations based on genetic profiles, enhancing disease prevention and management strategies.
Defining Nutrigenomics: Understanding Gene-Nutrient Interactions
Nutrigenomics examines how nutrients and bioactive food compounds influence gene expression, enabling personalized dietary interventions to optimize health and prevent disease. This field analyzes molecular mechanisms that regulate gene-nutrient interactions, including epigenetic modifications, transcription factors, and signaling pathways. Understanding these complex genetic responses to nutrition enhances precision nutrition strategies and advances medical research in metabolic disorders and chronic diseases.
Exploring Nutrigenetics: Personalized Nutrition Based on Genes
Nutrigenetics examines how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism and dietary responses, enabling personalized nutrition plans tailored to one's genetic profile. This field identifies gene-diet interactions that affect risk factors for chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity. Personalized nutrition strategies derived from nutrigenetic insights optimize health outcomes by considering genetic predispositions to nutrient absorption and metabolism.
Key Differences Between Nutrigenomics and Nutrigenetics
Nutrigenomics explores how nutrients influence gene expression and affect overall health, while nutrigenetics studies how individual genetic variations impact nutrient metabolism and dietary responses. Nutrigenomics focuses on modifying diet based on gene expression changes, whereas nutrigenetics emphasizes personalized nutrition tailored to genetic differences. Understanding these distinctions aids in developing targeted dietary interventions for disease prevention and health optimization.
How Nutrigenomics Influences Disease Prevention
Nutrigenomics examines how nutrients affect gene expression, playing a crucial role in disease prevention by modulating molecular pathways linked to chronic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. This field enables personalized nutrition plans that target gene-environment interactions to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which are key factors in the development of many diseases. Understanding individual genomic responses to dietary components allows for optimized interventions promoting long-term health and reduced disease risk.
The Role of Nutrigenetics in Tailored Dietary Plans
Nutrigenetics explores how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism and dietary response, enabling personalized nutrition strategies. By analyzing genetic markers related to metabolism, taste preferences, and disease susceptibility, nutrigenetics helps tailor dietary plans that optimize health and prevent chronic diseases. Integrating nutrigenetic insights into dietary recommendations improves the efficacy of nutritional interventions and promotes long-term wellness.
Scientific Advances in Nutrigenomics and Nutrigenetics
Scientific advances in nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics have revolutionized personalized nutrition by elucidating how dietary components influence gene expression and how genetic variations affect nutrient metabolism. High-throughput technologies such as next-generation sequencing and genome-wide association studies (GWAS) enable precise identification of gene-diet interactions, leading to targeted dietary recommendations. These innovations facilitate the development of individualized nutritional interventions that optimize health outcomes and mitigate chronic disease risks.
Practical Applications in Clinical Nutrition
Nutrigenomics explores how nutrients influence gene expression, enabling personalized dietary recommendations to optimize health outcomes and prevent chronic diseases. Nutrigenetics investigates genetic variations that affect individual nutrient metabolism, guiding tailored nutrient supplementation and dietary adjustments in clinical nutrition. Integrating both fields enhances precision nutrition strategies, improving patient-specific interventions for disease management and health promotion.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Nutrigenomics faces challenges in accurately interpreting complex gene-diet interactions due to individual variability and polygenic traits, complicating personalized nutrition advice. Nutrigenetics encounters ethical concerns related to genetic data privacy, potential discrimination, and informed consent in the use of personal genetic information for dietary recommendations. Both fields require stringent regulatory frameworks and public awareness to address risks of misuse and ensure equitable access to nutrigenetic and nutrigenomic advancements.
Future Directions in Personalized Nutrition Science
Future directions in personalized nutrition science emphasize integrating nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics to tailor dietary recommendations based on individual genetic profiles and gene expression patterns. Advances in high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics enable more precise identification of gene-diet interactions that influence metabolic pathways and disease susceptibility. Emerging research aims to develop dynamic nutritional interventions that adapt to real-time changes in gene expression, enhancing preventive healthcare and chronic disease management.
Nutrigenomics vs Nutrigenetics Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com