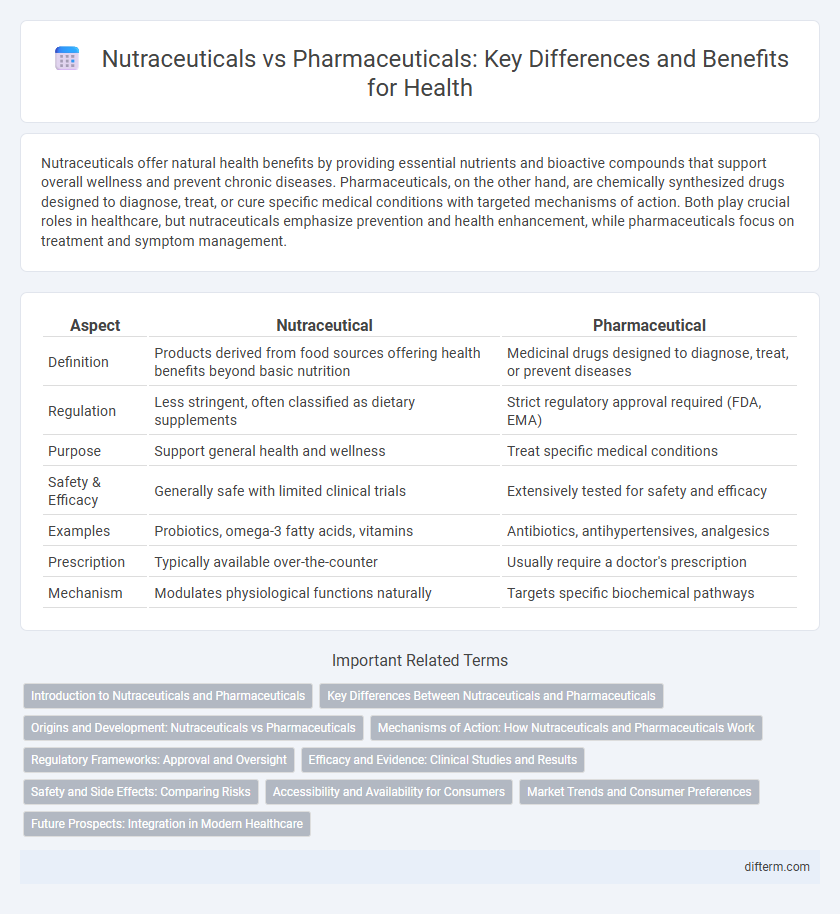
Nutraceuticals offer natural health benefits by providing essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that support overall wellness and prevent chronic diseases. Pharmaceuticals, on the other hand, are chemically synthesized drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or cure specific medical conditions with targeted mechanisms of action. Both play crucial roles in healthcare, but nutraceuticals emphasize prevention and health enhancement, while pharmaceuticals focus on treatment and symptom management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nutraceutical | Pharmaceutical |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Products derived from food sources offering health benefits beyond basic nutrition | Medicinal drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or prevent diseases |
| Regulation | Less stringent, often classified as dietary supplements | Strict regulatory approval required (FDA, EMA) |
| Purpose | Support general health and wellness | Treat specific medical conditions |
| Safety & Efficacy | Generally safe with limited clinical trials | Extensively tested for safety and efficacy |
| Examples | Probiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins | Antibiotics, antihypertensives, analgesics |
| Prescription | Typically available over-the-counter | Usually require a doctor's prescription |
| Mechanism | Modulates physiological functions naturally | Targets specific biochemical pathways |
Introduction to Nutraceuticals and Pharmaceuticals
Nutraceuticals are products derived from food sources that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, often used to prevent chronic diseases and promote overall wellness. Pharmaceuticals are chemically synthesized drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or cure diseases through targeted therapeutic effects. The key distinction lies in nutraceuticals' natural origin and preventive approach versus pharmaceuticals' clinical focus on disease management and symptom relief.
Key Differences Between Nutraceuticals and Pharmaceuticals
Nutraceuticals are products derived from food sources that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, often used for prevention and wellness, while pharmaceuticals are chemically formulated drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or cure specific medical conditions. Nutraceuticals typically have fewer regulatory restrictions and a lower risk of side effects compared to pharmaceuticals, which require rigorous clinical trials for safety and efficacy. The key differences lie in their origin, regulatory frameworks, intended use, and evidence-based therapeutic outcomes.
Origins and Development: Nutraceuticals vs Pharmaceuticals
Nutraceuticals originate from natural food sources and have been developed through traditional dietary practices combined with modern scientific research to promote health and prevent chronic diseases. Pharmaceuticals are synthesized chemical compounds or biologics designed through rigorous drug development processes, including clinical trials, to diagnose, treat, or cure specific medical conditions. The development of pharmaceuticals involves strict regulatory approval, whereas nutraceuticals often focus on supplementing diet without requiring extensive clinical validation.
Mechanisms of Action: How Nutraceuticals and Pharmaceuticals Work
Nutraceuticals primarily interact with cellular pathways by modulating nutrient-sensitive signaling, antioxidant defenses, and gene expression to promote overall health and prevent disease. Pharmaceuticals typically target specific molecular receptors, enzymes, or ion channels to produce a therapeutic effect with precise biochemical mechanisms. Understanding these distinct modes of action helps optimize prevention strategies and treatment interventions in health management.
Regulatory Frameworks: Approval and Oversight
Nutraceuticals are regulated primarily as dietary supplements under frameworks like the US Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), requiring less rigorous pre-market approval compared to pharmaceuticals. Pharmaceuticals undergo stringent evaluation by agencies such as the FDA and EMA, involving extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy before approval. Regulatory oversight for nutraceuticals emphasizes manufacturing standards and labeling, while pharmaceuticals are subject to continuous monitoring post-market for adverse effects and therapeutic outcomes.
Efficacy and Evidence: Clinical Studies and Results
Nutraceuticals often show promising health benefits supported by observational studies but generally lack the rigorous, large-scale clinical trials that pharmaceuticals undergo to establish efficacy and safety. Pharmaceuticals are subjected to extensive randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and meta-analyses, providing robust evidence for therapeutic outcomes and dosage standards. The clinical evidence for pharmaceuticals is typically stronger, enabling precise treatment recommendations, whereas nutraceuticals require further high-quality research to confirm their effectiveness and optimal use.
Safety and Side Effects: Comparing Risks
Nutraceuticals often present fewer and milder side effects compared to pharmaceuticals, as they are typically derived from natural sources and regulated as dietary supplements. Pharmaceuticals undergo rigorous clinical trials and strict regulatory scrutiny, providing clearer safety profiles but potentially higher risks of adverse reactions due to synthetic compounds and higher potency. The risk comparison depends on individual conditions, dosage, and drug interactions, making it crucial to consult healthcare professionals before use.
Accessibility and Availability for Consumers
Nutraceuticals are generally more accessible to consumers as they are available over-the-counter in health stores and online without prescription, offering greater convenience and affordability. Pharmaceuticals often require prescription and regulatory approval, limiting immediate availability but ensuring standardized dosages and clinical efficacy. The growing demand for natural health products boosts nutraceutical availability, while pharmaceuticals maintain critical roles in treating specific medical conditions.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
The nutraceutical market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for natural and preventive health solutions, with a global valuation projected to exceed $460 billion by 2030. Pharmaceutical markets, while steady, face challenges from consumers increasingly favoring plant-based supplements and functional foods perceived as safer and supporting overall wellness. Market trends highlight a shift towards personalized nutrition and evidence-backed nutraceuticals, signaling evolving consumer preferences that prioritize holistic health management over conventional drug therapies.
Future Prospects: Integration in Modern Healthcare
Nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals are increasingly converging, with future healthcare systems aiming to integrate both for enhanced personalized treatment strategies. Advances in genomics and bioinformatics enable tailored nutraceutical interventions that complement pharmaceutical therapies, optimizing patient outcomes and reducing adverse effects. Emerging regulatory frameworks and clinical trials support the validation and incorporation of nutraceuticals as adjunctive or preventive options alongside conventional medicines.
Nutraceutical vs Pharmaceutical Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com