Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats that play crucial roles in maintaining overall health, including brain function and inflammation regulation. Omega-3s, commonly found in fish oil and flaxseeds, help reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health, while Omega-6 fatty acids, prevalent in vegetable oils and processed foods, can promote inflammation when consumed in excess. Balancing the intake of Omega-3 and Omega-6 is vital for preventing chronic diseases and supporting immune function.
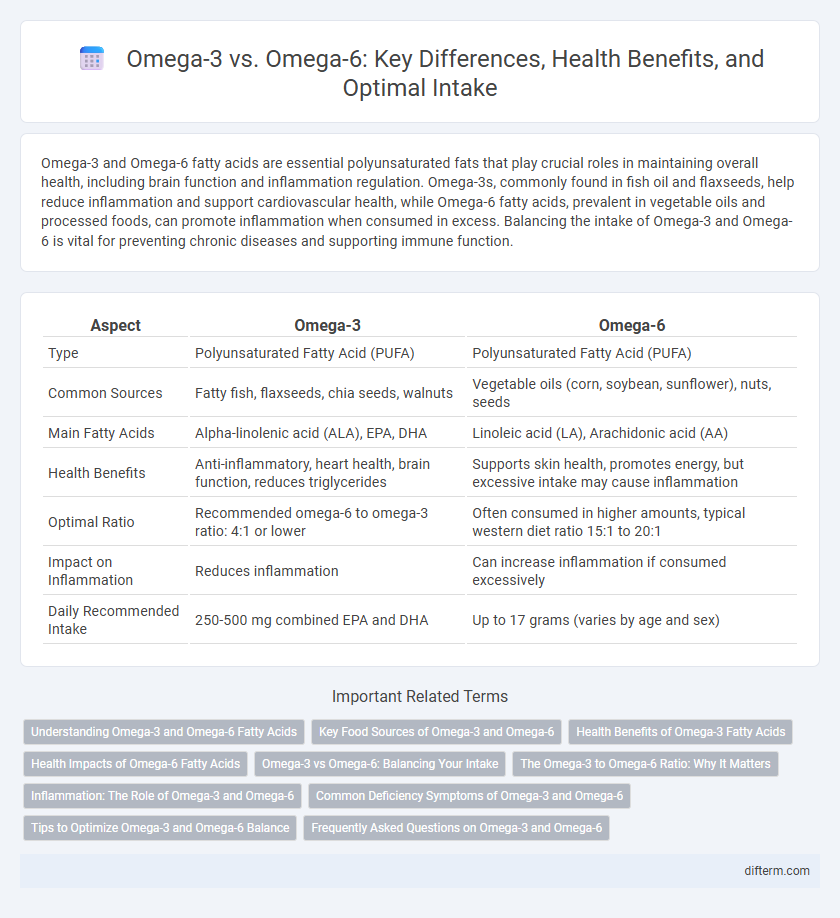
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Omega-3 | Omega-6 |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (PUFA) | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (PUFA) |
| Common Sources | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts | Vegetable oils (corn, soybean, sunflower), nuts, seeds |
| Main Fatty Acids | Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), EPA, DHA | Linoleic acid (LA), Arachidonic acid (AA) |
| Health Benefits | Anti-inflammatory, heart health, brain function, reduces triglycerides | Supports skin health, promotes energy, but excessive intake may cause inflammation |
| Optimal Ratio | Recommended omega-6 to omega-3 ratio: 4:1 or lower | Often consumed in higher amounts, typical western diet ratio 15:1 to 20:1 |
| Impact on Inflammation | Reduces inflammation | Can increase inflammation if consumed excessively |
| Daily Recommended Intake | 250-500 mg combined EPA and DHA | Up to 17 grams (varies by age and sex) |
Understanding Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats crucial for brain function, cell growth, and inflammation regulation. Omega-3s, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, primarily reduce inflammation and support heart health, while Omega-6s, abundant in vegetable oils and processed foods, tend to promote inflammatory responses when consumed in excess. Maintaining a balanced intake ratio between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids is vital to prevent chronic diseases and support overall health.
Key Food Sources of Omega-3 and Omega-6
Key food sources of Omega-3 include fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, which provide essential alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). Omega-6 is predominantly found in vegetable oils like sunflower, corn, and soybean oils, along with nuts and seeds such as pumpkin seeds and pine nuts. Balancing the intake of Omega-3 and Omega-6 is crucial for maintaining optimal inflammatory response and overall cardiovascular health.
Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in reducing inflammation, lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, and supporting brain health. They contribute to improved cardiovascular function by reducing triglyceride levels and blood pressure while enhancing arterial flexibility. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts can promote better cognitive function and joint health.
Health Impacts of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids play a crucial role in brain function and normal growth, but excessive intake, especially from processed foods, may promote inflammation linked to chronic diseases like cardiovascular conditions and arthritis. Balancing omega-6 with omega-3 fatty acids is essential to reduce the risk of inflammatory disorders and support overall heart health. Research highlights that an ideal omega-6 to omega-3 ratio ranges from 1:1 to 4:1, promoting optimal immune function and metabolic health.
Omega-3 vs Omega-6: Balancing Your Intake
Balancing Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acid intake is crucial for optimal health, as excessive Omega-6 consumption can promote inflammation while Omega-3s possess anti-inflammatory properties. The ideal ratio of Omega-6 to Omega-3 is approximately 4:1 or lower, yet many Western diets exceed 15:1, increasing the risk of chronic diseases. Prioritizing sources rich in EPA and DHA, such as fatty fish and flaxseeds, helps restore this balance and supports cardiovascular, cognitive, and joint health.
The Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio: Why It Matters
Maintaining an optimal Omega-3 to Omega-6 ratio is crucial for reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health. Modern diets often contain excessive Omega-6 fatty acids, which can promote chronic diseases when unbalanced by sufficient Omega-3 intake. Research suggests a ratio close to 1:1 to 1:4 optimizes immune function, brain health, and reduces the risk of metabolic disorders.
Inflammation: The Role of Omega-3 and Omega-6
Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fish oil and flaxseeds, play a crucial role in reducing inflammation by producing anti-inflammatory eicosanoids and resolvins. In contrast, Omega-6 fatty acids, abundant in vegetable oils like corn and soybean, tend to promote inflammation through pro-inflammatory eicosanoids when consumed in excess. Maintaining a balanced ratio of Omega-3 to Omega-6 is essential for controlling chronic inflammation and supporting overall health.
Common Deficiency Symptoms of Omega-3 and Omega-6
Omega-3 deficiency commonly manifests as dry skin, brittle hair, and chronic fatigue, while Omega-6 deficiency often leads to poor wound healing, scaly skin, and impaired immune response. Both essential fatty acids are critical for maintaining cellular health, and imbalances can trigger inflammation and cognitive disturbances. Monitoring symptoms like joint pain and mood swings can help identify deficiency in either Omega-3 or Omega-6 fatty acids.
Tips to Optimize Omega-3 and Omega-6 Balance
Maintaining an optimal omega-3 to omega-6 ratio supports cardiovascular health and reduces inflammation by emphasizing intake of omega-3-rich foods such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts while limiting omega-6-heavy processed oils like soybean and corn oil. Incorporating supplements like fish oil or algae oil can further enhance omega-3 levels, promoting balanced cell membrane function and metabolic regulation. Prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods and reading nutrition labels help manage the omega fatty acid ratio crucial for immune modulation and cognitive health.
Frequently Asked Questions on Omega-3 and Omega-6
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats crucial for brain function, inflammation regulation, and heart health. Common questions include the ideal intake ratio, with experts recommending a lower Omega-6 to Omega-3 ratio to reduce inflammation, typically around 4:1 or less. Another frequent inquiry addresses food sources, where Omega-3 is abundant in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, while Omega-6 is found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds.
Omega-3 vs Omega-6 Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com