Allergens trigger immune system reactions causing symptoms like hives, swelling, and anaphylaxis, while intolerances primarily affect digestion, leading to discomfort such as bloating and diarrhea. Allergies involve an immediate hypersensitivity response, whereas intolerances do not involve the immune system but result from enzyme deficiencies or sensitivity to certain substances. Proper diagnosis is essential for managing both conditions effectively and avoiding serious health risks.
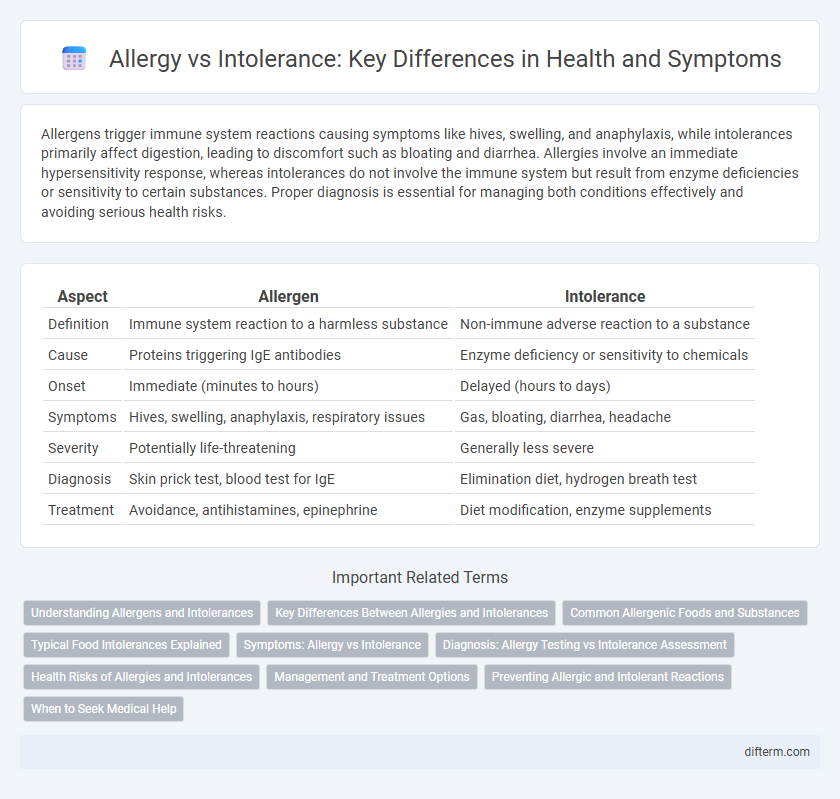
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Allergen | Intolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immune system reaction to a harmless substance | Non-immune adverse reaction to a substance |
| Cause | Proteins triggering IgE antibodies | Enzyme deficiency or sensitivity to chemicals |
| Onset | Immediate (minutes to hours) | Delayed (hours to days) |
| Symptoms | Hives, swelling, anaphylaxis, respiratory issues | Gas, bloating, diarrhea, headache |
| Severity | Potentially life-threatening | Generally less severe |
| Diagnosis | Skin prick test, blood test for IgE | Elimination diet, hydrogen breath test |
| Treatment | Avoidance, antihistamines, epinephrine | Diet modification, enzyme supplements |
Understanding Allergens and Intolerances
Allergens trigger immune system reactions causing symptoms like hives, swelling, or anaphylaxis, while intolerances involve digestive system responses due to difficulty processing certain substances such as lactose or gluten. Allergens include proteins from foods, pollen, or insect stings that stimulate IgE antibodies, whereas intolerances usually lack an immune component and result from enzyme deficiencies or sensitivities. Accurate diagnosis through skin tests or elimination diets is essential to manage symptoms and avoid potentially serious health complications.
Key Differences Between Allergies and Intolerances
Allergies involve an immune system response triggered by proteins in foods or environmental substances, causing symptoms like hives, swelling, or anaphylaxis. Intolerances, such as lactose intolerance, stem from the digestive system's inability to process certain substances, leading to gastrointestinal discomfort without immune activation. Key differences include the involvement of the immune system in allergies and the typically less severe symptoms associated with intolerances.
Common Allergenic Foods and Substances
Common allergenic foods include peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, fish, milk, eggs, wheat, and soy, which can trigger immune system responses in sensitive individuals. Intolerances, such as lactose intolerance, involve digestive system reactions rather than immune responses and commonly occur with dairy products, gluten-containing grains, and certain food additives. Identifying allergenic substances versus intolerant compounds is critical for accurate diagnosis and effective dietary management.
Typical Food Intolerances Explained
Typical food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance and gluten sensitivity, occur when the digestive system struggles to break down certain substances, leading to symptoms like bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Unlike food allergies, which involve an immune system reaction to proteins, intolerances are often caused by enzyme deficiencies or chemical sensitivities. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management and symptom relief through dietary adjustments.
Symptoms: Allergy vs Intolerance
Allergic reactions typically involve the immune system and can cause symptoms such as hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, and anaphylaxis. Intolerances generally affect the digestive system, leading to symptoms like bloating, gas, diarrhea, and stomach pain. Distinguishing between allergy and intolerance is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment in health management.
Diagnosis: Allergy Testing vs Intolerance Assessment
Allergy testing involves skin prick tests or serum-specific IgE blood tests to identify immune system reactions triggered by allergens, providing a clear diagnosis of allergic responses. Intolerance assessment relies on elimination diets, food challenges, and sometimes hydrogen breath tests to detect digestive system sensitivities or enzymatic deficiencies without immune involvement. Accurate diagnosis is essential for tailored management and symptom relief in patients experiencing adverse food reactions.
Health Risks of Allergies and Intolerances
Allergies trigger immune system reactions that can cause symptoms ranging from mild rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis, posing significant health risks. Intolerances, such as lactose intolerance, involve digestive system responses that may lead to discomfort but rarely result in severe complications. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management and preventing serious health outcomes.
Management and Treatment Options
Management of allergens involves strict avoidance of identified triggers and the use of antihistamines or epinephrine for severe allergic reactions. Intolerance treatment primarily focuses on dietary modifications to eliminate or reduce exposure to specific foods, such as lactose or gluten. Both conditions benefit from consultation with healthcare professionals for tailored management plans and monitoring.
Preventing Allergic and Intolerant Reactions
Preventing allergic reactions requires strict avoidance of allergens such as peanuts, shellfish, and pollen, alongside carrying emergency medication like epinephrine auto-injectors for anaphylaxis. Managing food intolerance involves dietary adjustments to limit or exclude trigger substances like lactose or gluten, often with the support of enzyme supplements or probiotics. Accurate diagnosis through allergy testing or hydrogen breath tests is essential for effective prevention and personalized treatment strategies.
When to Seek Medical Help
Seek medical help immediately if symptoms such as swelling of the throat, difficulty breathing, or anaphylaxis occur, as these are signs of a severe allergic reaction requiring urgent intervention. Persistent gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, or fatigue following certain food intake may indicate food intolerance and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out underlying conditions. Accurate diagnosis through allergen testing or elimination diets is essential to manage symptoms effectively and prevent complications.
Allergen vs Intolerance Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com