An allergen is a type of antigen that triggers an allergic reaction by overstimulating the immune system, whereas antigens are substances recognized as foreign by the immune system to induce a defensive response. Allergens often include pollen, pet dander, and certain foods, while antigens can be bacteria, viruses, or toxins. Understanding the distinction between allergens and antigens is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of immune-related conditions.
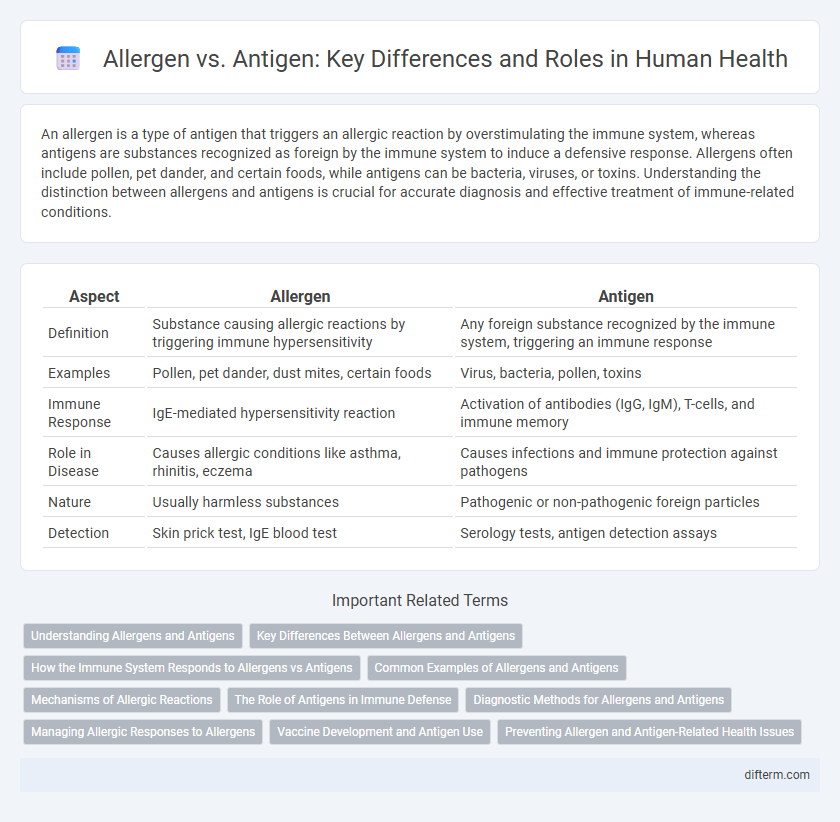
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Allergen | Antigen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Substance causing allergic reactions by triggering immune hypersensitivity | Any foreign substance recognized by the immune system, triggering an immune response |
| Examples | Pollen, pet dander, dust mites, certain foods | Virus, bacteria, pollen, toxins |
| Immune Response | IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction | Activation of antibodies (IgG, IgM), T-cells, and immune memory |
| Role in Disease | Causes allergic conditions like asthma, rhinitis, eczema | Causes infections and immune protection against pathogens |
| Nature | Usually harmless substances | Pathogenic or non-pathogenic foreign particles |
| Detection | Skin prick test, IgE blood test | Serology tests, antigen detection assays |
Understanding Allergens and Antigens
Allergens are specific types of antigens that trigger allergic reactions by overstimulating the immune system. While antigens refer broadly to any substance that the immune system recognizes as foreign, allergens uniquely provoke hypersensitivity responses in susceptible individuals. Understanding the difference between allergens and general antigens is crucial for diagnosing and treating allergic conditions effectively.
Key Differences Between Allergens and Antigens
Allergens are specific types of antigens that trigger hypersensitive immune responses leading to allergies, while antigens broadly refer to any substances recognized by the immune system as foreign, provoking an immune reaction. Allergens typically cause IgE-mediated immune responses, resulting in symptoms like hives, asthma, or anaphylaxis, whereas antigens can initiate various immune pathways including antibody production and cell-mediated immunity. Understanding this distinction is crucial for diagnosing and treating allergic conditions effectively.
How the Immune System Responds to Allergens vs Antigens
The immune system recognizes allergens as harmless substances, triggering an exaggerated IgE antibody response that leads to allergic reactions such as histamine release, inflammation, and symptoms like itching or swelling. In contrast, antigens are typically harmful pathogens or foreign molecules that activate a targeted immune response involving both antibody production and cellular immunity, aiming to neutralize or eliminate the threat. This difference in immune system recognition and response underlies the distinct mechanisms of allergy development versus protective immunity against infections.
Common Examples of Allergens and Antigens
Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold spores, and certain foods like peanuts and shellfish, which trigger allergic reactions by overstimulating the immune system. Antigens encompass a broader range of substances, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and toxins, that the immune system recognizes as foreign to initiate a defense response. Understanding the distinction and examples of allergens and antigens aids in diagnosing and managing immune-related health conditions.
Mechanisms of Allergic Reactions
Allergens are specific types of antigens that trigger hypersensitive immune responses by binding to Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies on mast cells and basophils, causing the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. Antigens, in general, are substances recognized as foreign by the immune system, initiating antibody production, but not all antigens cause allergic reactions. The mechanism of allergic reactions involves sensitization to the allergen, followed by subsequent exposure that leads to an exaggerated immune response characterized by inflammation and tissue damage.
The Role of Antigens in Immune Defense
Antigens are molecules, often proteins, found on the surface of pathogens that trigger an immune response by activating lymphocytes. Their detection by the immune system leads to the production of antibodies specifically designed to neutralize or eliminate the invading microorganism. This antigen-driven mechanism is crucial for adaptive immunity, enabling the body to recognize and remember pathogens for faster responses in future infections.
Diagnostic Methods for Allergens and Antigens
Diagnostic methods for allergens primarily include skin prick tests and specific IgE blood assays that detect immune responses to allergenic proteins. Antigen detection often involves immunoassays like enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to identify specific pathogen components. Advanced techniques such as mass spectrometry and flow cytometry enhance sensitivity and specificity in distinguishing allergens from antigens in clinical diagnostics.
Managing Allergic Responses to Allergens
Managing allergic responses to allergens involves understanding the difference between allergens and antigens, where allergens are specific types of antigens that trigger hypersensitive immune reactions. Effective strategies include minimizing exposure to known allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, alongside using antihistamines or immunotherapy to reduce immune system overreactions. Monitoring symptoms and consulting with allergists enable personalized treatment plans that improve quality of life for individuals with allergic conditions.
Vaccine Development and Antigen Use
Antigens are molecular structures that trigger immune responses and are essential in vaccine development as they help the body recognize pathogens. Allergens are specific types of antigens that cause allergic reactions by overstimulating the immune system. Vaccines utilize carefully selected antigens to train the immune system without causing disease, differentiating them from allergens that provoke hypersensitivity.
Preventing Allergen and Antigen-Related Health Issues
Preventing allergen and antigen-related health issues involves minimizing exposure to common triggers such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods by maintaining a clean environment and using air purifiers. Implementing strategies like regular hand washing, using hypoallergenic bedding, and adhering to prescribed immunotherapy can reduce the immune system's overreaction to allergens and antigens. Early identification and management of sensitivities through allergy testing and consultation with healthcare professionals significantly lower the risk of severe allergic reactions and autoimmune complications.
Allergen vs Antigen Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com