Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies that establish broad legal principles and frameworks, while regulations are detailed rules created by government agencies to implement and enforce those statutes. Regulations provide specific guidance on how the general mandates of statutes should be applied and followed in practice. Understanding the distinction between statutes and regulations is essential for navigating government policies and ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
Table of Comparison
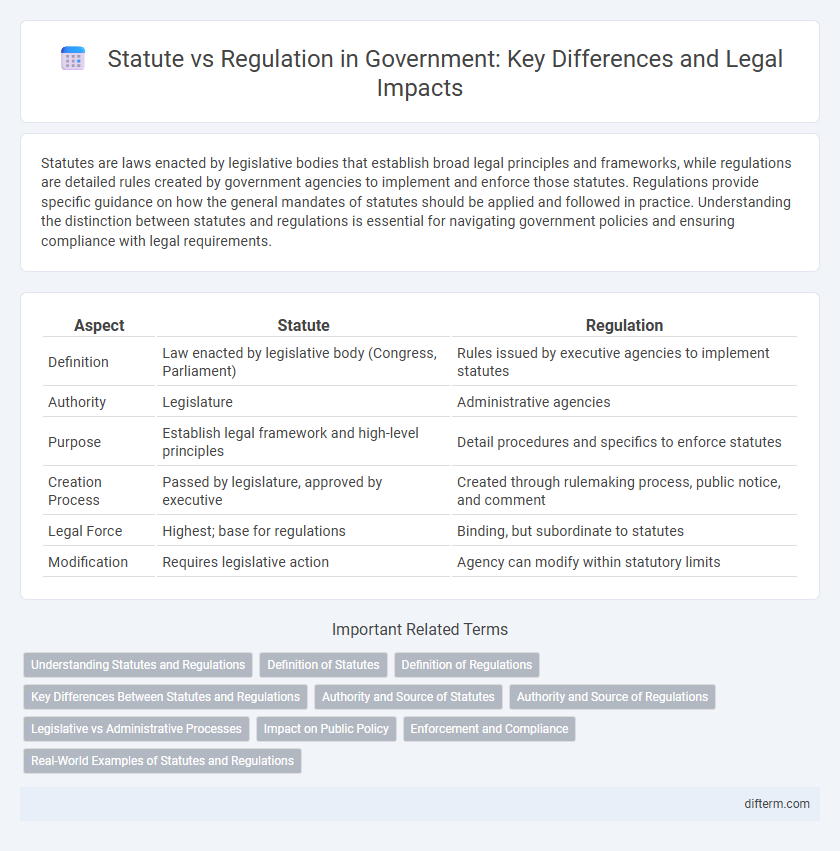
| Aspect | Statute | Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Law enacted by legislative body (Congress, Parliament) | Rules issued by executive agencies to implement statutes |
| Authority | Legislature | Administrative agencies |
| Purpose | Establish legal framework and high-level principles | Detail procedures and specifics to enforce statutes |
| Creation Process | Passed by legislature, approved by executive | Created through rulemaking process, public notice, and comment |
| Legal Force | Highest; base for regulations | Binding, but subordinate to statutes |
| Modification | Requires legislative action | Agency can modify within statutory limits |
Understanding Statutes and Regulations
Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies that establish broad legal principles, while regulations are detailed rules created by government agencies to implement and enforce those statutes. Understanding the relationship between statutes and regulations is crucial because statutes provide the legal authority and framework, whereas regulations specify the practical requirements and procedures necessary for compliance. Effective governance relies on interpreting statutes alongside relevant regulations to ensure lawful and efficient public administration.
Definition of Statutes
Statutes are formal written laws enacted by legislative bodies such as Congress or state legislatures, establishing legal obligations and authorities within a jurisdiction. These laws provide the foundational legal framework that governs various aspects of society, distinct from regulations which are detailed rules created by administrative agencies based on statutory authority. Understanding statutes is essential for interpreting the scope and limits of governmental power and ensuring compliance with established legal standards.
Definition of Regulations
Regulations are detailed rules issued by government agencies based on statutes enacted by the legislature, designed to implement and enforce statutory provisions. These legally binding directives provide specific operational guidelines to ensure compliance and uniform application of laws across relevant sectors. Unlike statutes, regulations have a narrower scope and are subject to administrative procedures and judicial review.
Key Differences Between Statutes and Regulations
Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies such as Congress or state legislatures, establishing broad legal principles and policies. Regulations are detailed rules created by government agencies based on statutes, providing specific guidelines for implementation and enforcement. Statutes have authority originating from elected representatives and require formal legislative processes, while regulations derive authority from statutes and are shaped through administrative rulemaking procedures.
Authority and Source of Statutes
Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies such as Congress or state legislatures, serving as the primary legal authority. They establish broad legal principles and frameworks that regulate behavior and govern society. Regulations derive their authority from statutes, with administrative agencies empowered to create detailed rules and procedures necessary for enforcing and implementing statutory mandates.
Authority and Source of Regulations
Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies, providing the foundational authority for regulatory agencies to create detailed regulations. Regulations derive their authority from statutes, serving as specific rules or standards issued by government agencies to implement and enforce legislative intent. The source of regulations is the statutory framework, which grants agencies delegated power to address complex policy areas through administrative rulemaking.
Legislative vs Administrative Processes
Statutes are laws enacted by legislative bodies such as Congress or state legislatures, establishing broad legal frameworks and policy mandates. Regulations are detailed rules created by administrative agencies based on statutory authority to implement and enforce laws within specific sectors. The legislative process involves debate, drafting, and approval by elected representatives, whereas the administrative process includes rulemaking, public notice, and agency enforcement actions.
Impact on Public Policy
Statutes, enacted by legislative bodies, establish broad legal frameworks that define public policy goals and priorities, shaping long-term governance and societal norms. Regulations, developed by administrative agencies under statutory authority, provide detailed rules and procedures to implement and enforce these policies effectively, ensuring compliance and operational consistency. The interplay between statutes and regulations drives policy adaptation, responsiveness, and practical impact on public services and citizen rights.
Enforcement and Compliance
Statutes provide the legal foundation enacted by legislatures, establishing broad rules and principles, while regulations are specific requirements developed by administrative agencies to implement those statutes. Enforcement mechanisms for statutes often involve judicial actions and penalties set by law, whereas regulatory compliance is monitored through agency inspections, permits, and administrative sanctions. Effective enforcement and compliance depend on clear regulatory frameworks aligned with statutory mandates and robust oversight by authorized governmental bodies.
Real-World Examples of Statutes and Regulations
The Clean Air Act is a key statute enacted by the U.S. Congress that sets nationwide air quality standards, while the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) develops regulations under this statute to enforce specific emission limits on industries. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is another statute that prohibits discrimination, with the Department of Justice issuing detailed regulations to implement accessibility standards in public facilities. These examples illustrate how statutes establish broad legal frameworks and agencies create regulations to define and enforce the specifics.
statute vs regulation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com