Open government promotes transparency, citizen participation, and accountability by making information accessible and encouraging public involvement in decision-making processes. Closed government restricts access to information, limiting citizen engagement and often leading to secrecy and reduced trust in public institutions. Embracing open government principles fosters democratic governance and enhances public confidence.
Table of Comparison
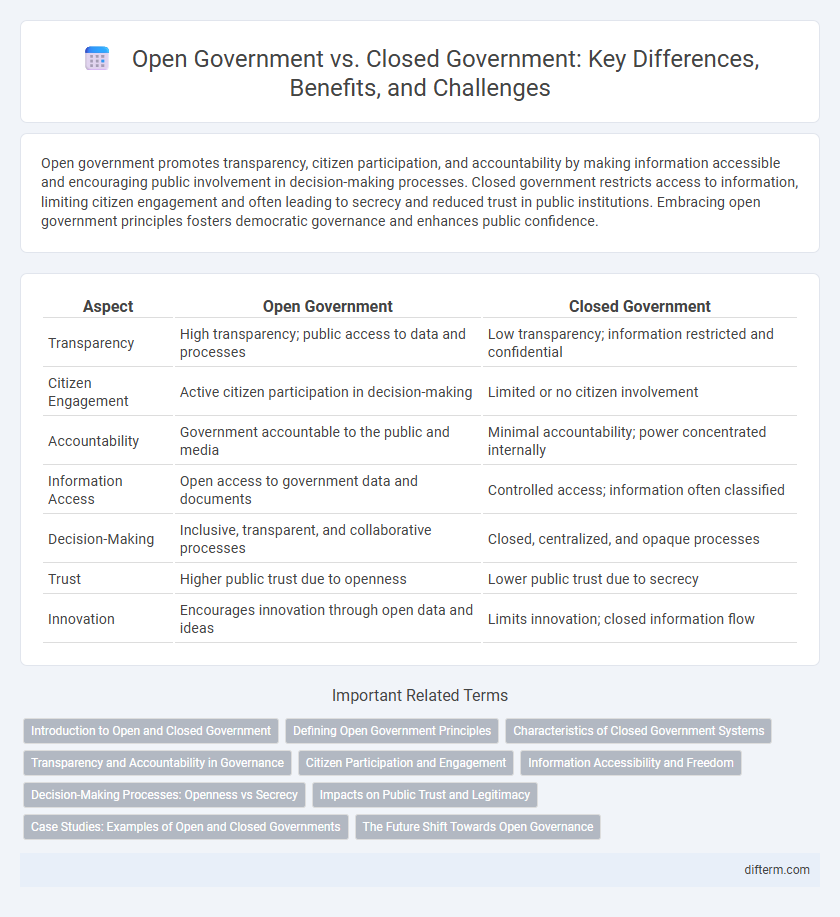
| Aspect | Open Government | Closed Government |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High transparency; public access to data and processes | Low transparency; information restricted and confidential |
| Citizen Engagement | Active citizen participation in decision-making | Limited or no citizen involvement |
| Accountability | Government accountable to the public and media | Minimal accountability; power concentrated internally |
| Information Access | Open access to government data and documents | Controlled access; information often classified |
| Decision-Making | Inclusive, transparent, and collaborative processes | Closed, centralized, and opaque processes |
| Trust | Higher public trust due to openness | Lower public trust due to secrecy |
| Innovation | Encourages innovation through open data and ideas | Limits innovation; closed information flow |
Introduction to Open and Closed Government
Open government promotes transparency, accountability, and public participation by making data and decision-making processes accessible to citizens. Closed government, in contrast, restricts access to information, limiting public oversight and often reducing trust in governmental institutions. The shift towards open government is driven by advances in technology and growing demands for civic engagement.
Defining Open Government Principles
Open government principles emphasize transparency, accountability, and public participation to foster trust and collaboration between citizens and government entities. These principles advocate for accessible government data, enabling citizens to scrutinize decision-making processes and contribute meaningfully to policy development. Emphasizing inclusivity and responsiveness, open government contrasts with closed government models that restrict information flow and limit civic engagement.
Characteristics of Closed Government Systems
Closed government systems restrict citizen access to information, limiting transparency and public participation in decision-making processes. These systems often centralize power within a small group of officials, reducing accountability and fostering secrecy. Control over media and communication channels ensures that dissenting voices are suppressed and government actions remain unchallenged.
Transparency and Accountability in Governance
Open government emphasizes transparency by making data, policies, and decision-making processes accessible to the public, enhancing accountability through citizen oversight and participatory mechanisms. Closed government restricts information flow, limiting public scrutiny and reducing opportunities for accountability, which can lead to corruption and inefficiency. Transparency and accountability in governance are critical for building trust, improving service delivery, and ensuring that public officials act in the best interests of citizens.
Citizen Participation and Engagement
Open government thrives on transparent policies and accessible communication channels, enabling robust citizen participation through public consultations and digital platforms. Closed government limits citizen engagement by restricting information flow and decision-making processes, often resulting in reduced public trust and accountability. Enhancing citizen participation in open government frameworks promotes democratic governance and improves policy outcomes.
Information Accessibility and Freedom
Open government prioritizes transparency, ensuring public access to information and fostering accountability through freely available data and documents. Closed government restricts information flow, limiting citizen access and reducing governmental accountability by controlling data dissemination. Enhanced information accessibility in open governments promotes freedom by empowering citizens with knowledge necessary for informed participation in democratic processes.
Decision-Making Processes: Openness vs Secrecy
Open government enhances decision-making processes by promoting transparency, stakeholder participation, and public accountability, leading to more informed and democratic outcomes. Closed government relies on secrecy and restricted information flow, often resulting in limited scrutiny, reduced trust, and potential inefficiencies in policy implementation. Transparency in open governments facilitates collaborative problem-solving and strengthens legitimacy, whereas secrecy in closed systems can hinder innovation and responsiveness.
Impacts on Public Trust and Legitimacy
Open government enhances public trust and legitimacy by promoting transparency, accountability, and citizen participation, which reduces corruption and increases confidence in government decisions. Closed government, characterized by secrecy and limited information access, often leads to suspicion, lower public engagement, and decreased legitimacy due to perceived lack of honesty and responsiveness. Empirical studies show that societies with open governance structures experience higher levels of social cohesion and institutional trust.
Case Studies: Examples of Open and Closed Governments
Open governments like Estonia demonstrate transparency through digital citizen engagement platforms, improving public trust and policy responsiveness. Conversely, North Korea exemplifies a closed government, where restricted information flow and centralized control limit accountability and civic participation. Comparative case studies reveal that open governments typically achieve higher democratic standards and socio-economic development than their closed counterparts.
The Future Shift Towards Open Governance
The future shift towards open governance emphasizes transparency, citizen participation, and accountability as core principles driving democratic innovation. Advances in digital technologies enable governments to share data openly, fostering collaborative policymaking and improved public trust. Embracing open governance models enhances responsiveness, combats corruption, and supports sustainable development goals globally.
open government vs closed government Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com