Government pets often symbolize the public sector's commitment to community engagement and transparency, contrasting with private sector pets that typically serve branding or promotional purposes. In the public sector, animals are frequently part of educational programs or public service campaigns, reflecting broader social objectives. Private sector pets, meanwhile, tend to enhance corporate identity and customer connection, prioritizing business interests over public welfare.
Table of Comparison
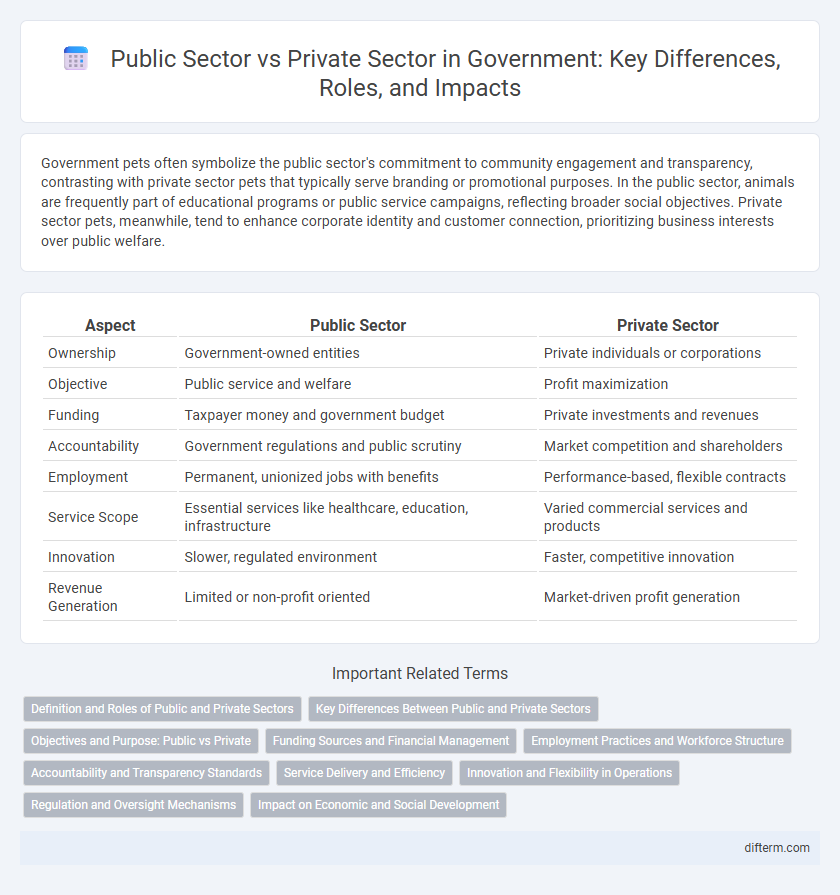
| Aspect | Public Sector | Private Sector |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Government-owned entities | Private individuals or corporations |
| Objective | Public service and welfare | Profit maximization |
| Funding | Taxpayer money and government budget | Private investments and revenues |
| Accountability | Government regulations and public scrutiny | Market competition and shareholders |
| Employment | Permanent, unionized jobs with benefits | Performance-based, flexible contracts |
| Service Scope | Essential services like healthcare, education, infrastructure | Varied commercial services and products |
| Innovation | Slower, regulated environment | Faster, competitive innovation |
| Revenue Generation | Limited or non-profit oriented | Market-driven profit generation |
Definition and Roles of Public and Private Sectors
The public sector comprises government-owned organizations that provide essential services such as healthcare, education, and public safety, focusing on social welfare and public interest rather than profit. The private sector includes businesses and enterprises owned by individuals or corporations, driven primarily by profit and market competition. Public sector roles emphasize policy implementation and regulation, while private sector roles center on innovation, economic growth, and job creation.
Key Differences Between Public and Private Sectors
The public sector operates under government control, focusing on providing essential services and public welfare, whereas the private sector prioritizes profit generation and efficiency through competitive markets. Public sector entities rely heavily on taxpayer funding and are subject to regulatory oversight, while private sector organizations utilize private capital and face market-driven accountability. Employment stability, decision-making processes, and objectives vary significantly, with public sector jobs often emphasizing social responsibility and private sector roles aiming at innovation and shareholder value.
Objectives and Purpose: Public vs Private
Public sector organizations prioritize delivering essential services and promoting social welfare, aiming to serve the public interest and ensure equitable access. Private sector businesses mainly focus on profit maximization, innovation, and market competitiveness to drive growth and shareholder value. Government agencies typically emphasize transparency, accountability, and regulatory compliance, whereas private firms prioritize efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Funding Sources and Financial Management
Public sector funding primarily derives from government budgets, tax revenues, and public borrowing, enabling the allocation of resources toward essential services and infrastructure with accountability to taxpayers. Private sector financial management relies on capital from investors, private equity, and sales revenue, emphasizing profitability, cost-efficiency, and investor returns. The differing funding sources influence budgeting processes, risk management strategies, and transparency standards between public institutions and private enterprises.
Employment Practices and Workforce Structure
Public sector employment practices emphasize job security, standardized pay scales, and collective bargaining agreements, often resulting in unionized workforces with clear hierarchical structures. The private sector prioritizes performance-based compensation, flexible working arrangements, and meritocratic promotion systems, fostering a more dynamic and competitive workforce. Workforce structure in the public sector tends to be more rigid with defined roles, while the private sector adapts quickly to market demands through decentralized and cross-functional teams.
Accountability and Transparency Standards
Public sector organizations operate under stringent accountability and transparency standards enforced by government regulations and public scrutiny, ensuring responsible use of taxpayer funds and open access to information. In contrast, private sector companies are primarily accountable to shareholders and customers, with transparency varying based on industry regulations and corporate governance practices. Enhanced public sector transparency fosters trust and civic engagement, while private sector accountability emphasizes financial performance and competitive advantage.
Service Delivery and Efficiency
The public sector, funded by government budgets, often faces challenges in service delivery efficiency due to bureaucratic procedures and regulatory constraints, potentially leading to slower response times compared to the private sector. Conversely, the private sector leverages competitive market dynamics and innovation to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction, often achieving faster and more flexible service delivery. However, public sector services prioritize equity and accessibility, ensuring essential services reach underserved populations despite efficiency trade-offs.
Innovation and Flexibility in Operations
Public sector organizations often face constraints due to regulatory frameworks and budgetary limitations, limiting their innovation capacity compared to the private sector. Private sector entities leverage market competition and flexible structures to rapidly implement innovative technologies and adapt operations. Emphasizing digital transformation and agile methodologies, private companies achieve higher operational flexibility, driving efficiency and customer-centric solutions.
Regulation and Oversight Mechanisms
Public sector entities operate under stringent regulatory frameworks established by government bodies, ensuring higher levels of transparency and accountability compared to private sector firms. Regulatory agencies such as the Government Accountability Office (GAO) and Office of Management and Budget (OMB) enforce compliance through rigorous oversight mechanisms, including audits, performance evaluations, and public reporting requirements. In contrast, private sector oversight largely depends on market-driven regulations and internal corporate governance, with enforcement varying significantly across industries and jurisdictions.
Impact on Economic and Social Development
The public sector drives economic stability through infrastructure investment, social welfare programs, and regulatory frameworks that promote equitable growth and reduce income inequality. The private sector fuels innovation, job creation, and efficiency, directly contributing to GDP expansion and improving living standards. Collaboration between both sectors enhances sustainable development by balancing profit motives with social responsibilities, fostering inclusive prosperity.
public sector vs private sector Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com