Codification organizes laws by systematically compiling them into a comprehensive code, ensuring clarity and accessibility for legal practitioners and the public. Consolidation merges multiple statutes on a related subject into a single, unified law without altering their original content or scope. Both processes enhance legal transparency and efficiency in government, but codification emphasizes structured reorganization while consolidation focuses on unifying existing laws.
Table of Comparison
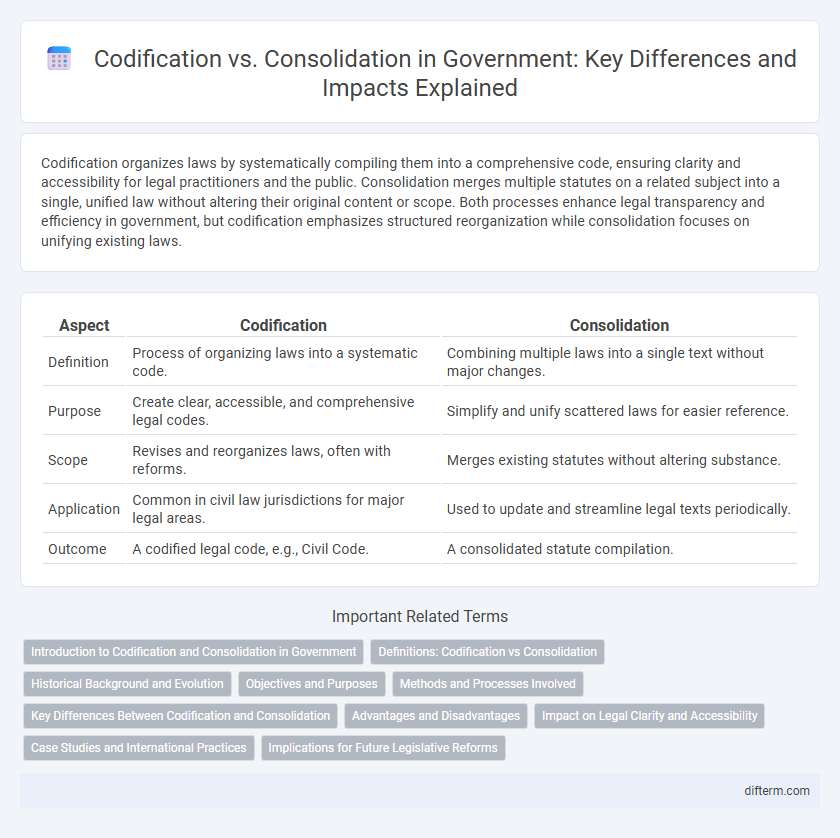
| Aspect | Codification | Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of organizing laws into a systematic code. | Combining multiple laws into a single text without major changes. |
| Purpose | Create clear, accessible, and comprehensive legal codes. | Simplify and unify scattered laws for easier reference. |
| Scope | Revises and reorganizes laws, often with reforms. | Merges existing statutes without altering substance. |
| Application | Common in civil law jurisdictions for major legal areas. | Used to update and streamline legal texts periodically. |
| Outcome | A codified legal code, e.g., Civil Code. | A consolidated statute compilation. |
Introduction to Codification and Consolidation in Government
Codification in government involves systematically arranging and recording laws to create a comprehensive legal code that enhances clarity and accessibility. Consolidation refers to the process of merging various statutes and amendments related to a specific legal area into a single, unified document, reducing redundancy and conflicting provisions. Both codification and consolidation streamline legal frameworks, improving governance and policy implementation efficiency.
Definitions: Codification vs Consolidation
Codification refers to the systematic arrangement and organization of laws or statutes into a code, making legal provisions clear and accessible. Consolidation involves combining multiple laws, amendments, or regulations into a single, unified statute without altering the substance of the legal rules. Both processes aim to simplify legal frameworks, but codification emphasizes structure and clarity, while consolidation focuses on unifying existing legal texts.
Historical Background and Evolution
Codification in government law emerged during the 18th century as an effort to systematically organize statutes into comprehensive legal codes, exemplified by the Napoleonic Code of 1804. Consolidation, however, developed as a legislative process aimed at merging various amendments and statutes into a single, coherent act to simplify legal referencing and reduce fragmentation. Over time, both approaches evolved to enhance legal clarity and accessibility, with codification providing structured legal frameworks while consolidation ensures updated and unified legislative texts.
Objectives and Purposes
Codification aims to systematically compile and organize existing laws into a coherent code, enhancing clarity and accessibility for citizens and legal professionals. Consolidation focuses on merging multiple statutes and amendments into a single, unified law to reduce redundancy and resolve inconsistencies. Both processes seek to improve legal coherence and facilitate effective governance by simplifying legislative frameworks.
Methods and Processes Involved
Codification involves systematically organizing and arranging existing laws by subject matter into a coherent legal code, ensuring clarity and consistency across statutes through a meticulous review and classification process. Consolidation merges multiple statutes or amendments relating to a specific legal topic into a single, unified text, simplifying legal frameworks by integrating previous enactments and removing redundancies. Both methods require rigorous legislative analysis, cross-referencing, and validation to create effective, accessible legal documents that support governance and judicial processes.
Key Differences Between Codification and Consolidation
Codification involves the systematic arrangement and classification of laws into a coherent code, enhancing accessibility and clarity for legal practitioners and the public. Consolidation refers to the process of combining multiple statutes or legislative provisions into a single comprehensive act, reducing fragmentation and eliminating inconsistencies within the legal framework. Key differences include codification's emphasis on organization and classification of laws versus consolidation's focus on merging existing statutes to form unified legislation.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Codification standardizes and organizes laws into systematic codes, enhancing clarity and accessibility for legal practitioners and citizens, but may struggle to keep pace with evolving legislation and risk oversimplification. Consolidation merges various statutes into a single comprehensive document, improving coherence and reducing contradictions, yet it can be time-consuming and costly to implement. Both methods support legal reform and transparency in government but require balancing thoroughness with practicality for effective governance.
Impact on Legal Clarity and Accessibility
Codification systematically organizes laws into a coherent code, enhancing legal clarity by reducing fragmentation and contradictions, which improves public accessibility and comprehension. Consolidation merges multiple statutes into a single text without fundamentally altering content, aiding accessibility but sometimes preserving outdated or inconsistent provisions that may hinder clarity. Effective legal frameworks often combine both processes to ensure laws are both clear and easily accessible for government officials, legal practitioners, and citizens.
Case Studies and International Practices
Codification in government legal frameworks involves systematically compiling statutes into comprehensive codes, ensuring clarity and accessibility, as seen in France's Napoleonic Code and India's legal system reforms. Consolidation focuses on merging scattered amendments into a single legislative text without altering substantive law, exemplified by the UK's legislative consolidation efforts to streamline statutes. International practices demonstrate codification facilitates uniformity across legal systems, while consolidation enhances legal clarity and reduces redundancies, improving governance efficiency.
Implications for Future Legislative Reforms
Codification streamlines laws by compiling statutes into a comprehensive legal code, enhancing clarity and accessibility for future legislative reforms. Consolidation merges multiple laws on similar subjects without altering their content, improving legislative coherence and reducing redundancy. These approaches impact legislative reforms by either promoting uniformity through codification or preserving legal nuances via consolidation, guiding policymakers in structuring effective legal frameworks.
Codification vs Consolidation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com