In a government pet context, autocracy centralizes power in a single ruler, limiting public participation and often suppressing dissent. Democracy distributes authority across elected representatives, promoting transparency and citizen involvement in decision-making. The contrast shapes governance effectiveness and individual freedoms within a society.
Table of Comparison
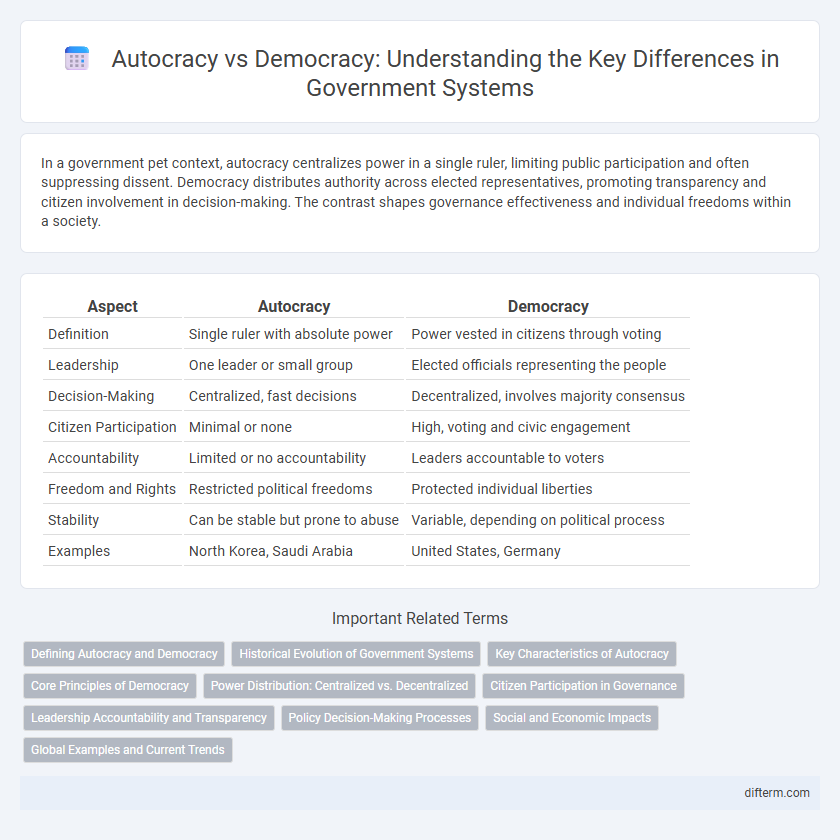
| Aspect | Autocracy | Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single ruler with absolute power | Power vested in citizens through voting |
| Leadership | One leader or small group | Elected officials representing the people |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, fast decisions | Decentralized, involves majority consensus |
| Citizen Participation | Minimal or none | High, voting and civic engagement |
| Accountability | Limited or no accountability | Leaders accountable to voters |
| Freedom and Rights | Restricted political freedoms | Protected individual liberties |
| Stability | Can be stable but prone to abuse | Variable, depending on political process |
| Examples | North Korea, Saudi Arabia | United States, Germany |
Defining Autocracy and Democracy
Autocracy is a form of government where absolute power is concentrated in the hands of a single ruler or a small group, often characterized by limited political pluralism and restricted individual freedoms. Democracy, in contrast, is a system of government where power is derived from the people through free and fair elections, emphasizing political equality, participation, and protection of individual rights. Key distinctions include the distribution of authority, citizen involvement in decision-making, and the rule of law safeguarding civil liberties.
Historical Evolution of Government Systems
The historical evolution of government systems traces the shift from autocracy, where power is centralized in a single ruler such as monarchs or dictators, to democracy, characterized by citizen participation and representation. Ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt exhibited early autocratic rule, while classical Athens pioneered democratic principles with direct citizen involvement. Modern political developments, including the Enlightenment and revolutions in America and France, cemented democracy's foundation by promoting individual rights and institutional checks on authority.
Key Characteristics of Autocracy
Autocracy centralizes power in a single ruler or a small group, limiting political pluralism and public participation. Key characteristics include unchecked authority, lack of competitive elections, and suppression of dissent to maintain control. These features contrast sharply with democratic principles of accountability, transparency, and citizen involvement.
Core Principles of Democracy
Democracy is founded on core principles such as popular sovereignty, political equality, and protection of individual rights, ensuring that power derives from the consent of the governed. Unlike autocracy, where authority is centralized in a single ruler or a small group, democracy promotes transparency, accountability, and the rule of law. Regular free and fair elections, separation of powers, and protection of civil liberties are essential components that uphold democratic governance.
Power Distribution: Centralized vs. Decentralized
Autocracy features centralized power concentrated in the hands of a single ruler or a small elite, limiting political pluralism and individual freedoms. Democracy emphasizes decentralized power through elected representatives and institutions, enabling broader participation and checks and balances. This distribution impacts governance efficiency, accountability, and citizen empowerment in each system.
Citizen Participation in Governance
Citizen participation in governance varies significantly between autocracy and democracy, with democracies emphasizing active involvement through voting, public consultations, and civil society engagement. In autocratic regimes, citizen input is often limited or controlled, restricting political freedom and minimizing influence on decision-making processes. Democratic systems prioritize transparency and accountability by empowering citizens to shape policies and hold leaders accountable through institutional mechanisms.
Leadership Accountability and Transparency
Autocracy concentrates power in a single leader or small group, often limiting transparency and reducing accountability due to centralized control over information and decision-making. Democracy emphasizes leadership accountability through mechanisms like free elections, independent media, and checks and balances that promote transparency. Transparent governance in democratic systems fosters citizen trust and enables public scrutiny of leaders, reducing corruption and enhancing policy effectiveness.
Policy Decision-Making Processes
Autocracy centralizes policy decision-making power in the hands of a single leader or a small group, enabling swift and often unilateral implementation of policies without public consultation. Democracy distributes decision-making authority among elected representatives, promoting transparency, accountability, and stakeholder participation through legislative debates and voting procedures. The effectiveness of policy outcomes in autocracies can be rapid but risks lacking legitimacy, whereas democracies emphasize inclusiveness and consensus, potentially leading to slower but more widely accepted policies.
Social and Economic Impacts
Autocratic regimes often centralize economic control, resulting in limited market competition and constrained individual freedoms, which can stifle innovation and exacerbate economic inequality. In contrast, democracies typically promote inclusive policies that encourage social mobility, economic diversification, and broader access to resources, fostering overall social welfare. The social impacts of autocracy frequently include restricted civil liberties and reduced public participation, while democratic systems tend to support human rights and collective decision-making processes.
Global Examples and Current Trends
Countries like China and Saudi Arabia exemplify autocracy with centralized power limiting political freedoms, while democracies such as the United States and Germany emphasize citizen participation through free elections and rule of law. Recent global trends highlight challenges to democracy, including rising authoritarianism in regions like Eastern Europe and Southeast Asia, alongside efforts to strengthen democratic institutions via digital transparency and civil society engagement. International organizations continually monitor these dynamics, promoting governance models that balance stability with human rights and civic involvement.
autocracy vs democracy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com