An ombudsman focuses on resolving complaints and protecting citizens' rights by investigating government actions and promoting accountability. An auditor primarily examines financial records and operations to ensure transparency, accuracy, and compliance with regulations. Both roles are essential in maintaining government integrity but address different aspects of governance oversight.
Table of Comparison
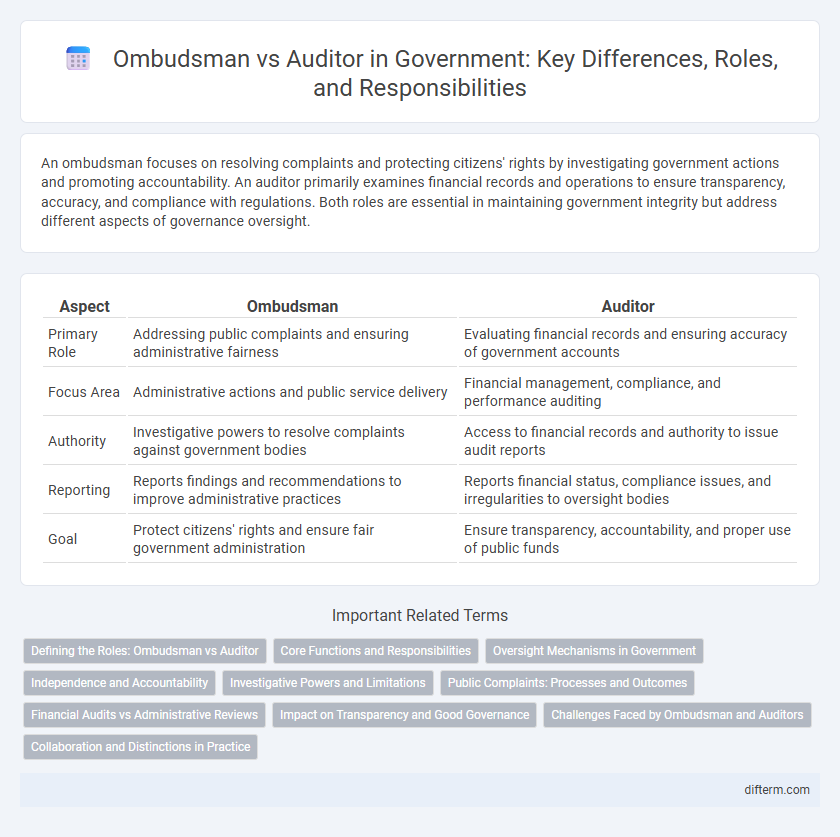
| Aspect | Ombudsman | Auditor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Addressing public complaints and ensuring administrative fairness | Evaluating financial records and ensuring accuracy of government accounts |
| Focus Area | Administrative actions and public service delivery | Financial management, compliance, and performance auditing |
| Authority | Investigative powers to resolve complaints against government bodies | Access to financial records and authority to issue audit reports |
| Reporting | Reports findings and recommendations to improve administrative practices | Reports financial status, compliance issues, and irregularities to oversight bodies |
| Goal | Protect citizens' rights and ensure fair government administration | Ensure transparency, accountability, and proper use of public funds |
Defining the Roles: Ombudsman vs Auditor
The ombudsman serves as an independent official who investigates public complaints against government agencies to ensure accountability and protect citizens' rights. The auditor, on the other hand, is responsible for examining and verifying the accuracy of government financial records and ensuring compliance with laws and regulations. While the ombudsman focuses on addressing grievances and promoting transparency, the auditor emphasizes financial integrity and proper use of public funds.
Core Functions and Responsibilities
An ombudsman investigates citizen complaints against government agencies, focusing on fairness, accountability, and conflict resolution to improve public service delivery. An auditor examines government financial records and operations to ensure compliance with regulations, accuracy in financial reporting, and prevention of fraud or mismanagement. Both roles promote transparency and accountability but differ in scope: the ombudsman addresses administrative grievances, while the auditor concentrates on financial oversight.
Oversight Mechanisms in Government
Ombudsmen serve as independent officials tasked with investigating citizen complaints and ensuring government accountability through impartial dispute resolution. Auditors focus on examining financial records and compliance to detect fraud, waste, and inefficiency in public sector spending. Together, these oversight mechanisms enhance transparency, promote good governance, and safeguard public resources within government institutions.
Independence and Accountability
The ombudsman operates as an independent authority tasked with investigating citizen complaints against government abuse, ensuring transparency and safeguarding public interest without external influence. In contrast, the auditor functions as a government-appointed official who reviews financial records and compliance, maintaining accountability through systematic evaluation of public funds. Both roles emphasize independence; the ombudsman through impartial dispute resolution, and the auditor through objective financial oversight to uphold governmental integrity.
Investigative Powers and Limitations
Ombudsmen possess the authority to investigate complaints from the public regarding maladministration and ensure government accountability through non-legal remedies, often focusing on fairness and transparency. Auditors exercise investigative powers centered on financial and procedural compliance by conducting audits and examining records to detect fraud, waste, and inefficiency within government agencies. Limitations for ombudsmen include lack of binding enforcement powers, while auditors may be restricted by legal frameworks governing access to sensitive information and the scope of financial oversight.
Public Complaints: Processes and Outcomes
The ombudsman handles public complaints by investigating grievances related to maladministration, ensuring citizens receive fair treatment and recommending corrective actions to government agencies. Auditors focus on examining financial records and compliance with regulations to detect fraud or inefficiency, providing accountability through formal reports. Both roles improve government transparency and responsiveness by addressing different aspects of public concern.
Financial Audits vs Administrative Reviews
Financial audits conducted by auditors focus on verifying the accuracy and compliance of government financial statements, ensuring transparency and accountability in the use of public funds. Ombudsman-led administrative reviews examine complaints related to government service delivery, maladministration, and fairness, addressing systemic issues beyond financial correctness. Both roles support good governance, with auditors concentrating on fiscal integrity and ombudsmen on administrative justice.
Impact on Transparency and Good Governance
The ombudsman enhances transparency by addressing public grievances and promoting accountability in government actions, fostering trust between citizens and institutions. Auditors contribute to good governance by systematically examining financial records and ensuring compliance with policies, thereby preventing fraud and mismanagement. Both roles are crucial for maintaining integrity and transparency, but while the ombudsman focuses on fairness and rights protection, auditors emphasize financial accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Challenges Faced by Ombudsman and Auditors
Ombudsmen face challenges such as limited authority to enforce recommendations, resource constraints, and the complexity of mediating disputes involving multiple government agencies. Auditors encounter difficulties in ensuring compliance with evolving regulations, detecting sophisticated financial fraud, and accessing timely, accurate data across decentralized government departments. Both roles require navigating political pressures and maintaining independence to uphold transparency and accountability in public sector governance.
Collaboration and Distinctions in Practice
Ombudsmen and auditors serve distinct yet complementary roles in government oversight, with ombudsmen addressing citizen complaints and ensuring fairness, while auditors focus on financial compliance and performance evaluation. Collaboration occurs through information sharing and joint investigations to enhance accountability and transparency within public institutions. Clear distinctions remain, as ombudsmen prioritize mediation and problem resolution whereas auditors emphasize systematic reviews and risk assessments.
ombudsman vs auditor Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com