Judicial review allows courts to assess the constitutionality of government actions, providing a legal check on executive and legislative decisions. Legislative oversight involves elected officials monitoring and evaluating government agencies to ensure accountability and proper implementation of laws. Both mechanisms serve as crucial tools in maintaining the balance of power within a democratic government system.
Table of Comparison
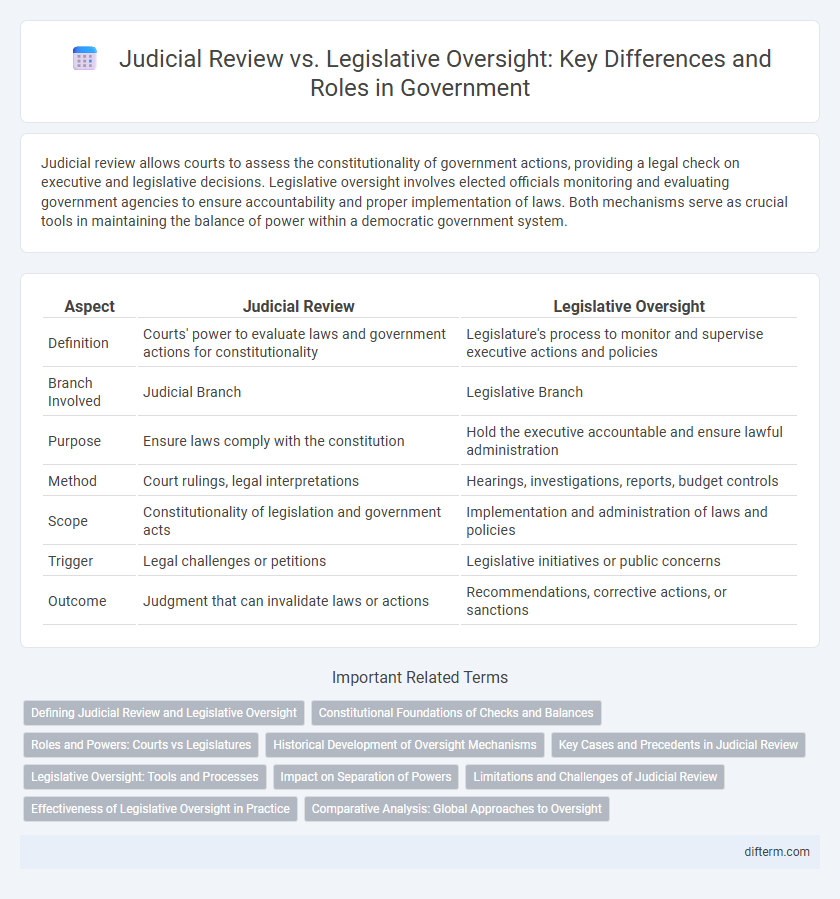
| Aspect | Judicial Review | Legislative Oversight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Courts' power to evaluate laws and government actions for constitutionality | Legislature's process to monitor and supervise executive actions and policies |
| Branch Involved | Judicial Branch | Legislative Branch |
| Purpose | Ensure laws comply with the constitution | Hold the executive accountable and ensure lawful administration |
| Method | Court rulings, legal interpretations | Hearings, investigations, reports, budget controls |
| Scope | Constitutionality of legislation and government acts | Implementation and administration of laws and policies |
| Trigger | Legal challenges or petitions | Legislative initiatives or public concerns |
| Outcome | Judgment that can invalidate laws or actions | Recommendations, corrective actions, or sanctions |
Defining Judicial Review and Legislative Oversight
Judicial review is the power of courts to examine laws and government actions to ensure they comply with the Constitution, safeguarding individual rights and preventing unconstitutional legislation. Legislative oversight refers to the process by which legislative bodies monitor, supervise, and review executive branch activities and public agencies to ensure accountability and proper implementation of laws. Both mechanisms serve as critical checks within the government, maintaining the balance of power and reinforcing the rule of law.
Constitutional Foundations of Checks and Balances
Judicial review empowers courts to assess the constitutionality of legislative acts, serving as a crucial check on legislative power derived from Marbury v. Madison (1803). Legislative oversight involves congressional committees monitoring executive actions to ensure compliance with laws and prevent abuse of power, rooted in Article I of the U.S. Constitution. Together, these mechanisms uphold the constitutional foundation of checks and balances by distributing authority among branches and preventing tyranny.
Roles and Powers: Courts vs Legislatures
Judicial review empowers courts to interpret the constitutionality of laws and executive actions, ensuring compliance with constitutional principles. Legislatures exercise legislative oversight by monitoring, investigating, and influencing the implementation of laws and government agencies to uphold accountability and transparency. While courts act as guardians of constitutional limits, legislatures shape policy and supervise government operations through hearings, reports, and budget controls.
Historical Development of Oversight Mechanisms
Judicial review emerged in the early 19th century with landmark cases like Marbury v. Madison, establishing courts' authority to invalidate unconstitutional laws. Legislative oversight evolved concurrently as legislatures developed committees and procedures to monitor executive actions and ensure accountability. Together, these mechanisms reflect a historical balance of power designed to safeguard constitutional governance and prevent arbitrary rule.
Key Cases and Precedents in Judicial Review
Key cases in judicial review such as Marbury v. Madison (1803) established the principle of courts interpreting constitutionality, setting a foundational precedent for limiting legislative power through judicial intervention. Subsequent rulings like Brown v. Board of Education (1954) reinforced the judiciary's role in protecting constitutional rights against legislative actions. Judicial review primarily ensures laws comply with the Constitution, whereas legislative oversight involves monitoring government agencies to enforce policy adherence without challenging constitutional validity.
Legislative Oversight: Tools and Processes
Legislative oversight employs tools such as committee hearings, budget controls, and subpoena powers to monitor and evaluate executive branch activities, ensuring accountability and adherence to legislative intent. These processes enable lawmakers to investigate government programs, scrutinize administrative decisions, and compel testimony or document production from officials. Effective legislative oversight strengthens checks and balances by promoting transparency, preventing abuse of power, and informing future policy development.
Impact on Separation of Powers
Judicial review reinforces the separation of powers by empowering courts to invalidate laws that violate constitutional principles, ensuring legislative actions remain within constitutional bounds. Legislative oversight complements this by holding the executive branch accountable through investigations and hearings, maintaining a balance of power among government branches. Together, these mechanisms prevent the concentration of authority and uphold the constitutional framework essential for democratic governance.
Limitations and Challenges of Judicial Review
Judicial review faces limitations such as judicial activism concerns, where courts may overstep by interpreting laws beyond their intent, impacting the balance of powers. Courts often encounter challenges in reviewing legislative actions due to vague statutory language and political questions deemed non-justiciable. Additionally, judicial review cannot address all policy issues, as some require legislative expertise and democratic accountability unavailable to the judiciary.
Effectiveness of Legislative Oversight in Practice
Legislative oversight ensures accountability by enabling elected representatives to monitor executive actions and enforce compliance with laws through hearings, investigations, and budgetary controls. Its effectiveness depends on the legislature's access to accurate information, political will, and institutional resources to challenge executive decisions. Compared to judicial review, which primarily addresses legal conformity post-factum, legislative oversight functions as a proactive mechanism to shape policy implementation and prevent abuses of power.
Comparative Analysis: Global Approaches to Oversight
Judicial review allows courts to invalidate laws conflicting with constitutional principles, ensuring legal conformity, while legislative oversight involves parliamentary committees monitoring executive actions to maintain accountability and transparency. In countries like the United States, judicial review serves as a strong check on legislative and executive powers, whereas the United Kingdom emphasizes robust legislative committees with limited judicial intervention due to parliamentary sovereignty. Comparative analysis reveals that blending judicial review with legislative oversight enhances governmental checks and balances, promoting a comprehensive framework for democratic governance worldwide.
judicial review vs legislative oversight Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com