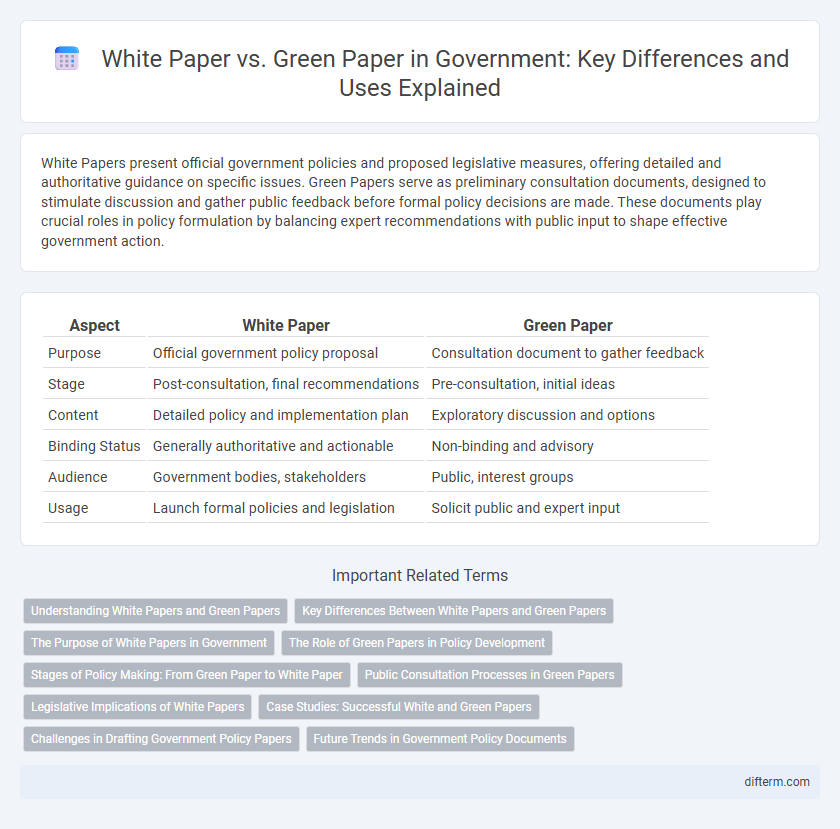
White Papers present official government policies and proposed legislative measures, offering detailed and authoritative guidance on specific issues. Green Papers serve as preliminary consultation documents, designed to stimulate discussion and gather public feedback before formal policy decisions are made. These documents play crucial roles in policy formulation by balancing expert recommendations with public input to shape effective government action.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | White Paper | Green Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Official government policy proposal | Consultation document to gather feedback |
| Stage | Post-consultation, final recommendations | Pre-consultation, initial ideas |
| Content | Detailed policy and implementation plan | Exploratory discussion and options |
| Binding Status | Generally authoritative and actionable | Non-binding and advisory |
| Audience | Government bodies, stakeholders | Public, interest groups |
| Usage | Launch formal policies and legislation | Solicit public and expert input |
Understanding White Papers and Green Papers
White Papers serve as authoritative reports that outline government policies, providing detailed proposals and guiding legislative decisions. Green Papers are consultative documents designed to stimulate public discussion and gather feedback on potential policy options before formal decisions are made. Understanding the distinct roles of White Papers and Green Papers is essential for engaging with government policy development and implementation effectively.
Key Differences Between White Papers and Green Papers
White Papers present definitive government policies and detailed proposals aimed at legislation or public implementation, while Green Papers serve as consultative documents designed to provoke discussion and gather feedback. White Papers typically follow extensive research and stakeholder consultation, offering clear recommendations, whereas Green Papers outline options and invite public debate to shape future policy decisions. The key difference lies in their purpose: White Papers confirm government intent, while Green Papers explore possibilities without firm commitments.
The Purpose of White Papers in Government
White Papers in government serve as authoritative reports or guides that present detailed policy proposals and recommendations aimed at informing decision-makers and stakeholders. They provide a clear framework for legislative or administrative action by outlining problems, evaluating options, and suggesting specific solutions. These documents play a crucial role in shaping public policy by fostering informed debate and guiding government strategy.
The Role of Green Papers in Policy Development
Green Papers play a crucial role in government policy development by serving as consultative documents designed to provoke discussion and gather feedback from stakeholders and the public. They outline preliminary ideas and options without committing to a final course of action, allowing for a wide range of input to shape effective and inclusive policies. This iterative consultation process helps refine proposals, which may later be formalized in a White Paper to guide legislative or administrative decisions.
Stages of Policy Making: From Green Paper to White Paper
Green Papers serve as preliminary reports in policy making, presenting proposals for public consultation and debate to gather feedback and assess potential impacts. The transition to a White Paper marks the stage where government solidifies policy direction, outlining definitive proposals and legislative intentions based on consultations. This progression from Green Paper to White Paper is pivotal for transparent decision-making and effective formulation of government policies.
Public Consultation Processes in Green Papers
Green Papers serve as preliminary government documents aimed at inviting public consultation and debate on proposed policies, fostering a participatory approach in policy formulation. Unlike White Papers, which present final government decisions and detailed proposals, Green Papers emphasize gathering diverse inputs from stakeholders and the general public to shape future legislative directions. This inclusive consultation process enhances transparency, accountability, and democratic engagement, ensuring policies reflect a broader spectrum of societal interests before formalization.
Legislative Implications of White Papers
White Papers serve as authoritative government reports outlining proposed legislation and detailed policy frameworks, providing a foundation for formal lawmaking processes. They present clear, actionable proposals intended to shape legislative agendas and facilitate parliamentary debate, enabling lawmakers to draft bills with a solid evidentiary basis. Green Papers, in contrast, function primarily as consultative documents designed to solicit public and stakeholder input prior to legislative formulation.
Case Studies: Successful White and Green Papers
Case studies highlight the impact of the UK Government's 1998 White Paper on Modernising Government, which successfully implemented digital services and improved public sector efficiency. The Australian Green Paper on National Disability Insurance Scheme (2010) effectively gathered stakeholder input, shaping policy development and addressing community needs. These examples demonstrate how White Papers can finalize policies, while Green Papers serve as consultative tools to refine government initiatives.
Challenges in Drafting Government Policy Papers
Drafting government policy papers such as White Papers and Green Papers involves navigating significant challenges including balancing stakeholder interests, ensuring clarity of complex policy issues, and anticipating political implications. White Papers require comprehensive analysis and definitive policy proposals, which can be difficult under conditions of uncertainty and divergent opinions. Green Papers demand presenting multiple options to foster public debate while maintaining unbiased language and avoiding premature conclusions.
Future Trends in Government Policy Documents
Future trends in government policy documents emphasize increased digital accessibility and interactive platforms for White Papers and Green Papers, facilitating broader public engagement and real-time feedback. Enhanced data analytics and AI integration enable more precise, evidence-based policy formulation with White Papers presenting definitive government positions while Green Papers encourage exploratory discussions. Emphasis on sustainability and inclusivity reflects in thematic shifts, ensuring that these documents address climate change, social equity, and technological innovation in alignment with global governance standards.
White Paper vs Green Paper Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com