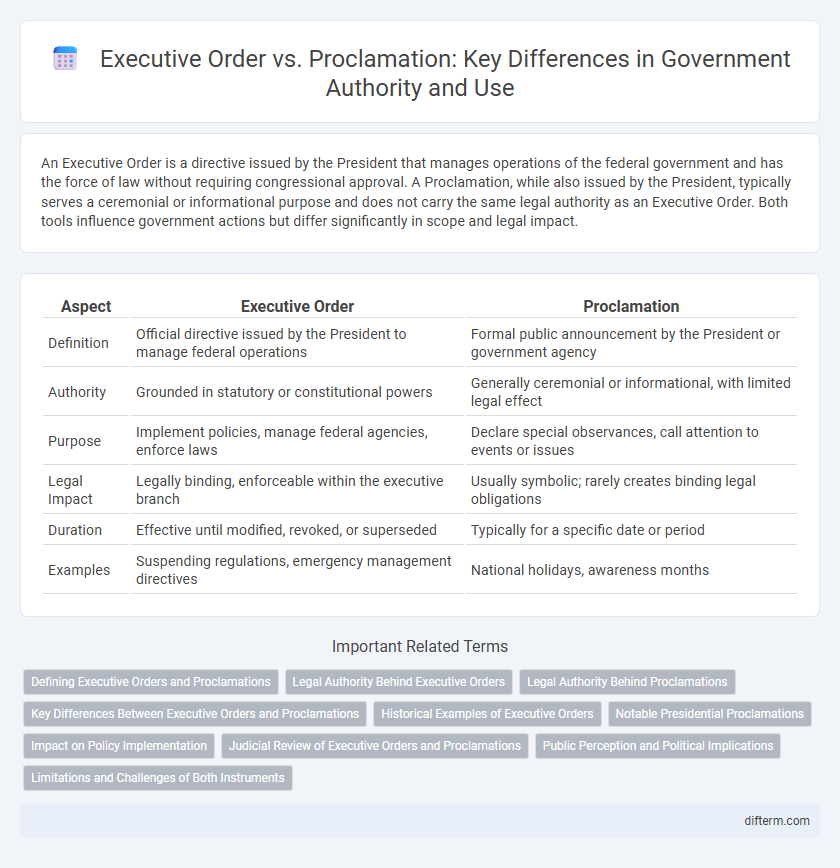
An Executive Order is a directive issued by the President that manages operations of the federal government and has the force of law without requiring congressional approval. A Proclamation, while also issued by the President, typically serves a ceremonial or informational purpose and does not carry the same legal authority as an Executive Order. Both tools influence government actions but differ significantly in scope and legal impact.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Executive Order | Proclamation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official directive issued by the President to manage federal operations | Formal public announcement by the President or government agency |
| Authority | Grounded in statutory or constitutional powers | Generally ceremonial or informational, with limited legal effect |
| Purpose | Implement policies, manage federal agencies, enforce laws | Declare special observances, call attention to events or issues |
| Legal Impact | Legally binding, enforceable within the executive branch | Usually symbolic; rarely creates binding legal obligations |
| Duration | Effective until modified, revoked, or superseded | Typically for a specific date or period |
| Examples | Suspending regulations, emergency management directives | National holidays, awareness months |
Defining Executive Orders and Proclamations
Executive orders are legally binding directives issued by the President of the United States to manage operations of the federal government. Proclamations serve primarily as formal announcements or statements of policy, often symbolic or ceremonial, without the force of law. Both tools are utilized in governance, but executive orders carry regulatory authority, whereas proclamations do not.
Legal Authority Behind Executive Orders
Executive orders derive their legal authority from the Constitution, specifically Article II, Section 1, which grants the President executive power to enforce federal law and manage the operations of the federal government. These orders serve as legally binding directives to federal agencies, enabling the President to implement policies without requiring congressional approval. Unlike proclamations, which are often ceremonial or symbolic without enforceable legal effect, executive orders carry the force of law and can significantly impact government administration and public policy.
Legal Authority Behind Proclamations
Executive Orders derive their legal authority from statutes passed by Congress and the Constitution, enabling the President to direct government operations. Proclamations, while often symbolic or ceremonial, can carry legal weight when authorized by specific statutes, such as declaring public lands or enforcing trade embargoes. The legal authority behind proclamations varies, depending on the statutory grant or constitutional provision empowering their issuance.
Key Differences Between Executive Orders and Proclamations
Executive Orders are legally binding directives issued by the President to manage operations of the federal government, while Proclamations are formal public announcements that may signal policy positions but typically lack direct legal effect. Executive Orders have the authority to direct government agencies and enforce laws, whereas Proclamations often serve ceremonial or informational purposes without mandating governmental action. The key difference lies in their enforcement power and scope of impact within the executive branch.
Historical Examples of Executive Orders
Executive Orders, such as President Franklin D. Roosevelt's Executive Order 9066 authorizing Japanese American internment during World War II, illustrate their powerful impact on civil liberties and national security policies. Another significant example includes President Harry S. Truman's Executive Order 9981, which desegregated the armed forces, showcasing the use of executive authority for social reform. These historical instances emphasize the direct and immediate effect Executive Orders have on shaping federal actions compared to proclamations, which are often ceremonial or advisory.
Notable Presidential Proclamations
Notable presidential proclamations often serve symbolic or public policy purposes, such as designating national holidays or conservation areas, reflecting the President's ability to influence cultural and environmental agendas. Executive orders, in contrast, carry the force of law and direct government operations or alter administrative agency rules. Both tools highlight presidential authority but differ in scope: proclamations shape ceremonial or policy environments, while executive orders impact government function and legal frameworks directly.
Impact on Policy Implementation
Executive Orders have direct and immediate effects on government operations, enabling swift policy implementation by providing detailed directives to federal agencies. Proclamations, while often symbolic or ceremonial, can also influence policy by raising public awareness and signaling government priorities, impacting regulatory or legislative agendas. The binding nature of Executive Orders typically results in more substantial and enforceable changes compared to the advisory or declarative role of Proclamations.
Judicial Review of Executive Orders and Proclamations
Judicial review of executive orders and proclamations ensures their compliance with constitutional and statutory limits, with courts frequently analyzing whether the executive action exceeds delegated authority or violates individual rights. Executive orders, generally carrying the force of law within the executive branch, are subject to scrutiny regarding their legal foundation and scope, while proclamations often address broader policy announcements and may be less directly enforceable but still vulnerable to judicial challenge when impacting legal rights. Courts tend to apply a balancing test considering the nature of the presidential directive, statutory authorization, and constitutional principles to determine the validity and enforceability of these executive instruments.
Public Perception and Political Implications
Executive orders often trigger intense public scrutiny due to their binding nature on federal agencies, influencing perceptions of executive power and legitimacy. Proclamations tend to carry symbolic weight, shaping national identity or commemorative narratives without the regulatory impact of executive orders. Political implications arise as executive orders can provoke legislative pushback or judicial review, while proclamations usually face less controversy but still signal administration priorities and values.
Limitations and Challenges of Both Instruments
Executive Orders face limitations such as potential legal challenges and constraints imposed by existing laws and judicial review, restricting the scope of executive action. Proclamations often lack enforceability and are primarily ceremonial or declaratory, which limits their practical impact on policy implementation. Both instruments encounter challenges in maintaining balance with legislative authority and ensuring constitutional compliance.
Executive Order vs Proclamation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com