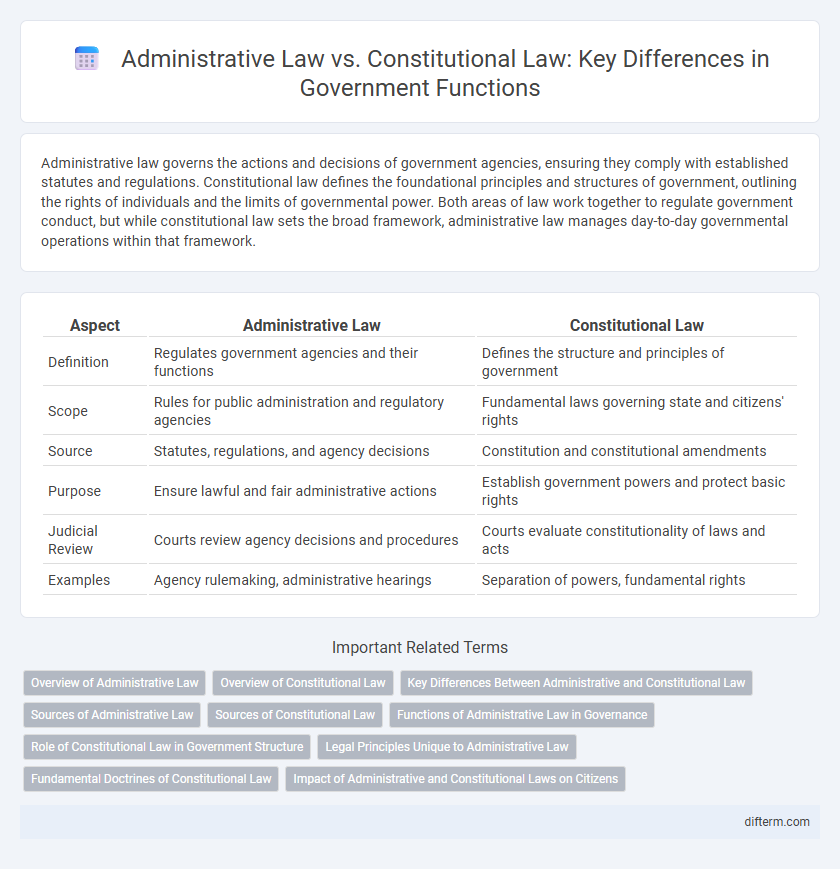
Administrative law governs the actions and decisions of government agencies, ensuring they comply with established statutes and regulations. Constitutional law defines the foundational principles and structures of government, outlining the rights of individuals and the limits of governmental power. Both areas of law work together to regulate government conduct, but while constitutional law sets the broad framework, administrative law manages day-to-day governmental operations within that framework.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Administrative Law | Constitutional Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulates government agencies and their functions | Defines the structure and principles of government |
| Scope | Rules for public administration and regulatory agencies | Fundamental laws governing state and citizens' rights |
| Source | Statutes, regulations, and agency decisions | Constitution and constitutional amendments |
| Purpose | Ensure lawful and fair administrative actions | Establish government powers and protect basic rights |
| Judicial Review | Courts review agency decisions and procedures | Courts evaluate constitutionality of laws and acts |
| Examples | Agency rulemaking, administrative hearings | Separation of powers, fundamental rights |
Overview of Administrative Law
Administrative law governs the activities of government agencies, ensuring compliance with statutory mandates and protecting citizens' rights in the regulatory process. It encompasses rulemaking, adjudication, and enforcement of agency regulations, providing mechanisms for oversight and accountability. Key components include administrative procedures, judicial review, and agency discretion within the framework established by constitutional and statutory law.
Overview of Constitutional Law
Constitutional law establishes the foundational legal framework that defines the structure, powers, and functions of government institutions and protects fundamental rights and liberties. It governs the interpretation and application of a country's constitution, ensuring the supremacy of constitutional provisions over other laws. Key elements include the separation of powers, judicial review, and the protection of civil rights, which collectively safeguard democratic governance and rule of law.
Key Differences Between Administrative and Constitutional Law
Administrative law governs the activities of government agencies, focusing on rule-making, enforcement, and adjudication within the executive branch. Constitutional law establishes the fundamental principles and framework of government, outlining the separation of powers, individual rights, and the limits of governmental authority. The key difference lies in administrative law's operational regulation of government functions versus constitutional law's role in defining the government's structure and protecting civil liberties.
Sources of Administrative Law
Administrative law derives primarily from statutes enacted by legislatures, executive orders issued by government agencies, and judicial decisions interpreting these rules, distinguishing it from constitutional law, which is grounded in a nation's constitution. Key sources include enabling acts that delegate authority to administrative bodies and agency regulations that carry the force of law. This framework governs the procedures and actions of public administration, ensuring compliance with statutory mandates and protecting citizens' rights under administrative processes.
Sources of Constitutional Law
Constitutional law derives primarily from written constitutions, judicial interpretations, and authoritative legal precedents that establish the fundamental principles of government structure and individual rights. Administrative law, in contrast, is rooted in statutes and regulations enacted by legislative bodies and executed by administrative agencies to manage public policy implementation. Understanding constitutional law's sources is essential to interpreting the limits of government power and protecting civil liberties.
Functions of Administrative Law in Governance
Administrative law governs the actions and operations of government agencies, ensuring compliance with statutory mandates and safeguarding public interest through regulatory oversight. It establishes frameworks for decision-making, accountability, and the enforcement of rules, thereby facilitating efficient public administration and dispute resolution. By controlling administrative discretion and providing mechanisms for redress, administrative law supports the practical implementation of governmental policies within constitutional boundaries.
Role of Constitutional Law in Government Structure
Constitutional law establishes the fundamental principles and framework of a government, delineating the separation of powers among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. It defines the scope and limits of governmental authority while protecting individual rights through codified rights in constitutions or charters. This legal foundation ensures that administrative law operates within constitutional boundaries, maintaining the rule of law and preventing arbitrary state action.
Legal Principles Unique to Administrative Law
Administrative law centers on the principle of judicial review, ensuring government agencies act within legal boundaries while maintaining procedural fairness through doctrines such as natural justice and the right to a fair hearing. It emphasizes the concept of delegated legislation, where statutory powers are entrusted to administrative bodies, distinguishing it from constitutional law's focus on the foundational distribution of governmental powers. The principle of reasonableness governs administrative decisions, requiring actions to be rational and proportional, a standard uniquely enforced through administrative tribunals and courts.
Fundamental Doctrines of Constitutional Law
Administrative law governs the activities of government agencies and ensures their actions comply with legal standards, focusing on rule-making, enforcement, and adjudication. Constitutional law establishes the fundamental doctrines that define the structure, powers, and limitations of government institutions, such as separation of powers, judicial review, and federalism. These core principles safeguard individual rights and maintain the balance between different branches of government, ensuring constitutional supremacy and rule of law.
Impact of Administrative and Constitutional Laws on Citizens
Administrative law governs the actions of government agencies and ensures they follow legal procedures, directly impacting citizens by regulating public services, benefits, and enforcement of regulations. Constitutional law establishes the fundamental rights and freedoms of individuals, shaping the limits of government power and protecting civil liberties. Together, these legal frameworks define the balance between government authority and individual rights, influencing public accountability and access to justice.
Administrative Law vs Constitutional Law Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com