A Sunset Clause sets an expiration date on a government policy or program, requiring periodic review and renewal to remain in effect. In contrast, a Grandfather Clause allows existing conditions or rights to continue under old rules, exempting them from new regulations. Both clauses serve to manage transitions but differ in approach: one phases out policies, while the other preserves prior arrangements.
Table of Comparison
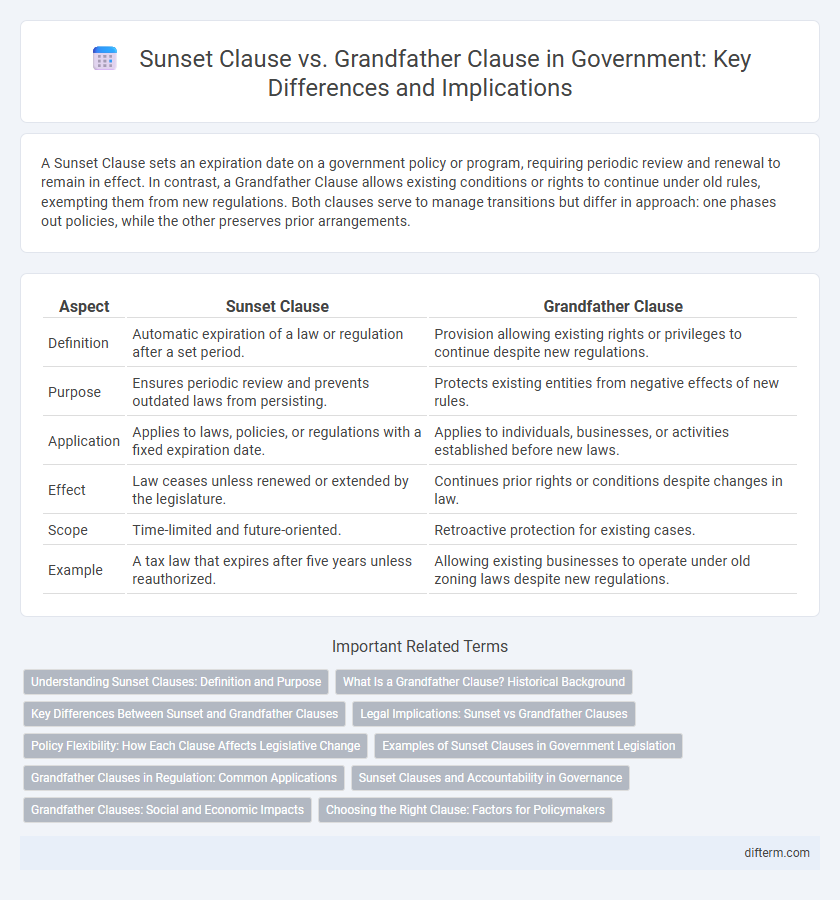
| Aspect | Sunset Clause | Grandfather Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatic expiration of a law or regulation after a set period. | Provision allowing existing rights or privileges to continue despite new regulations. |
| Purpose | Ensures periodic review and prevents outdated laws from persisting. | Protects existing entities from negative effects of new rules. |
| Application | Applies to laws, policies, or regulations with a fixed expiration date. | Applies to individuals, businesses, or activities established before new laws. |
| Effect | Law ceases unless renewed or extended by the legislature. | Continues prior rights or conditions despite changes in law. |
| Scope | Time-limited and future-oriented. | Retroactive protection for existing cases. |
| Example | A tax law that expires after five years unless reauthorized. | Allowing existing businesses to operate under old zoning laws despite new regulations. |
Understanding Sunset Clauses: Definition and Purpose
Sunset clauses are legislative provisions that set an automatic expiration date for a law or regulation unless further legislative action is taken to renew it. These clauses ensure periodic review and prevent outdated or ineffective laws from remaining in force indefinitely. By requiring timely evaluation, sunset clauses promote accountability and adaptability in government policy-making.
What Is a Grandfather Clause? Historical Background
A grandfather clause is a regulatory provision allowing existing rights or privileges to continue despite new laws or regulations that would otherwise prohibit them. Historically, this legal mechanism emerged in the late 19th century in the United States, often associated with voting rights where certain exemptions were granted to individuals whose ancestors had voting privileges before specific dates. This clause aimed to prevent retroactive application of new legislation and maintain continuity for pre-existing legal conditions.
Key Differences Between Sunset and Grandfather Clauses
Sunset clauses mandate the automatic expiration of a law or regulation after a specific period unless renewed, ensuring periodic review and preventing outdated policies. Grandfather clauses allow existing entities or rights to continue operating under old rules despite new regulations, providing exemptions to avoid disruption. The key difference lies in sunset clauses imposing a time limit on laws, while grandfather clauses protect pre-existing conditions from new legal changes.
Legal Implications: Sunset vs Grandfather Clauses
Sunset clauses mandate the automatic expiration of a law or regulation after a predetermined period unless actively renewed by the legislature, ensuring periodic review and preventing outdated statutes from persisting. Grandfather clauses legally exempt existing entities or conditions from new regulations, preserving prior rights and avoiding retroactive application of laws. The key legal implication lies in balancing dynamic regulatory oversight through sunset clauses with stability and fairness for established parties via grandfather clauses.
Policy Flexibility: How Each Clause Affects Legislative Change
Sunset clauses impose automatic expiration dates on laws, forcing legislatures to review and renew policies to maintain their validity, which enhances policy flexibility by encouraging periodic reassessment. Grandfather clauses allow existing conditions or rights to continue despite new regulations, providing stability but limiting immediate legislative change. This creates a balance where sunset clauses promote dynamic policy updates, while grandfather clauses protect entrenched interests from abrupt shifts in law.
Examples of Sunset Clauses in Government Legislation
Sunset clauses are commonly applied in government legislation to ensure periodic review and prevent outdated laws from remaining in force indefinitely; for instance, the USA PATRIOT Act initially included a sunset clause in 2005, requiring Congress to reauthorize key provisions. Another example is the Affordable Care Act's temporary Medicaid expansion funding, which incorporated sunset clauses to evaluate its long-term fiscal impact. These clauses promote legislative accountability by mandating evaluation before extension or termination.
Grandfather Clauses in Regulation: Common Applications
Grandfather clauses in government regulation allow pre-existing entities or practices to continue operating under old rules despite new laws or standards, ensuring stability and fairness. Common applications include zoning laws, where existing buildings or land uses are exempt from new restrictions, and environmental regulations that exclude facilities built before certain compliance dates. This approach minimizes disruption while facilitating gradual transitions to updated regulatory frameworks.
Sunset Clauses and Accountability in Governance
Sunset clauses are legislative provisions that set expiration dates on government programs or laws unless explicitly renewed, promoting accountability by requiring regular review and justification of continued operation. They prevent outdated or ineffective policies from persisting indefinitely, ensuring government actions remain relevant and effective. This mechanism enforces transparency and responsiveness, holding policymakers accountable for the ongoing impact and necessity of their initiatives.
Grandfather Clauses: Social and Economic Impacts
Grandfather clauses in government policies often preserve pre-existing rights or conditions for certain groups, mitigating immediate economic disruptions and social resistance. These clauses can stabilize markets by allowing businesses and individuals to continue operations under old regulations, fostering gradual adaptation. However, they may also perpetuate inequalities by maintaining outdated privileges or exemptions.
Choosing the Right Clause: Factors for Policymakers
Policymakers must evaluate the long-term implications of Sunset Clauses, which enforce automatic expiration of laws, against Grandfather Clauses that allow existing entities to operate under previous regulations. Key factors include administrative feasibility, regulatory certainty, stakeholder impact, and adaptability to evolving social or economic conditions. The choice hinges on balancing flexibility in governance with protection for current rights and investments.
Sunset Clause vs Grandfather Clause Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com