Early voting allows eligible voters to cast their ballots in person at designated polling locations before Election Day, providing convenience and reducing wait times. Absentee voting permits individuals to submit their ballots by mail or drop-off without appearing in person, ensuring accessibility for those unable to visit polling sites. Both methods enhance voter participation and accommodate diverse needs, strengthening democratic processes.
Table of Comparison
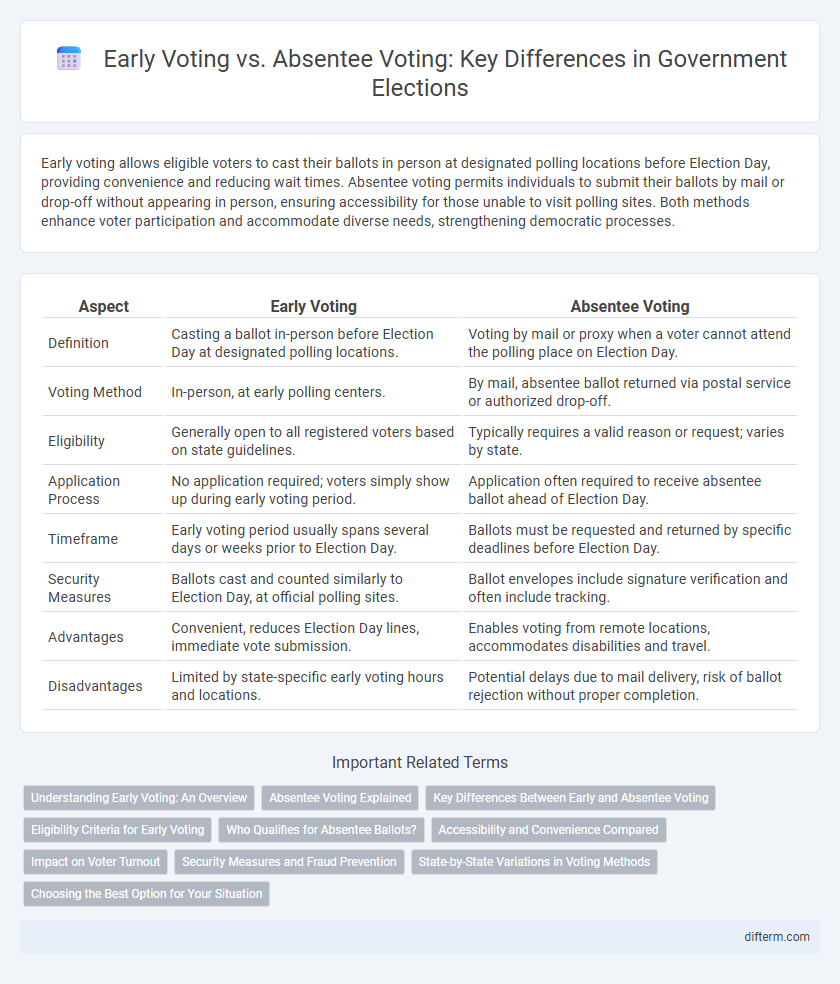
| Aspect | Early Voting | Absentee Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Casting a ballot in-person before Election Day at designated polling locations. | Voting by mail or proxy when a voter cannot attend the polling place on Election Day. |
| Voting Method | In-person, at early polling centers. | By mail, absentee ballot returned via postal service or authorized drop-off. |
| Eligibility | Generally open to all registered voters based on state guidelines. | Typically requires a valid reason or request; varies by state. |
| Application Process | No application required; voters simply show up during early voting period. | Application often required to receive absentee ballot ahead of Election Day. |
| Timeframe | Early voting period usually spans several days or weeks prior to Election Day. | Ballots must be requested and returned by specific deadlines before Election Day. |
| Security Measures | Ballots cast and counted similarly to Election Day, at official polling sites. | Ballot envelopes include signature verification and often include tracking. |
| Advantages | Convenient, reduces Election Day lines, immediate vote submission. | Enables voting from remote locations, accommodates disabilities and travel. |
| Disadvantages | Limited by state-specific early voting hours and locations. | Potential delays due to mail delivery, risk of ballot rejection without proper completion. |
Understanding Early Voting: An Overview
Early voting allows registered voters to cast their ballots in person before Election Day at designated polling locations, increasing accessibility and reducing wait times. It typically spans a specific period set by state law, often starting 15 to 30 days prior to the election, and requires voters to present valid identification. This voting method enhances participation by providing flexibility and convenience, particularly for those unable to vote on Election Day.
Absentee Voting Explained
Absentee voting allows eligible voters to cast ballots by mail without appearing in person at polling stations, accommodating those who are unable to vote on Election Day due to travel, illness, or disability. This method requires registered voters to request an absentee ballot within specific deadlines set by state election laws to ensure timely processing and counting. Absentee voting enhances electoral participation while maintaining ballot security through verification processes and strict handling protocols.
Key Differences Between Early and Absentee Voting
Early voting allows registered voters to cast their ballots in person prior to Election Day, providing convenience and immediate ballot submission. Absentee voting requires voters to request, complete, and return a mail-in ballot if they cannot or prefer not to vote in person. The key differences lie in the voting method, timeline for ballot submission, and eligibility requirements tied to each process.
Eligibility Criteria for Early Voting
Eligibility criteria for early voting typically require registered voters to cast their ballots at designated locations before Election Day, without needing to provide a specific reason or excuse. Most U.S. states permit any registered voter to participate in early voting, contrasting with absentee voting, which often mandates a valid justification such as being out of the voting district or having a disability. Some states impose age or residency requirements for early voting eligibility, ensuring compliance with local election laws and voter identification regulations.
Who Qualifies for Absentee Ballots?
Absentee ballots are available to voters who cannot physically visit polling stations on Election Day due to reasons such as disability, illness, travel, or military deployment. Eligibility requirements vary by state but commonly include being out of the voting jurisdiction or having a scheduling conflict with work or caregiving responsibilities. Voters typically must submit a formal request or application to receive an absentee ballot before the election deadline.
Accessibility and Convenience Compared
Early voting offers in-person access at designated polling sites before Election Day, increasing convenience for voters who prefer direct engagement and reducing congestion on the official day. Absentee voting allows ballots to be submitted by mail or dropbox, providing high accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges, those living abroad, or residents with unpredictable schedules. Both methods enhance participation rates by catering to diverse voter needs and facilitating flexible voting options.
Impact on Voter Turnout
Early voting increases voter turnout by providing flexible in-person options that accommodate work schedules and reduce Election Day congestion. Absentee voting expands participation by allowing voters to cast ballots remotely, particularly benefiting military personnel, elderly citizens, and those with disabilities. Both methods enhance democratic engagement, with studies showing jurisdictions adopting early and absentee voting experience higher overall voter participation rates.
Security Measures and Fraud Prevention
Early voting and absentee voting both implement robust security measures to safeguard electoral integrity, including voter identification verification and secure ballot tracking systems. Absentee voting relies heavily on signature verification and secure ballot drop-off locations to prevent fraud, while early voting employs in-person identity checks and monitored voting environments. Both methods utilize advanced encryption and auditing processes to ensure accurate vote counting and minimize the risk of electoral fraud.
State-by-State Variations in Voting Methods
State-by-state variations in early voting and absentee voting significantly impact voter accessibility and election outcomes. Some states offer extensive early voting periods with multiple in-person locations, while others limit early voting opportunities or rely more heavily on absentee ballots requiring specific eligibility criteria. These differences influence voter turnout by shaping convenience, trust, and voting method preferences across diverse demographics.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Situation
Early voting allows voters to cast ballots in person before Election Day, providing convenience and immediate ballot submission, while absentee voting involves requesting and returning a mail-in ballot, ideal for those unable to visit polling stations. Factors such as travel plans, work schedules, and health concerns influence the optimal choice. Selecting the best option depends on individual availability, voter registration deadlines, and the specific rules governing early and absentee voting in each state.
Early Voting vs Absentee Voting Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com