The Ombudsman serves as an independent authority addressing complaints from the public against government agencies to ensure fairness and accountability. The Inspector General typically operates within specific government departments, conducting audits and investigations to detect waste, fraud, and abuse. Both roles enhance transparency but differ in scope, with the Ombudsman focusing on citizen grievances and the Inspector General on internal oversight.
Table of Comparison
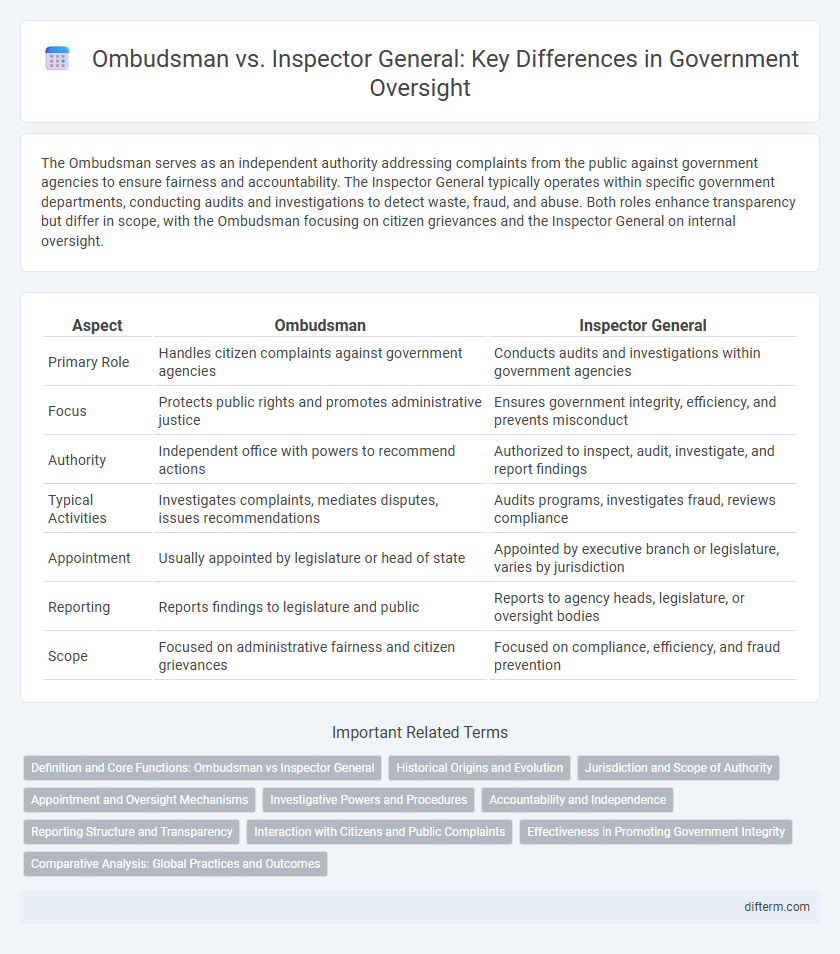
| Aspect | Ombudsman | Inspector General |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Handles citizen complaints against government agencies | Conducts audits and investigations within government agencies |
| Focus | Protects public rights and promotes administrative justice | Ensures government integrity, efficiency, and prevents misconduct |
| Authority | Independent office with powers to recommend actions | Authorized to inspect, audit, investigate, and report findings |
| Typical Activities | Investigates complaints, mediates disputes, issues recommendations | Audits programs, investigates fraud, reviews compliance |
| Appointment | Usually appointed by legislature or head of state | Appointed by executive branch or legislature, varies by jurisdiction |
| Reporting | Reports findings to legislature and public | Reports to agency heads, legislature, or oversight bodies |
| Scope | Focused on administrative fairness and citizen grievances | Focused on compliance, efficiency, and fraud prevention |
Definition and Core Functions: Ombudsman vs Inspector General
An Ombudsman is a government official appointed to investigate complaints from citizens against public authorities, ensuring fairness and accountability in administrative actions. The Inspector General is a supervisory official responsible for auditing, investigating fraud, waste, and abuse within government agencies to promote integrity and efficiency. While the Ombudsman primarily addresses public grievances, the Inspector General focuses on internal oversight and compliance enforcement.
Historical Origins and Evolution
The Ombudsman role originated in Sweden in 1809 as a parliamentary authority designed to oversee government administration and protect citizens' rights, evolving globally as a mediator between the public and the state. The Inspector General position emerged in 18th-century military contexts, primarily in Prussia, to provide systematic oversight, audits, and investigations within government agencies and departments. Over time, both roles have expanded in scope, with Ombudsmen focusing on complaint resolution and fairness, while Inspectors General emphasize accountability, integrity, and fraud prevention in government operations.
Jurisdiction and Scope of Authority
The Ombudsman primarily addresses complaints regarding government malfeasance, administrative injustice, and citizen grievances, focusing on individual cases and ensuring accountability in public services. The Inspector General exercises broad jurisdiction over investigations involving fraud, waste, abuse, and misconduct within government agencies, often possessing authority to conduct audits and enforce compliance with laws and regulations. While both serve oversight functions, the Ombudsman typically handles public complaints and promotes transparency, whereas the Inspector General focuses on internal controls and systemic integrity within government operations.
Appointment and Oversight Mechanisms
Ombudsmen are typically appointed through parliamentary approval or by the head of state to serve as independent watchdogs focusing on public grievances, with oversight often provided by legislative committees or independent commissions ensuring impartiality. Inspectors General are usually appointed by executive authorities, such as the president or agency heads, and their oversight is maintained through internal government structures and periodic legislative reviews to monitor compliance and detect misconduct. Both roles emphasize transparency and accountability, yet their appointment and oversight frameworks reflect their distinct mandates within government institutions.
Investigative Powers and Procedures
The Ombudsman primarily investigates complaints from the public regarding maladministration and abuses of power, operating independently with broad authority to access government documents and summon witnesses. The Inspector General focuses on auditing and investigating government agencies' compliance with laws and regulations, employing formal procedures including subpoenas, audits, and performance reviews. Both roles enhance government accountability but differ in scope, with the Ombudsman emphasizing citizen grievances and the Inspector General targeting internal oversight and fraud detection.
Accountability and Independence
The Ombudsman operates as an independent entity focused on ensuring government accountability by investigating complaints and maladministration directly affecting citizens. The Inspector General serves within government agencies to promote internal accountability through audits, investigations, and oversight of agency operations. Both roles maintain independence to prevent conflicts of interest, but the Ombudsman typically addresses external grievances while the Inspector General emphasizes internal compliance and integrity.
Reporting Structure and Transparency
The Ombudsman typically reports directly to the legislature or an independent commission, ensuring a high level of transparency and accountability to the public. In contrast, the Inspector General usually reports within the executive branch, often to the head of the agency or department, which can limit external transparency. The Ombudsman's reporting structure facilitates greater public access to investigation outcomes, while the Inspector General balances internal oversight with protecting sensitive information.
Interaction with Citizens and Public Complaints
Ombudsmen serve as independent intermediaries between citizens and government agencies, facilitating complaint resolution and ensuring administrative fairness. Inspectors General primarily investigate allegations of fraud, waste, and abuse within government operations, often working internally to audit and recommend corrective actions. Citizens typically engage directly with Ombudsmen for assistance, while Inspectors General handle complaints through formal investigative processes.
Effectiveness in Promoting Government Integrity
Ombudsmen enhance government integrity by providing accessible, impartial grievance mechanisms for citizens, fostering transparency and accountability in public administration. Inspectors General contribute to effectiveness through rigorous investigations, audits, and oversight within government agencies, detecting fraud, waste, and abuse to ensure compliance with laws and regulations. Both roles are crucial, but Inspectors General typically have greater enforcement powers, making them more effective in promoting systemic integrity and organizational reforms.
Comparative Analysis: Global Practices and Outcomes
Ombudsmen and Inspectors General serve as critical oversight entities within governments, with Ombudsmen primarily addressing citizen complaints about administrative injustice, while Inspectors General focus on internal audits, investigations, and fraud prevention. Globally, countries like Sweden and Canada employ Ombudsmen to enhance public trust through independent complaint resolution, whereas the United States and South Africa utilize Inspectors General to strengthen accountability within government agencies by conducting rigorous inspections and evaluations. Comparative studies reveal that integrating both roles can optimize transparency, but challenges persist in balancing independence, scope of authority, and public accessibility across different jurisdictions.
Ombudsman vs Inspector General Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com