Government pets symbolize the tension between statism and libertarianism, embodying the debate over state control versus individual freedom. Statism advocates for centralized authority to regulate and provide for public needs, often justifying the existence of government dependencies. Libertarianism emphasizes minimal state intervention, promoting personal responsibility and market-driven solutions without reliance on government support.
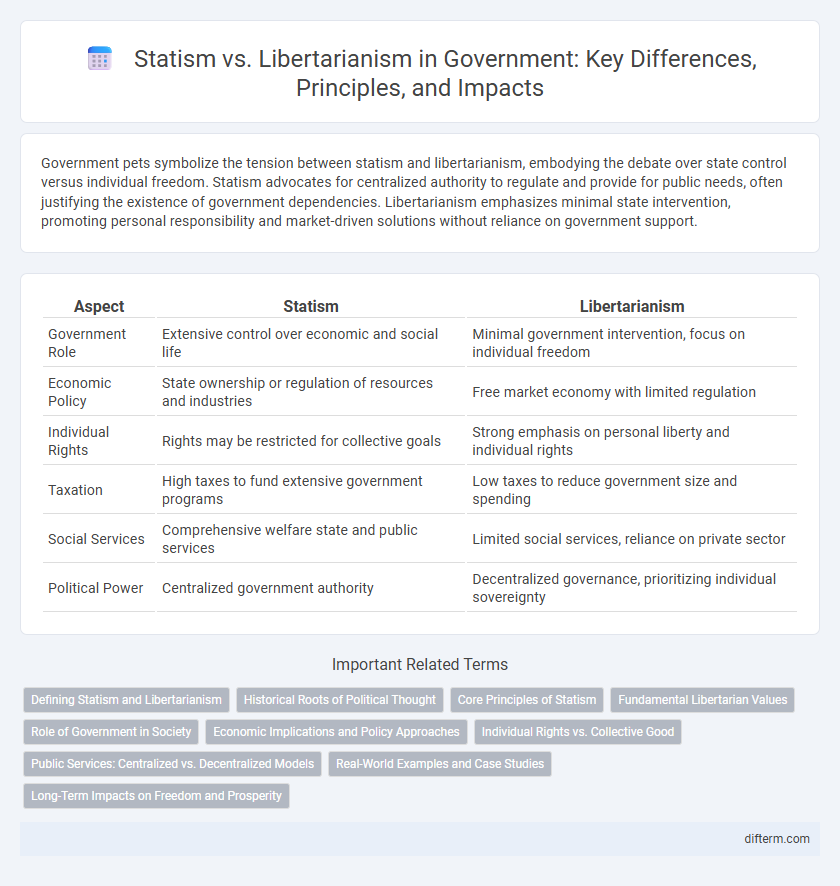
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Statism | Libertarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Government Role | Extensive control over economic and social life | Minimal government intervention, focus on individual freedom |
| Economic Policy | State ownership or regulation of resources and industries | Free market economy with limited regulation |
| Individual Rights | Rights may be restricted for collective goals | Strong emphasis on personal liberty and individual rights |
| Taxation | High taxes to fund extensive government programs | Low taxes to reduce government size and spending |
| Social Services | Comprehensive welfare state and public services | Limited social services, reliance on private sector |
| Political Power | Centralized government authority | Decentralized governance, prioritizing individual sovereignty |
Defining Statism and Libertarianism
Statism advocates for substantial government control over economic and social policies, emphasizing centralized authority to achieve societal goals and maintain order. Libertarianism promotes individual liberty, minimal government intervention, and free-market principles, prioritizing personal freedom and limited regulation. The ideological divide centers on the balance between state power and individual rights in governance.
Historical Roots of Political Thought
Statism traces its roots to early centralized governance models, such as those in ancient Mesopotamia and the Byzantine Empire, where state control ensured social order and resource distribution. Libertarianism emerged from Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke and Adam Smith, emphasizing individual liberty, limited government, and free markets. These ideological origins reflect contrasting views on the role of state power versus personal freedom in shaping political institutions and societal structures.
Core Principles of Statism
Statism emphasizes centralized government control as essential for maintaining order, promoting social welfare, and regulating economic activities to prevent inequality. It prioritizes collective interests over individual autonomy, advocating state intervention to ensure stability and public services. Key principles include authority concentration, regulation enforcement, and the belief that government is the primary agent of societal progress and protection.
Fundamental Libertarian Values
Fundamental libertarian values emphasize individual liberty, limited government intervention, and the protection of private property rights as essential components of a free society. Statism advocates for a more expansive government role in regulating economic and social life to promote collective welfare and equity. Libertarians argue that minimizing state power maximizes personal freedom and economic efficiency, fostering innovation and voluntary cooperation.
Role of Government in Society
Statism emphasizes a strong governmental role in regulating economic activities and providing extensive public services to maintain social order and promote collective welfare. Libertarianism advocates for minimal state intervention, prioritizing individual liberties and free-market principles to foster personal responsibility and innovation. The debate centers on balancing government authority with individual freedom to achieve societal stability and prosperity.
Economic Implications and Policy Approaches
Statism advocates for substantial government intervention in the economy, promoting policies such as centralized planning, higher taxation, and extensive social welfare programs to redistribute wealth and regulate markets. Libertarianism emphasizes minimal state involvement, supporting free-market capitalism, lower taxes, deregulation, and privatization to foster individual entrepreneurship and economic growth. These contrasting approaches significantly impact fiscal policy, economic efficiency, and the balance between public goods provision and personal economic freedom.
Individual Rights vs. Collective Good
Statism emphasizes the role of government in promoting the collective good through regulations, social programs, and centralized decision-making, often prioritizing societal welfare over individual liberties. Libertarianism champions individual rights, advocating minimal government interference to protect personal freedom, private property, and voluntary exchange. The balance between collective responsibility and personal autonomy remains a central debate in political philosophy and governance policy design.
Public Services: Centralized vs. Decentralized Models
Statism advocates for centralized public services managed by the government to ensure uniform standards and equitable resource distribution across regions. Libertarianism supports decentralized models, promoting local autonomy and community-driven solutions that increase efficiency and responsiveness to specific needs. Comparative studies show decentralized services often foster innovation and adaptability, while centralized systems provide broader access and consistency in essential public goods.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Statism, exemplified by China's centralized government control, prioritizes state intervention in economic and social affairs to maintain stability and growth, while libertarianism, as seen in Hong Kong's historical emphasis on free markets and minimal regulation, advocates for individual freedoms and limited government influence. Countries like Sweden implement a hybrid model, balancing welfare state principles with market-based strategies, showcasing a pragmatic middle ground. These real-world cases highlight the tension between governmental authority and personal liberty, influencing policy outcomes and citizen experiences worldwide.
Long-Term Impacts on Freedom and Prosperity
Statism often leads to centralized control that can restrict individual freedoms and hinder economic innovation, potentially limiting long-term prosperity. Libertarianism advocates for minimal government intervention, promoting individual liberty and free markets that can drive sustainable economic growth and personal autonomy. Evaluations of historical data reveal that societies with greater emphasis on libertarian principles tend to experience higher levels of innovation, wealth generation, and protection of civil liberties over extended periods.
statism vs libertarianism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com