Energy efficiency involves using technology or methods that require less energy to perform the same task, reducing overall consumption without sacrificing performance. Energy conservation focuses on behavioral changes that decrease energy use, such as turning off lights or reducing heating and cooling. Both strategies lessen environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions and conserving natural resources.
Table of Comparison
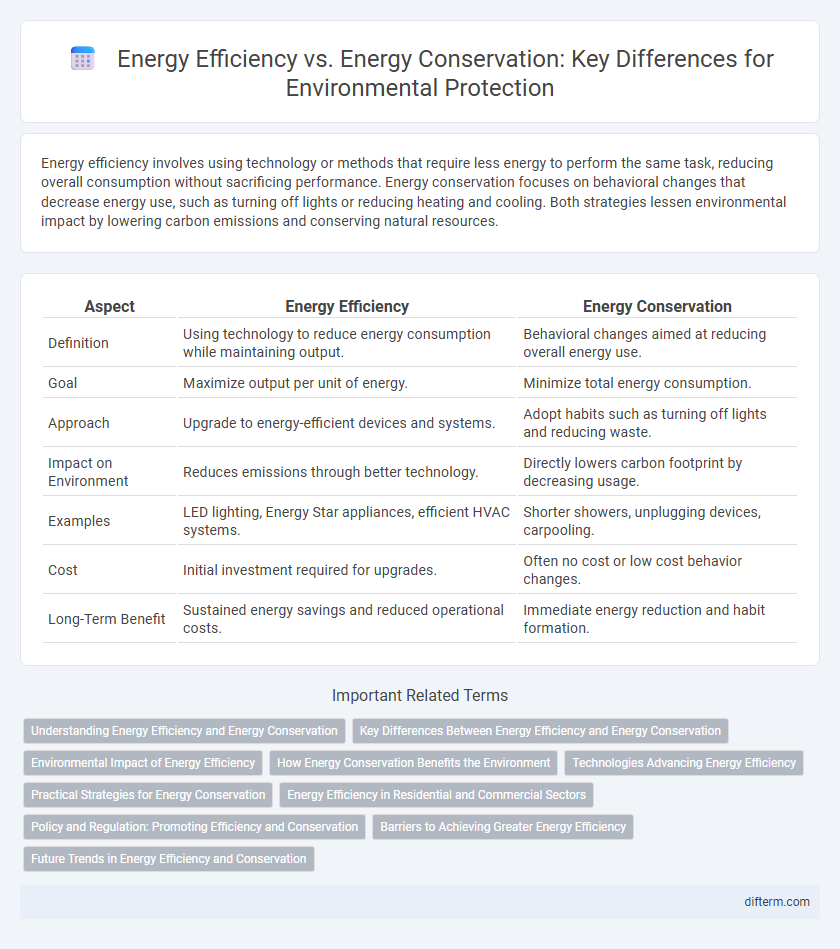
| Aspect | Energy Efficiency | Energy Conservation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using technology to reduce energy consumption while maintaining output. | Behavioral changes aimed at reducing overall energy use. |
| Goal | Maximize output per unit of energy. | Minimize total energy consumption. |
| Approach | Upgrade to energy-efficient devices and systems. | Adopt habits such as turning off lights and reducing waste. |
| Impact on Environment | Reduces emissions through better technology. | Directly lowers carbon footprint by decreasing usage. |
| Examples | LED lighting, Energy Star appliances, efficient HVAC systems. | Shorter showers, unplugging devices, carpooling. |
| Cost | Initial investment required for upgrades. | Often no cost or low cost behavior changes. |
| Long-Term Benefit | Sustained energy savings and reduced operational costs. | Immediate energy reduction and habit formation. |
Understanding Energy Efficiency and Energy Conservation
Energy efficiency involves using technology and methods that require less energy to perform the same task, such as LED lighting or high-efficiency appliances, thereby reducing overall energy consumption without sacrificing productivity. Energy conservation focuses on behavioral changes that reduce energy use, like turning off lights when not needed or lowering thermostat settings to decrease demand. Both strategies play crucial roles in minimizing environmental impact by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources.
Key Differences Between Energy Efficiency and Energy Conservation
Energy efficiency involves using technology or methods that require less energy to perform the same task, such as LED lighting or energy-efficient appliances. Energy conservation refers to behavioral changes that reduce overall energy consumption, like turning off lights when not in use or reducing heating and cooling demands. Key differences lie in energy efficiency focusing on technological improvements, while energy conservation emphasizes changing human habits to minimize energy use.
Environmental Impact of Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency reduces the amount of energy required to provide the same service, significantly decreasing carbon emissions and minimizing environmental degradation. Technologies like LED lighting and high-efficiency HVAC systems lower energy consumption without sacrificing performance, which directly cuts fossil fuel burning and air pollution. Reduced energy use through efficiency supports climate change mitigation by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and lessening habitat disruption associated with energy production.
How Energy Conservation Benefits the Environment
Energy conservation reduces overall energy demand, leading to fewer fossil fuels burned and lowering greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. By minimizing wasteful energy use in homes, industries, and transportation, ecosystems are preserved and air quality improves, promoting biodiversity and public health. Energy conservation also decreases the strain on natural resources, ensuring sustainable energy availability for future generations.
Technologies Advancing Energy Efficiency
Technologies advancing energy efficiency focus on optimizing energy use through innovations such as smart grids, LED lighting, and high-efficiency HVAC systems, reducing overall energy consumption without compromising output. These technologies integrate IoT sensors and AI algorithms to monitor and adjust energy usage in real time, enhancing performance in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Compared to energy conservation, which relies on behavioral changes to reduce consumption, energy efficiency technologies provide sustainable solutions that maintain productivity while lowering environmental impact.
Practical Strategies for Energy Conservation
Energy conservation involves practical strategies such as turning off unused appliances, using programmable thermostats, and adopting behavioral changes to reduce energy demand. Implementing efficient lighting solutions like LED bulbs and optimizing appliance usage schedules contribute significantly to lowering overall energy consumption. These methods not only conserve energy but also help reduce environmental impact and utility costs.
Energy Efficiency in Residential and Commercial Sectors
Energy efficiency in residential and commercial sectors significantly reduces energy consumption by utilizing advanced technologies such as LED lighting, high-efficiency HVAC systems, and smart thermostats, leading to lower utility bills and decreased greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing energy-efficient building designs, including improved insulation, energy-efficient windows, and renewable energy integration, enhances sustainability and occupant comfort. These strategies contribute to sustainable development goals by optimizing energy use without compromising productivity or comfort, distinguishing energy efficiency from the behavioral focus of energy conservation.
Policy and Regulation: Promoting Efficiency and Conservation
Energy efficiency policies target reducing energy waste through advanced technologies and standards, thereby lowering consumption without sacrificing productivity. Energy conservation regulations encourage behavioral changes and reduced energy use through incentives and awareness programs. Combining both approaches strengthens environmental protection by optimizing resource use and minimizing carbon emissions.
Barriers to Achieving Greater Energy Efficiency
Barriers to achieving greater energy efficiency include high upfront costs, limited access to advanced technologies, and lack of awareness or technical expertise among consumers and businesses. Regulatory hurdles and market failures often impede investments in energy-efficient solutions, while split incentives between landlords and tenants reduce motivation to upgrade infrastructure. Overcoming these challenges requires targeted policies, financial incentives, and education to promote widespread adoption of energy-efficient practices.
Future Trends in Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Future trends in energy efficiency highlight the integration of smart technologies and AI-driven systems to optimize energy consumption across industries and households. Energy conservation emphasizes behavioral shifts and policy frameworks that encourage reduced energy use and sustainable practices. Innovations like advanced building materials and real-time energy monitoring platforms are driving both efficiency gains and conservation efforts toward a low-carbon future.
energy efficiency vs energy conservation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com