Agroforestry integrates trees with crops, enhancing biodiversity and improving soil health by reducing erosion and increasing nutrient cycling. Silvopasture combines trees with livestock grazing, offering shade and shelter that boosts animal welfare while diversifying farm income. Both practices promote sustainable land use, but agroforestry emphasizes crop production alongside trees, whereas silvopasture centers on harmonizing tree growth with pasture and animal management.
Table of Comparison
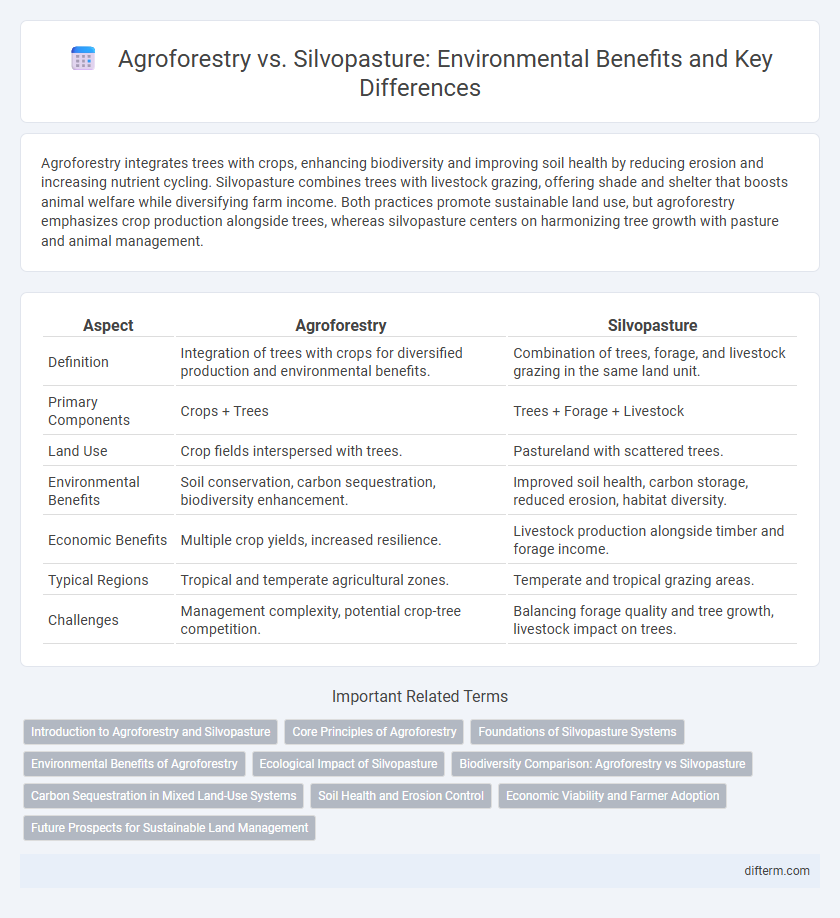
| Aspect | Agroforestry | Silvopasture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of trees with crops for diversified production and environmental benefits. | Combination of trees, forage, and livestock grazing in the same land unit. |
| Primary Components | Crops + Trees | Trees + Forage + Livestock |
| Land Use | Crop fields interspersed with trees. | Pastureland with scattered trees. |
| Environmental Benefits | Soil conservation, carbon sequestration, biodiversity enhancement. | Improved soil health, carbon storage, reduced erosion, habitat diversity. |
| Economic Benefits | Multiple crop yields, increased resilience. | Livestock production alongside timber and forage income. |
| Typical Regions | Tropical and temperate agricultural zones. | Temperate and tropical grazing areas. |
| Challenges | Management complexity, potential crop-tree competition. | Balancing forage quality and tree growth, livestock impact on trees. |
Introduction to Agroforestry and Silvopasture
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs with crop and livestock farming to enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and increase agricultural productivity. Silvopasture combines forestry and grazing of domesticated animals in a mutually beneficial way, promoting sustainable land use by balancing tree cover with pastureland. Both practices support ecological resilience, carbon sequestration, and diversified income for farmers.
Core Principles of Agroforestry
Agroforestry integrates trees, crops, and sometimes livestock on the same land to enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and increase productivity through ecological interactions. Its core principles emphasize sustainable land management by balancing agricultural production with conservation and promoting resource-use efficiency across spatial and temporal scales. This approach supports ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, water regulation, and habitat provision, distinguishing it from silvopasture, which primarily combines forestry and grazing livestock.
Foundations of Silvopasture Systems
Silvopasture systems integrate trees, forage, and livestock to enhance land productivity, biodiversity, and soil health. The foundation relies on selecting compatible tree species that provide shade and fodder while supporting pasture growth and animal welfare. Effective silvopasture management balances tree density, pasture species, and grazing pressure to optimize ecological and economic benefits.
Environmental Benefits of Agroforestry
Agroforestry enhances biodiversity by integrating trees with crops, creating habitats for various species and promoting ecosystem resilience. It improves soil health through nutrient cycling and reduces erosion by stabilizing the ground with root systems. Carbon sequestration in agroforestry systems helps mitigate climate change by capturing atmospheric CO2 more effectively than conventional agriculture.
Ecological Impact of Silvopasture
Silvopasture enhances biodiversity by integrating trees, pasture, and livestock, creating a multi-layered ecosystem that supports diverse flora and fauna. It improves soil health through increased organic matter and reduced erosion, while also promoting carbon sequestration which mitigates climate change effects. This sustainable land-use practice optimizes resource use and strengthens ecosystem resilience compared to monoculture grazing or agriculture systems.
Biodiversity Comparison: Agroforestry vs Silvopasture
Agroforestry systems integrate trees with crops, enhancing biodiversity by providing diverse habitats for plants, insects, and wildlife, and promoting soil health through varied root structures. Silvopasture combines trees with livestock grazing, fostering biodiversity by supporting both arboreal species and ground-level fauna while improving habitat complexity and nutrient cycling. Studies reveal that agroforestry often supports higher plant species richness, whereas silvopasture benefits animal biodiversity, creating complementary ecosystems with unique conservation values.
Carbon Sequestration in Mixed Land-Use Systems
Agroforestry and silvopasture significantly enhance carbon sequestration by integrating trees with crops or livestock, promoting diverse root structures and increased biomass. Studies reveal agroforestry systems can sequester up to 9.8 tons of carbon per hectare annually, while silvopasture improves soil organic carbon through combined tree-grass-livestock interactions. Mixed land-use approaches optimize carbon storage by balancing aboveground and belowground carbon pools, contributing to climate change mitigation.
Soil Health and Erosion Control
Agroforestry integrates diverse tree species with crops, enhancing soil fertility through improved nutrient cycling and organic matter retention, which significantly reduces erosion by stabilizing soil structure. Silvopasture combines trees with grazing livestock, promoting soil health by increasing ground cover and root biomass that minimize surface runoff and soil compaction. Both systems offer robust erosion control, but agroforestry's crop-tree synergy provides greater soil nutrient enhancement compared to the grazing-focused benefits of silvopasture.
Economic Viability and Farmer Adoption
Agroforestry integrates trees with crops, enhancing economic viability through diversified income sources such as timber, fruits, and crop yields, appealing to farmers seeking risk reduction and long-term financial stability. Silvopasture combines trees with livestock grazing, promoting economic benefits by improving pasture productivity and animal welfare, leading to higher-quality meat and dairy products that attract market premiums. Farmer adoption rates tend to favor agroforestry in regions with crop dependence, while silvopasture gains traction where livestock farming dominates, influenced by local market demands and ecological conditions.
Future Prospects for Sustainable Land Management
Agroforestry integrates trees and crops, enhancing biodiversity and soil health while improving crop yields, positioning it as a vital approach for sustainable land management. Silvopasture combines forestry with livestock grazing, optimizing land use by promoting ecological balance and carbon sequestration. Future prospects for both systems lie in their potential to mitigate climate change, restore degraded lands, and support resilient agricultural landscapes.
Agroforestry vs Silvopasture Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com