Ecological efficiency measures the impact of resource use on ecosystems, emphasizing sustainability and minimal environmental harm. Energy efficiency focuses on reducing energy consumption while maintaining performance, often contributing to lower emissions but not always addressing broader ecological effects. Balancing both approaches ensures practical energy savings and promotes overall environmental health.
Table of Comparison
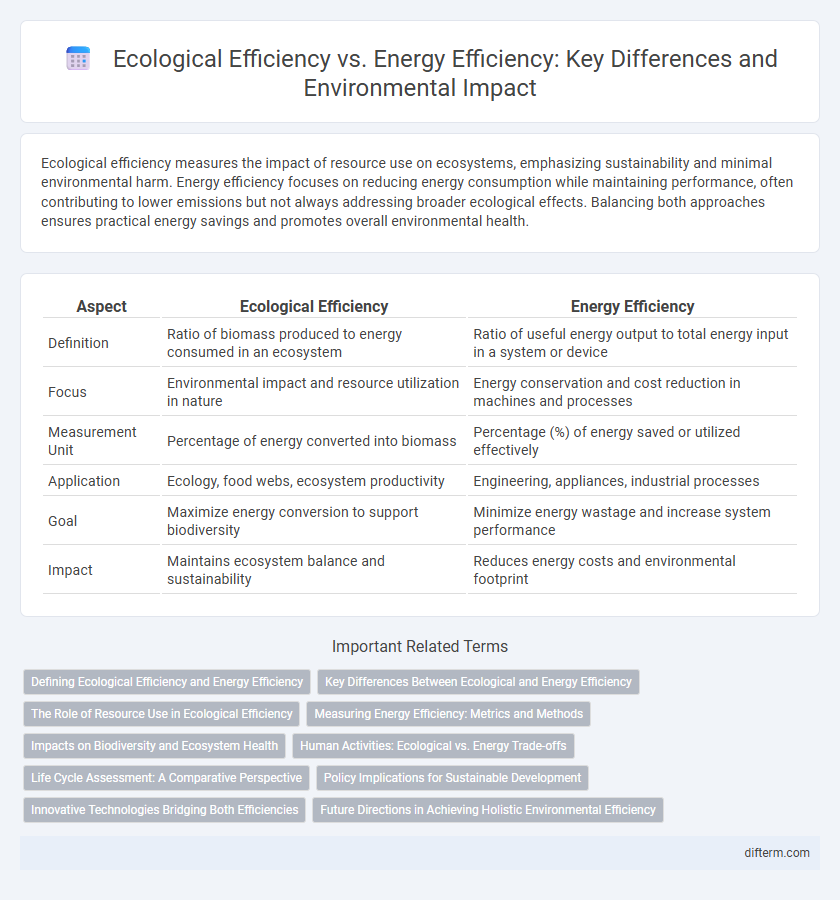
| Aspect | Ecological Efficiency | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of biomass produced to energy consumed in an ecosystem | Ratio of useful energy output to total energy input in a system or device |
| Focus | Environmental impact and resource utilization in nature | Energy conservation and cost reduction in machines and processes |
| Measurement Unit | Percentage of energy converted into biomass | Percentage (%) of energy saved or utilized effectively |
| Application | Ecology, food webs, ecosystem productivity | Engineering, appliances, industrial processes |
| Goal | Maximize energy conversion to support biodiversity | Minimize energy wastage and increase system performance |
| Impact | Maintains ecosystem balance and sustainability | Reduces energy costs and environmental footprint |
Defining Ecological Efficiency and Energy Efficiency
Ecological efficiency measures the energy transfer between trophic levels in an ecosystem, reflecting how effectively organisms convert consumed energy into biomass. Energy efficiency refers to the ratio of useful energy output to the total energy input in human systems such as machines or buildings. Understanding the distinction between ecological efficiency and energy efficiency is crucial for optimizing sustainability in natural and engineered environments.
Key Differences Between Ecological and Energy Efficiency
Ecological efficiency measures the energy transfer between trophic levels in an ecosystem, reflecting how much energy is converted into biomass versus lost as heat, while energy efficiency quantifies the ratio of useful energy output to input in mechanical or electrical systems. Ecological efficiency emphasizes biological processes and energy flow within natural food webs, whereas energy efficiency focuses on reducing energy consumption and waste in human-engineered systems. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimizing resource use in environmental management and sustainable technology development.
The Role of Resource Use in Ecological Efficiency
Ecological efficiency measures how effectively ecosystems convert energy and materials into biomass, emphasizing the sustainable use of resources to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem services. Resource use plays a crucial role by minimizing waste and reducing the depletion of natural capital through optimized nutrient cycling and energy flow. In contrast to energy efficiency, which focuses primarily on minimizing energy input for a specific output, ecological efficiency integrates the broader impact of resource utilization within ecological networks.
Measuring Energy Efficiency: Metrics and Methods
Measuring energy efficiency involves metrics such as the Energy Use Intensity (EUI), which quantifies energy consumption per square foot of a building or facility. Methods include direct monitoring with energy meters, sub-metering specific systems, and implementing building energy modeling software to simulate energy performance. Accurate assessment of energy efficiency aids in optimizing resource use, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and improving overall ecological sustainability.
Impacts on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
Ecological efficiency emphasizes the sustainable use of natural resources to maintain ecosystem functions, thereby supporting biodiversity and reducing habitat degradation, whereas energy efficiency primarily targets minimizing energy consumption with less direct impact on ecosystem health. High ecological efficiency ensures nutrient cycling and species diversity remain intact, which is critical for resilient ecosystems, while energy efficiency improvements mainly reduce emissions that indirectly benefit ecosystem stability. Prioritizing ecological efficiency can lead to more balanced ecosystems and stronger biodiversity preservation compared to solely focusing on energy efficiency metrics.
Human Activities: Ecological vs. Energy Trade-offs
Human activities often reveal a complex trade-off between ecological efficiency and energy efficiency, where optimizing energy consumption can lead to increased ecological degradation. For example, large-scale industrial processes may reduce energy waste but simultaneously disrupt local ecosystems or deplete biodiversity. Balancing these trade-offs requires integrated strategies that minimize carbon footprints while preserving habitat integrity and promoting sustainable resource use.
Life Cycle Assessment: A Comparative Perspective
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) provides a comprehensive framework to evaluate ecological efficiency by measuring environmental impacts across all stages of a product's life, from raw material extraction to disposal. Unlike energy efficiency metrics that focus solely on energy consumption and savings during use phases, LCA captures broader factors including resource depletion, emissions, and waste generation. This comparative perspective highlights how ecological efficiency through LCA better informs sustainable decision-making by addressing multi-dimensional environmental effects beyond just energy use.
Policy Implications for Sustainable Development
Ecological efficiency emphasizes minimizing environmental impact by optimizing the use of natural resources, while energy efficiency focuses on reducing energy consumption and improving energy use technologies. Policy frameworks that integrate both ecological and energy efficiency promote sustainable development by balancing resource conservation with economic growth, encouraging renewable energy adoption, and incentivizing sustainable production practices. Governments adopting such comprehensive policies can drive systemic change to reduce carbon footprints and enhance ecosystem resilience, aligning with global climate goals.
Innovative Technologies Bridging Both Efficiencies
Innovative technologies such as smart grids and advanced energy management systems enhance ecological efficiency by optimizing resource use while boosting energy efficiency through reduced consumption and waste. Integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind with AI-driven analytics enables simultaneous improvements in environmental impact reduction and operational performance. These advancements create a synergistic approach, balancing ecological preservation with energy-saving objectives for sustainable development.
Future Directions in Achieving Holistic Environmental Efficiency
Future directions in achieving holistic environmental efficiency emphasize integrating ecological efficiency with energy efficiency through innovative technologies and sustainable design. Embracing circular economy principles and renewable energy adoption enhances resource conservation and reduces environmental impact. Advanced monitoring systems and life cycle assessments enable precise optimization of energy use while preserving ecosystems and biodiversity.
ecological efficiency vs energy efficiency Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com