Carbon-neutral refers to balancing emitted carbon dioxide with an equivalent amount of carbon removal or offsetting to achieve net-zero carbon emissions. Climate-neutral expands this concept to include all greenhouse gases and broader environmental impacts, aiming for no overall harm to the climate system. Choosing between carbon-neutral and climate-neutral strategies depends on the scope of environmental goals and the desired impact on reducing global warming.
Table of Comparison
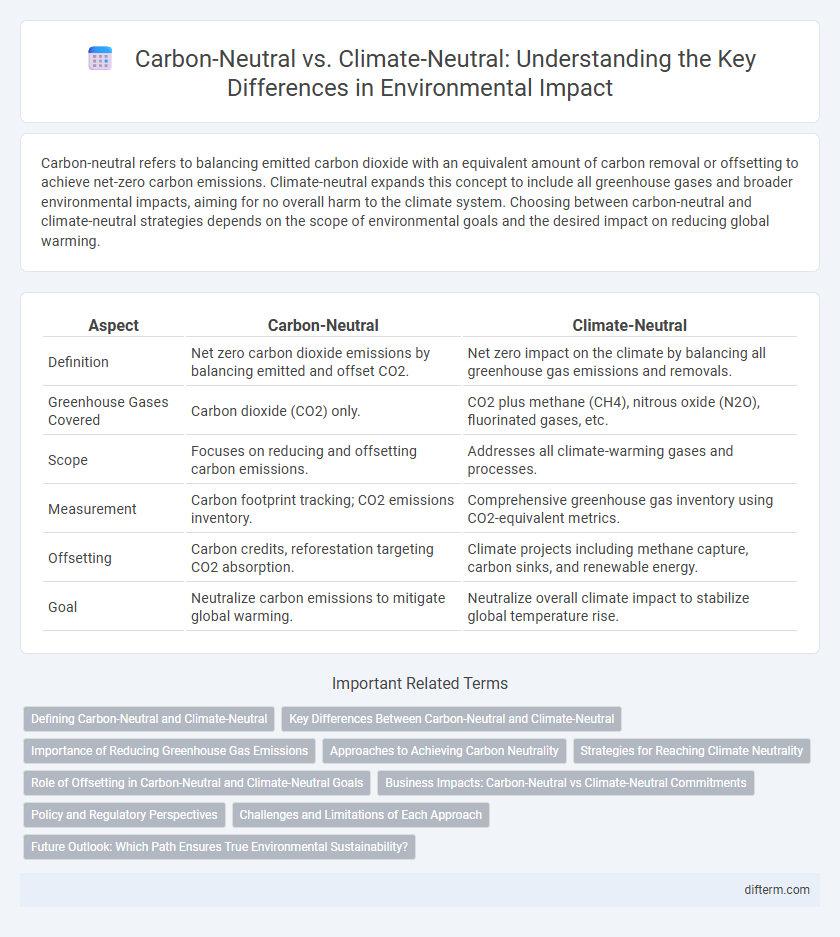
| Aspect | Carbon-Neutral | Climate-Neutral |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Net zero carbon dioxide emissions by balancing emitted and offset CO2. | Net zero impact on the climate by balancing all greenhouse gas emissions and removals. |
| Greenhouse Gases Covered | Carbon dioxide (CO2) only. | CO2 plus methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), fluorinated gases, etc. |
| Scope | Focuses on reducing and offsetting carbon emissions. | Addresses all climate-warming gases and processes. |
| Measurement | Carbon footprint tracking; CO2 emissions inventory. | Comprehensive greenhouse gas inventory using CO2-equivalent metrics. |
| Offsetting | Carbon credits, reforestation targeting CO2 absorption. | Climate projects including methane capture, carbon sinks, and renewable energy. |
| Goal | Neutralize carbon emissions to mitigate global warming. | Neutralize overall climate impact to stabilize global temperature rise. |
Defining Carbon-Neutral and Climate-Neutral
Carbon-neutral refers to achieving net-zero carbon dioxide emissions by balancing emitted carbon with carbon removal or offsetting measures. Climate-neutral encompasses a broader spectrum, targeting the reduction of all greenhouse gas emissions to minimize overall climate impact, not just carbon dioxide. Both concepts aim to mitigate global warming, but climate-neutral strategies address a wider range of environmental pollutants affecting climate change.
Key Differences Between Carbon-Neutral and Climate-Neutral
Carbon-neutral initiatives specifically target the reduction and offsetting of carbon dioxide emissions to achieve net-zero carbon output, primarily addressing greenhouse gas effects related to CO2 alone. Climate-neutral strategies encompass a broader approach, aiming to balance all greenhouse gases, including methane, nitrous oxide, and fluorinated gases, thereby reducing the overall climate impact. The key difference lies in carbon neutrality's narrower focus on CO2, while climate neutrality targets comprehensive mitigation of various climate-altering emissions for a more holistic environmental impact.
Importance of Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential for achieving both carbon-neutral and climate-neutral goals, as it directly mitigates the primary drivers of global warming and climate change. Carbon-neutral efforts focus on balancing emitted carbon dioxide with equivalent offsets, while climate-neutral strategies encompass a broader range of greenhouse gases including methane and nitrous oxide. Prioritizing emission cuts accelerates the transition to sustainable energy systems and enhances resilience against adverse environmental impacts.
Approaches to Achieving Carbon Neutrality
Approaches to achieving carbon neutrality involve reducing greenhouse gas emissions through energy efficiency, renewable energy adoption, and carbon offset projects such as reforestation and carbon capture. Measuring and monitoring carbon footprints with standardized protocols enables precise emission reductions and accountability. Investing in sustainable practices across supply chains supports long-term carbon neutrality goals while fostering environmental resilience.
Strategies for Reaching Climate Neutrality
Achieving climate neutrality involves comprehensive strategies such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions across all sectors, investing in renewable energy sources, and implementing carbon capture and storage technologies. Carbon-neutral initiatives primarily focus on balancing emitted carbon dioxide with carbon offsets like reforestation and carbon trading. Integrating energy efficiency, sustainable transportation, and circular economy principles further accelerates progress towards climate-neutral goals.
Role of Offsetting in Carbon-Neutral and Climate-Neutral Goals
Carbon-neutral goals primarily focus on balancing emitted carbon dioxide through offsets such as reforestation and carbon capture technologies, targeting the net-zero carbon footprint specifically. Climate-neutral goals encompass a broader spectrum, addressing not only carbon emissions but also other greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide by integrating offset projects that mitigate diverse climate impacts. Offsetting plays a critical role in both strategies, enabling organizations to compensate for unavoidable emissions while advancing sustainable practices and technological innovation.
Business Impacts: Carbon-Neutral vs Climate-Neutral Commitments
Businesses adopting carbon-neutral commitments focus on balancing emitted carbon dioxide with equivalent carbon removal efforts, directly targeting CO2 emissions from operations and supply chains to reduce their environmental footprint. Climate-neutral commitments encompass a broader scope, addressing all greenhouse gases and considering wider climate impacts such as methane, nitrous oxide, and indirect emissions linked to products and services. Companies pursuing climate neutrality often implement comprehensive strategies including energy efficiency, renewable energy adoption, and sustainable resource management, which can lead to enhanced brand reputation, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational resilience.
Policy and Regulatory Perspectives
Carbon-neutral policies aim to balance emitted and offset carbon dioxide through carbon credits or sequestration, emphasizing CO2-specific regulations. Climate-neutral frameworks encompass a broader spectrum of greenhouse gases, integrating methane and nitrous oxide controls under comprehensive climate legislation. Regulatory perspectives increasingly prioritize climate-neutral approaches to address multi-gas impacts, aligning national commitments with global climate goals like the Paris Agreement.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Carbon-neutral initiatives primarily address direct carbon dioxide emissions but may overlook other greenhouse gases, limiting their overall climate impact. Climate-neutral approaches encompass a broader range of greenhouse gases and environmental factors, yet they face challenges in measurement accuracy and the integration of diverse climate impacts. Both strategies encounter difficulties in verification, potential carbon offset quality, and aligning with global climate targets to ensure meaningful emissions reductions.
Future Outlook: Which Path Ensures True Environmental Sustainability?
Carbon-neutral efforts focus on balancing emitted carbon dioxide with equivalent carbon removal, primarily addressing CO2 from specific sources. Climate-neutral initiatives expand this scope by targeting all greenhouse gases and considering broader impacts like land use and biodiversity, offering a more holistic approach. Embracing climate-neutral strategies ensures comprehensive environmental sustainability by mitigating diverse climate drivers crucial for a resilient future.
carbon-neutral vs climate-neutral Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com