Habitat conservation focuses on protecting existing natural environments to prevent further degradation and loss of biodiversity. Habitat restoration involves actively repairing damaged ecosystems to recover their functionality and support wildlife populations. Both strategies are crucial for sustaining healthy environments and ensuring long-term survival of species in changing landscapes.
Table of Comparison
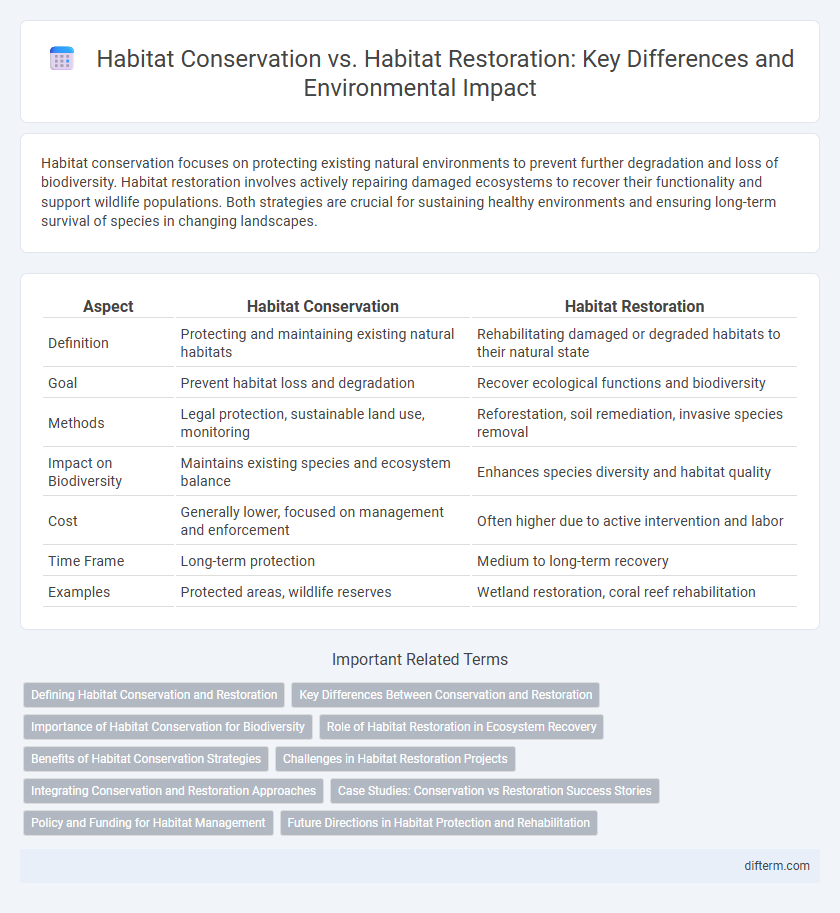
| Aspect | Habitat Conservation | Habitat Restoration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protecting and maintaining existing natural habitats | Rehabilitating damaged or degraded habitats to their natural state |
| Goal | Prevent habitat loss and degradation | Recover ecological functions and biodiversity |
| Methods | Legal protection, sustainable land use, monitoring | Reforestation, soil remediation, invasive species removal |
| Impact on Biodiversity | Maintains existing species and ecosystem balance | Enhances species diversity and habitat quality |
| Cost | Generally lower, focused on management and enforcement | Often higher due to active intervention and labor |
| Time Frame | Long-term protection | Medium to long-term recovery |
| Examples | Protected areas, wildlife reserves | Wetland restoration, coral reef rehabilitation |
Defining Habitat Conservation and Restoration
Habitat conservation involves protecting and maintaining existing natural environments to preserve biodiversity and ecosystem services, emphasizing prevention of habitat loss and degradation. Habitat restoration, by contrast, entails actively repairing and rehabilitating damaged or destroyed ecosystems to return them to their original state or improve their ecological functions. Both strategies are crucial for sustaining wildlife populations and ensuring long-term environmental health.
Key Differences Between Conservation and Restoration
Habitat conservation involves protecting existing natural environments to prevent degradation and maintain biodiversity, while habitat restoration focuses on actively repairing damaged or destroyed ecosystems to return them to their original condition. Conservation prioritizes preventing further loss through strategies like establishing protected areas and enforcing regulations, whereas restoration employs techniques such as reforestation, invasive species removal, and soil rehabilitation to rebuild ecosystem functions. The key difference lies in conservation's preventative approach versus restoration's corrective actions to support long-term ecosystem health.
Importance of Habitat Conservation for Biodiversity
Habitat conservation plays a critical role in maintaining biodiversity by preserving intact ecosystems that sustain diverse species and ecological processes. Protecting natural habitats prevents habitat fragmentation and degradation, which are leading causes of species decline and extinction. Conservation efforts preserve genetic diversity and ecosystem services essential for the resilience and stability of the environment.
Role of Habitat Restoration in Ecosystem Recovery
Habitat restoration plays a critical role in ecosystem recovery by actively rebuilding degraded environments to support native species and ecological functions. Restoration projects often reestablish natural processes such as hydrology and nutrient cycling, which are essential for long-term biodiversity and resilience. Unlike habitat conservation, which aims to protect existing habitats from further degradation, restoration addresses past damages, enabling ecosystems to regain stability and productivity.
Benefits of Habitat Conservation Strategies
Habitat conservation strategies protect existing ecosystems by maintaining biodiversity and essential ecological functions, which support species survival and resilience against climate change. Conserved habitats serve as natural carbon sinks, reducing atmospheric CO2 and mitigating global warming effects. Long-term conservation reduces the need for costly restoration efforts by preserving soil quality, water resources, and native vegetation.
Challenges in Habitat Restoration Projects
Habitat restoration projects face significant challenges including high costs, long timelines, and complexities in replicating original ecosystem functions. Invasive species management and climate change impacts further complicate restoration efforts, often requiring adaptive strategies. Limited funding and stakeholder coordination issues also hinder the successful implementation and sustainability of habitat restoration initiatives.
Integrating Conservation and Restoration Approaches
Integrating habitat conservation and restoration approaches enhances ecosystem resilience by preserving existing biodiversity while actively rehabilitating degraded areas. Strategic land management combines protection of critical habitats with reforestation, invasive species control, and soil stabilization to maximize ecological benefits. Coordinated efforts between conservation policies and restoration projects promote long-term sustainability and support climate adaptation goals.
Case Studies: Conservation vs Restoration Success Stories
The Florida Everglades showcase habitat conservation success through long-term protection of wetlands supporting endangered species like the Florida panther. In contrast, the Chesapeake Bay restoration project highlights habitat restoration by reducing nutrient pollution and replanting submerged aquatic vegetation to revive aquatic ecosystems. Both approaches demonstrate significant biodiversity benefits, with conservation preventing further habitat loss and restoration repairing degraded environments.
Policy and Funding for Habitat Management
Effective habitat conservation relies on proactive policy frameworks that prioritize the protection of existing ecosystems through regulatory measures and incentives. Habitat restoration requires targeted funding allocations to rehabilitate degraded areas, often involving large-scale projects supported by government grants and private investments. Policymakers must balance resource distribution between preservation initiatives and restoration efforts to maximize biodiversity outcomes and ecosystem resilience.
Future Directions in Habitat Protection and Rehabilitation
Future directions in habitat protection emphasize integrative approaches combining habitat conservation with restoration to enhance ecosystem resilience. Advances in remote sensing and ecological modeling enable precise identification of degraded areas requiring focused rehabilitation efforts. Prioritizing native species reintroduction alongside sustainable land-use policies fosters long-term biodiversity preservation and climate adaptation.
habitat conservation vs habitat restoration Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com