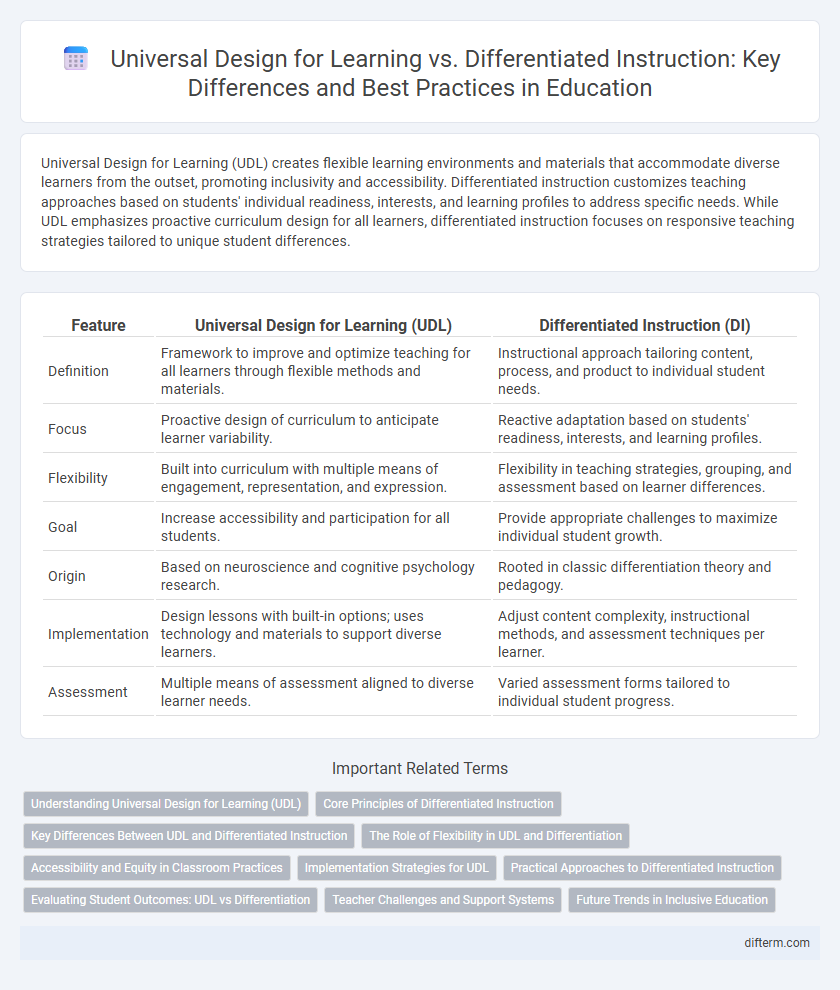
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) creates flexible learning environments and materials that accommodate diverse learners from the outset, promoting inclusivity and accessibility. Differentiated instruction customizes teaching approaches based on students' individual readiness, interests, and learning profiles to address specific needs. While UDL emphasizes proactive curriculum design for all learners, differentiated instruction focuses on responsive teaching strategies tailored to unique student differences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Universal Design for Learning (UDL) | Differentiated Instruction (DI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework to improve and optimize teaching for all learners through flexible methods and materials. | Instructional approach tailoring content, process, and product to individual student needs. |
| Focus | Proactive design of curriculum to anticipate learner variability. | Reactive adaptation based on students' readiness, interests, and learning profiles. |
| Flexibility | Built into curriculum with multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. | Flexibility in teaching strategies, grouping, and assessment based on learner differences. |
| Goal | Increase accessibility and participation for all students. | Provide appropriate challenges to maximize individual student growth. |
| Origin | Based on neuroscience and cognitive psychology research. | Rooted in classic differentiation theory and pedagogy. |
| Implementation | Design lessons with built-in options; uses technology and materials to support diverse learners. | Adjust content complexity, instructional methods, and assessment techniques per learner. |
| Assessment | Multiple means of assessment aligned to diverse learner needs. | Varied assessment forms tailored to individual student progress. |
Understanding Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) provides a framework that emphasizes flexible learning environments to accommodate diverse learner needs by incorporating multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression. Unlike differentiated instruction, which adapts teaching methods based on individual student readiness, interests, or learning profiles, UDL proactively designs curricula accessible to all learners from the start. Implementing UDL enhances educational equity by reducing barriers and promoting inclusive access to knowledge for students with varied abilities and backgrounds.
Core Principles of Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction is centered on tailoring teaching methods to address students' diverse learning needs, readiness levels, and interests through flexible content, process, and product adjustments. Its core principles emphasize ongoing assessment, respectful tasks that challenge each learner appropriately, and creating a supportive learning environment that fosters growth. This approach contrasts with Universal Design for Learning, which proactively designs curricula to be accessible and effective for all learners from the outset.
Key Differences Between UDL and Differentiated Instruction
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes creating flexible learning environments that accommodate all learners by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression, whereas Differentiated Instruction targets modifying teaching methods, content, and assessments to address specific student readiness, interests, and learning profiles. UDL is proactive, focusing on curriculum design to preempt barriers, while Differentiated Instruction is reactive, tailoring instruction during lesson delivery based on student needs. The strategic implementation of UDL fosters inclusivity at the systemic level, whereas Differentiated Instruction operates within classroom practices to personalize learning experiences.
The Role of Flexibility in UDL and Differentiation
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes flexibility by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to accommodate diverse learner needs from the outset. Differentiated instruction adapts teaching methods, materials, and assessments in response to individual student readiness, interests, and learning profiles within the classroom. Both approaches leverage flexibility to create inclusive learning environments, but UDL proactively designs curricula for variability while differentiation reactively modifies instruction based on ongoing student assessment.
Accessibility and Equity in Classroom Practices
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) ensures accessibility by providing multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression, addressing diverse learner needs universally. Differentiated instruction targets equity by tailoring teaching methods and materials to individual student profiles, promoting personalized learning experiences. Both approaches foster inclusive classrooms, but UDL emphasizes proactive accessibility while differentiated instruction responds adaptively to learner variability.
Implementation Strategies for UDL
Implementation strategies for Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasize creating flexible learning environments that accommodate diverse student needs through multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression. Key methods include providing varied instructional materials, offering customizable assessments, and integrating technology to support individualized learning pathways. These approaches contrast with differentiated instruction by proactively designing curricula that anticipate learner variability rather than reacting to it.
Practical Approaches to Differentiated Instruction
Practical approaches to differentiated instruction emphasize tailoring teaching methods, materials, and assessments to accommodate diverse learner needs by adjusting content, process, and product based on student readiness, interests, and learning profiles. Unlike universal design for learning (UDL), which proactively designs flexible learning environments accessible to all students from the outset, differentiated instruction requires ongoing formative assessment and teacher responsiveness within the classroom. Effective differentiation strategies include small group instruction, tiered assignments, and choice boards that actively engage students while addressing varied abilities and learning preferences.
Evaluating Student Outcomes: UDL vs Differentiation
Evaluating student outcomes in Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes accessible, flexible assessment methods that accommodate diverse learning preferences, leading to inclusive success metrics. Differentiated instruction evaluation focuses on tailored assessment strategies aligned with individual readiness, interests, and learning profiles to measure personalized growth. Data-driven analysis reveals UDL broadens engagement while differentiation intensifies targeted skill mastery, both contributing distinctively to effective educational outcomes.
Teacher Challenges and Support Systems
Teachers implementing Universal Design for Learning (UDL) face challenges in creating flexible curricula that accommodate diverse learning needs without overwhelming planning demands. Differentiated instruction requires ongoing assessment and personalized strategies, often limited by time constraints and resource availability. Support systems such as professional development, collaborative teaching teams, and technology integration are essential to help educators effectively address these challenges in inclusive classrooms.
Future Trends in Inclusive Education
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes creating flexible learning environments that accommodate all students from the outset, using multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to support diverse learners. Differentiated instruction tailors teaching strategies and resources to address individual student needs, preferences, and readiness levels within the classroom. Future trends in inclusive education point towards integrating UDL principles with technology-enhanced differentiation, utilizing AI-driven tools to provide personalized learning experiences that promote equity and accessibility for every student.
universal design for learning vs differentiated instruction Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com