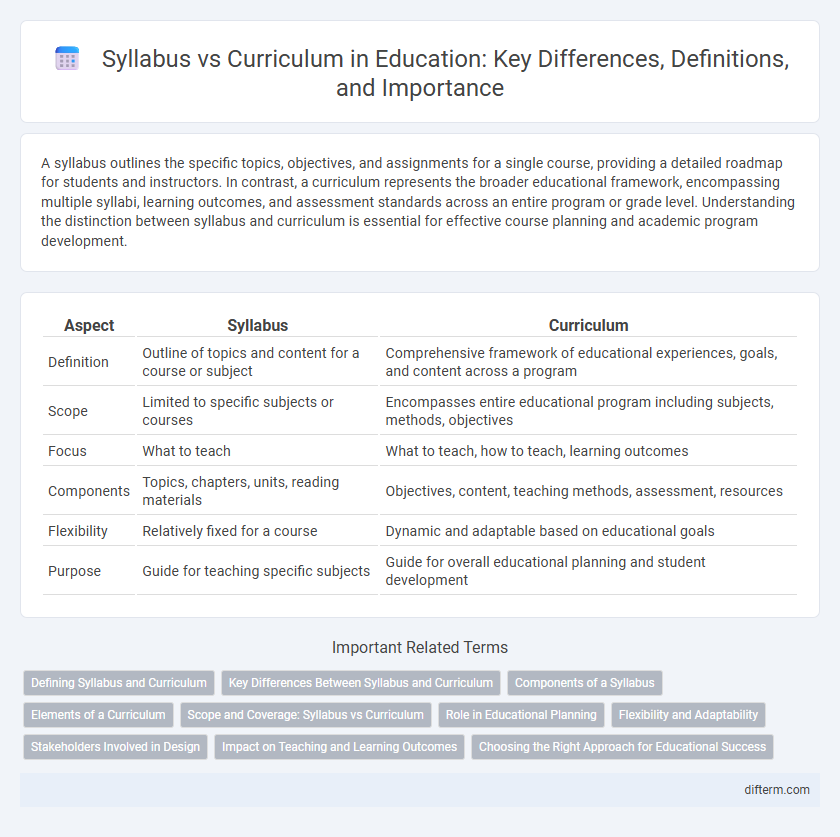
A syllabus outlines the specific topics, objectives, and assignments for a single course, providing a detailed roadmap for students and instructors. In contrast, a curriculum represents the broader educational framework, encompassing multiple syllabi, learning outcomes, and assessment standards across an entire program or grade level. Understanding the distinction between syllabus and curriculum is essential for effective course planning and academic program development.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Syllabus | Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outline of topics and content for a course or subject | Comprehensive framework of educational experiences, goals, and content across a program |
| Scope | Limited to specific subjects or courses | Encompasses entire educational program including subjects, methods, objectives |
| Focus | What to teach | What to teach, how to teach, learning outcomes |
| Components | Topics, chapters, units, reading materials | Objectives, content, teaching methods, assessment, resources |
| Flexibility | Relatively fixed for a course | Dynamic and adaptable based on educational goals |
| Purpose | Guide for teaching specific subjects | Guide for overall educational planning and student development |
Defining Syllabus and Curriculum
A syllabus is a detailed outline of topics, objectives, assignments, and schedules for a specific course or subject, serving as a guide for both instructors and students throughout the learning process. Curriculum encompasses the complete educational content, including multiple syllabi, learning goals, assessment methods, and instructional strategies designed for an entire program or academic level. Understanding the distinction between syllabus and curriculum is essential for effective educational planning and implementation.
Key Differences Between Syllabus and Curriculum
A syllabus defines the specific topics, objectives, and assessment methods for a particular course or subject, serving as a detailed guide for teachers and students. In contrast, a curriculum encompasses the overall educational framework, including the goals, content, learning experiences, and standards across multiple courses within a program or institution. While the syllabus is a subset focused on individual classes, the curriculum provides a comprehensive roadmap for the entire educational journey.
Components of a Syllabus
A syllabus outlines the specific components of a course, including objectives, topics, assignments, grading criteria, and schedules, serving as a detailed guide for both instructors and students. It acts as a roadmap that delineates what content will be covered, the methods of assessment, and expectations for student performance. Unlike a curriculum, which encompasses a broader educational framework, the syllabus focuses on the granular elements necessary for effective course delivery.
Elements of a Curriculum
A curriculum encompasses the overall educational plan including goals, content, learning experiences, assessment methods, and instructional strategies, while a syllabus serves as a detailed outline for a specific course or subject within that curriculum. Key elements of a curriculum include learning objectives, course content, teaching methods, assessment techniques, and alignment with educational standards. Effective curriculum design ensures coherent progression of knowledge and skills, addressing cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains for holistic student development.
Scope and Coverage: Syllabus vs Curriculum
The syllabus defines specific topics and objectives covered in a particular course or subject, providing a detailed outline for daily teaching and assessment. In contrast, the curriculum encompasses the broader educational framework, including the overall learning goals, skills development, and knowledge integration across multiple courses and grade levels. While the syllabus focuses on immediate scope and content delivery, the curriculum ensures comprehensive coverage of educational standards and progression throughout an academic program.
Role in Educational Planning
The syllabus outlines specific topics, lessons, and timelines designed for individual courses, serving as a detailed guide for teachers and students. The curriculum encompasses the overall educational goals, content standards, and learning outcomes set by educational authorities for an entire program or grade level. Effective educational planning relies on the curriculum to establish broad objectives while the syllabus provides a practical framework to achieve those objectives within classrooms.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Syllabus provides a structured outline of topics and objectives for a specific course, ensuring consistency in content delivery, while curriculum encompasses a broader educational framework that integrates various syllabi across grades or subjects, allowing for flexibility in learning pathways. Curriculum design prioritizes adaptability by incorporating evolving educational standards, diverse student needs, and interdisciplinary approaches. This flexibility enables institutions to modify content, teaching methods, and assessment strategies in response to technological advancements and societal changes.
Stakeholders Involved in Design
Syllabus development primarily involves teachers and subject matter experts who determine the specific content, learning objectives, and instructional materials for a course. Curriculum design engages a broader set of stakeholders, including educational administrators, policymakers, community members, and sometimes students, to establish overarching educational goals, standards, and assessment frameworks at institutional or regional levels. Collaboration among these groups ensures alignment between specific course syllabi and the wider educational goals of schools and districts.
Impact on Teaching and Learning Outcomes
Syllabus defines specific course content and assessment criteria, guiding daily instructional activities and ensuring alignment with learning objectives. Curriculum encompasses the broader educational framework, integrating syllabi across subjects to promote cohesive skill development and knowledge acquisition. Effective alignment between syllabus and curriculum enhances teaching strategies, fosters comprehensive understanding, and improves student learning outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Educational Success
A well-defined syllabus outlines specific topics and learning objectives for each course session, providing a clear roadmap for both instructors and students. In contrast, the curriculum encompasses the broader educational goals, content scope, instructional methods, and assessment strategies across an entire program or grade level. Selecting the appropriate blend of syllabus and curriculum design ensures targeted learning outcomes and overall academic achievement tailored to students' needs.
syllabus vs curriculum Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com