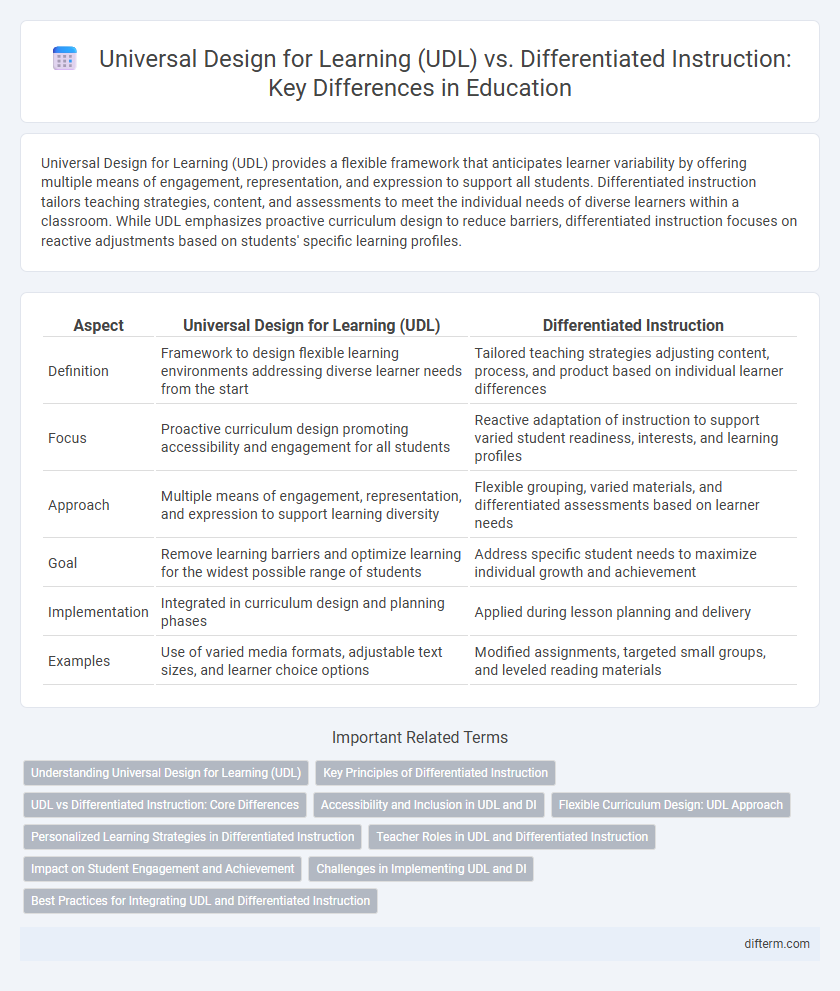
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) provides a flexible framework that anticipates learner variability by offering multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to support all students. Differentiated instruction tailors teaching strategies, content, and assessments to meet the individual needs of diverse learners within a classroom. While UDL emphasizes proactive curriculum design to reduce barriers, differentiated instruction focuses on reactive adjustments based on students' specific learning profiles.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Universal Design for Learning (UDL) | Differentiated Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework to design flexible learning environments addressing diverse learner needs from the start | Tailored teaching strategies adjusting content, process, and product based on individual learner differences |
| Focus | Proactive curriculum design promoting accessibility and engagement for all students | Reactive adaptation of instruction to support varied student readiness, interests, and learning profiles |
| Approach | Multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to support learning diversity | Flexible grouping, varied materials, and differentiated assessments based on learner needs |
| Goal | Remove learning barriers and optimize learning for the widest possible range of students | Address specific student needs to maximize individual growth and achievement |
| Implementation | Integrated in curriculum design and planning phases | Applied during lesson planning and delivery |
| Examples | Use of varied media formats, adjustable text sizes, and learner choice options | Modified assignments, targeted small groups, and leveled reading materials |
Understanding Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework aimed at improving and optimizing teaching and learning for all people based on scientific insights into how humans learn. UDL emphasizes providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to accommodate diverse learners and minimize barriers in education. Unlike Differentiated Instruction, which adapts content for specific student groups, UDL proactively designs flexible learning environments that benefit every learner from the outset.
Key Principles of Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction centers on tailoring teaching strategies to address diverse learners' readiness, interests, and learning profiles through flexible content, process, and product options. It emphasizes ongoing assessment and responsive teaching to optimize individual student growth within heterogeneous classrooms. Contrasting with Universal Design for Learning's proactive, guideline-based framework, differentiated instruction adapts dynamically to specific student needs.
UDL vs Differentiated Instruction: Core Differences
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes creating flexible learning environments that accommodate all learners by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and activities to meet the specific needs, readiness, and interests of individual students within the classroom. The core difference lies in UDL's proactive, systemic framework designed for universal accessibility, whereas differentiated instruction focuses on reactive, personalized adjustments based on student variability.
Accessibility and Inclusion in UDL and DI
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes creating flexible learning environments that accommodate diverse learners by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression, ensuring accessibility and inclusion for all students. Differentiated instruction tailors teaching strategies and content based on individual learner profiles, addressing specific needs and preferences to promote inclusion through personalized support. Both UDL and differentiated instruction enhance accessibility, but UDL integrates inclusive design at a systemic level, while differentiated instruction focuses on adaptive teaching practices within the classroom.
Flexible Curriculum Design: UDL Approach
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasizes flexible curriculum design by providing multiple means of representation, engagement, and expression tailored to diverse learner needs. This approach integrates technology and customizable materials to ensure accessibility and inclusivity, promoting equitable learning opportunities for all students. Unlike differentiated instruction, which adapts teaching based on student readiness and interests, UDL proactively designs curriculum frameworks that accommodate variability from the outset.
Personalized Learning Strategies in Differentiated Instruction
Personalized learning strategies in differentiated instruction tailor educational experiences to individual student needs, preferences, and readiness levels by adjusting content, process, and product based on ongoing assessment data. Unlike Universal Design for Learning (UDL), which provides multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression to support all learners broadly, differentiated instruction specifically targets diverse learner profiles within a classroom. This approach enhances student motivation and achievement by delivering targeted interventions and scaffolded support that align with each student's strengths and challenges.
Teacher Roles in UDL and Differentiated Instruction
Teacher roles in Universal Design for Learning (UDL) emphasize creating flexible learning environments that accommodate diverse student needs through proactive curriculum design and multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. In Differentiated Instruction, teachers assess individual student readiness, interests, and learning profiles to tailor content, process, and products on the fly, responding dynamically within the classroom context. Both approaches demand educators to act as facilitators and designers who promote equity and personalized learning pathways to ensure all students achieve academic success.
Impact on Student Engagement and Achievement
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) enhances student engagement by offering multiple means of representation, expression, and engagement, making learning accessible to diverse learners and boosting achievement across varied abilities. Differentiated instruction targets individual student needs through tailored content, process, and product, which fosters motivation and improves academic outcomes by addressing specific learning styles and readiness levels. Both strategies promote inclusive education, but UDL's proactive framework has a broader impact on engagement and achievement by anticipating learner variability rather than reacting to it.
Challenges in Implementing UDL and DI
Challenges in implementing Universal Design for Learning (UDL) include the need for extensive teacher training and the complexity of designing flexible learning materials that address diverse learner needs simultaneously. Differentiated Instruction (DI) faces obstacles such as time constraints for lesson planning and difficulties in effectively managing varied student groups within one classroom environment. Both approaches require significant resource allocation and ongoing professional development to ensure successful integration into educational settings.
Best Practices for Integrating UDL and Differentiated Instruction
Best practices for integrating Universal Design for Learning (UDL) and differentiated instruction emphasize flexible curricula that accommodate diverse learning needs through multiple means of engagement, representation, and expression. Educators implement UDL guidelines alongside targeted differentiation strategies to tailor instruction based on learner profiles, ensuring accessibility and personalized support. Utilizing formative assessments and adaptive technologies enhances the synergy between UDL frameworks and differentiated teaching, fostering inclusive and effective learning environments.
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) vs Differentiated instruction Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com