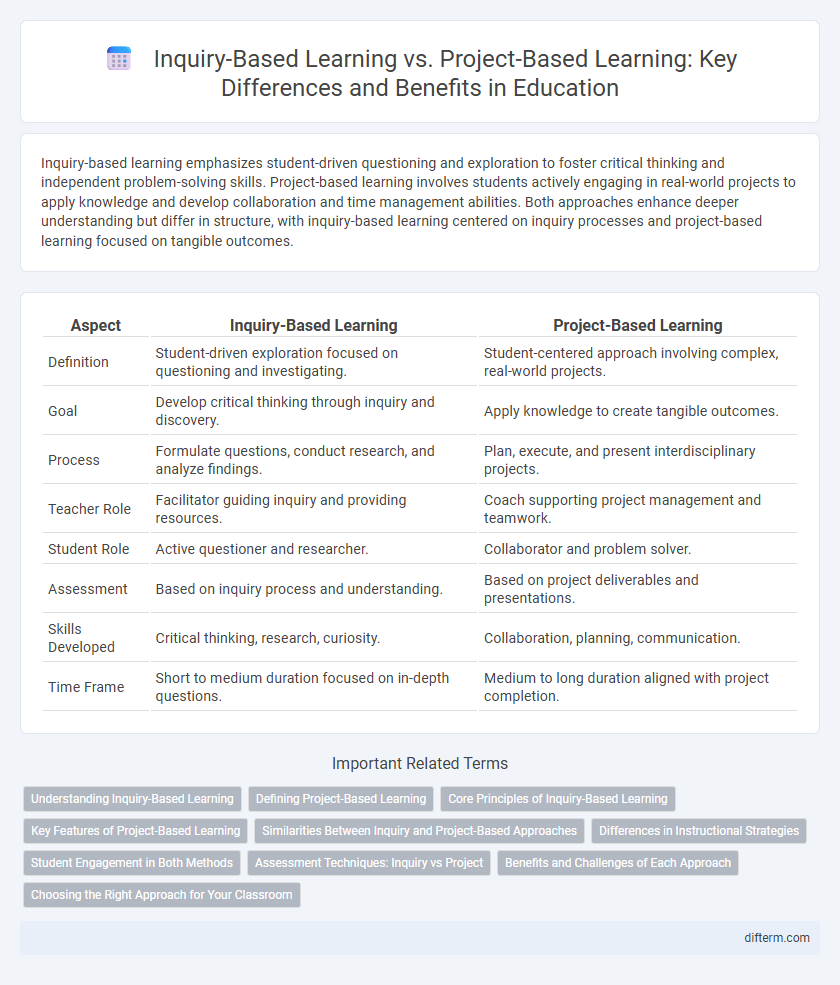
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes student-driven questioning and exploration to foster critical thinking and independent problem-solving skills. Project-based learning involves students actively engaging in real-world projects to apply knowledge and develop collaboration and time management abilities. Both approaches enhance deeper understanding but differ in structure, with inquiry-based learning centered on inquiry processes and project-based learning focused on tangible outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Project-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven exploration focused on questioning and investigating. | Student-centered approach involving complex, real-world projects. |
| Goal | Develop critical thinking through inquiry and discovery. | Apply knowledge to create tangible outcomes. |
| Process | Formulate questions, conduct research, and analyze findings. | Plan, execute, and present interdisciplinary projects. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator guiding inquiry and providing resources. | Coach supporting project management and teamwork. |
| Student Role | Active questioner and researcher. | Collaborator and problem solver. |
| Assessment | Based on inquiry process and understanding. | Based on project deliverables and presentations. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, research, curiosity. | Collaboration, planning, communication. |
| Time Frame | Short to medium duration focused on in-depth questions. | Medium to long duration aligned with project completion. |
Understanding Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based learning centers on students exploring questions and problems through investigation, fostering critical thinking and deeper comprehension of subject matter. This approach encourages learners to develop skills such as research, analysis, and reflection by actively engaging in the learning process. Unlike project-based learning, which culminates in a tangible product, inquiry-based learning emphasizes the process of discovery and understanding over the final outcome.
Defining Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional approach where students actively explore real-world problems and challenges through extended projects. This method emphasizes student-driven inquiry, collaboration, and the application of knowledge to create tangible outcomes or presentations. PBL fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and deeper understanding by integrating academic content with practical tasks.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based learning centers on student-driven questioning, exploration, and reflection to foster deep understanding and critical thinking skills. It emphasizes active engagement with content through curiosity, investigation, and evidence-based reasoning, promoting learner autonomy and conceptual comprehension. This approach contrasts with project-based learning by prioritizing the formulation of questions and ongoing inquiry rather than solely completing a defined project outcome.
Key Features of Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning emphasizes student-driven projects that integrate real-world problems, fostering critical thinking and collaboration skills. Key features include sustained inquiry over extended periods, authentic assessments, and public presentations of work. This approach enhances engagement by connecting academic content to practical application and teamwork.
Similarities Between Inquiry and Project-Based Approaches
Inquiry-based learning and project-based learning both emphasize active student engagement and foster critical thinking by encouraging learners to explore real-world problems. Both approaches promote collaboration, self-directed research, and the application of knowledge to develop deeper understanding. These methods support learner autonomy and integrate formative assessment to enhance cognitive skills and content mastery.
Differences in Instructional Strategies
Inquiry-based learning centers on students exploring questions through guided investigation, emphasizing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Project-based learning involves students creating tangible products or presentations, promoting collaboration, time management, and application of knowledge over extended periods. These instructional strategies differ primarily in focus: inquiry-based learning prioritizes questioning and exploration, while project-based learning emphasizes production and real-world application.
Student Engagement in Both Methods
Inquiry-based learning fosters student engagement through curiosity-driven questioning and exploration, encouraging active participation and critical thinking. Project-based learning enhances engagement by involving students in hands-on, real-world projects that require collaboration, problem-solving, and creativity. Both methods increase motivation and deepen understanding by promoting student autonomy and meaningful connection to the material.
Assessment Techniques: Inquiry vs Project
Inquiry-based learning assessment techniques emphasize formative evaluation through reflective journals, open-ended questioning, and concept maps to gauge students' critical thinking and understanding of underlying concepts. Project-based learning assessment incorporates rubrics, presentations, and peer evaluations that measure the application of knowledge, collaboration skills, and the final product's quality. Both approaches benefit from ongoing feedback, but inquiry-based assessments prioritize depth of inquiry while project-based assessments focus on real-world problem-solving and tangible outcomes.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Approach
Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to explore questions and problems independently, but it may challenge learners who need more guidance and structure. Project-based learning enhances collaboration and real-world application skills through extended tasks, yet it can demand significant time management and resource coordination. Both approaches develop essential 21st-century competencies but require balance between autonomy and support to maximize effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions and explore concepts independently, making it ideal for developing problem-solving skills. Project-based learning emphasizes hands-on collaboration and real-world application, enhancing teamwork and practical knowledge. Selecting the right approach depends on classroom goals, student needs, and curriculum objectives to maximize engagement and learning outcomes.
inquiry-based learning vs project-based learning Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com