Pedagogy emphasizes teacher-directed learning tailored for children, focusing on structured guidance and knowledge acquisition. Andragogy centers on self-directed learning suited for adults, highlighting practical, experience-based education. Understanding the distinct needs and motivations of learners enhances instructional effectiveness and engagement.
Table of Comparison
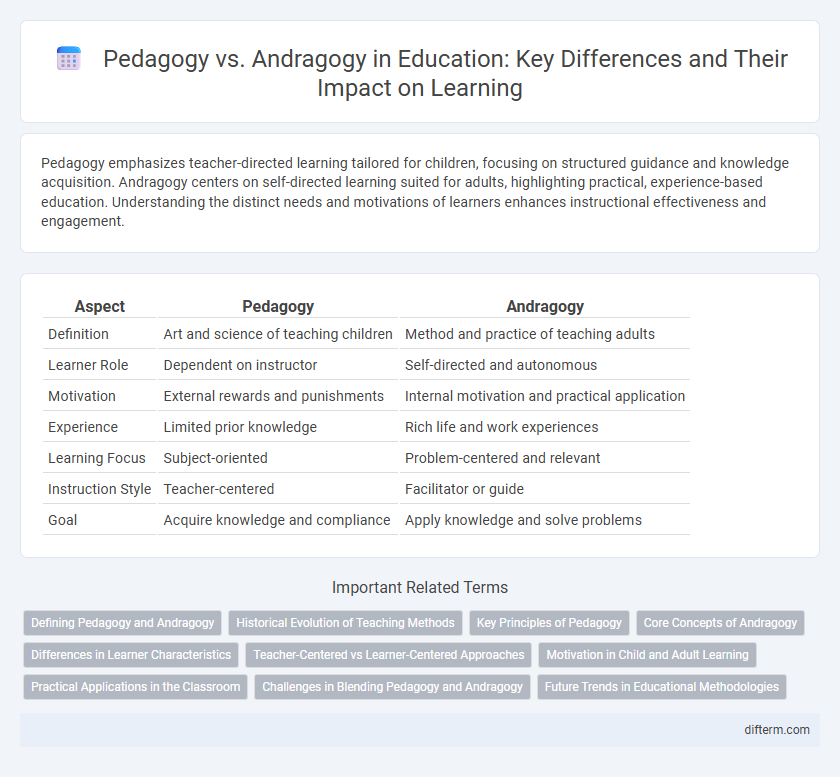
| Aspect | Pedagogy | Andragogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art and science of teaching children | Method and practice of teaching adults |
| Learner Role | Dependent on instructor | Self-directed and autonomous |
| Motivation | External rewards and punishments | Internal motivation and practical application |
| Experience | Limited prior knowledge | Rich life and work experiences |
| Learning Focus | Subject-oriented | Problem-centered and relevant |
| Instruction Style | Teacher-centered | Facilitator or guide |
| Goal | Acquire knowledge and compliance | Apply knowledge and solve problems |
Defining Pedagogy and Andragogy
Pedagogy refers to the art and science of teaching children, emphasizing structured guidance and content delivery tailored to learners who depend on the instructor for knowledge acquisition. Andragogy focuses on adult learning, highlighting self-directed education where adults bring prior experience and motivation, requiring practical and problem-centered approaches. Understanding these distinctions aids educators in designing effective instructional strategies suited to the developmental stages and learning needs of their audience.
Historical Evolution of Teaching Methods
Pedagogy, rooted in ancient educational traditions, historically emphasizes teacher-directed instruction primarily for children, focusing on structured curriculum and knowledge transmission. Andragogy emerged as a distinct concept in the 20th century, recognizing the self-directed learning capacities of adults and emphasizing experiential, problem-centered methods. This shift in teaching methods reflects an evolving understanding of learner autonomy and cognitive development across different life stages.
Key Principles of Pedagogy
Pedagogy centers on teacher-directed learning wherein the educator controls content delivery, assessment, and motivation, emphasizing structured curriculum and clear objectives tailored to the developmental stages of children. Key principles include scaffolded instruction, where foundational knowledge is built progressively, and differentiated learning to accommodate varied cognitive abilities in the classroom. Emphasis on external motivation and reinforcement, coupled with formative assessments, drives student engagement and mastery in pedagogical settings.
Core Concepts of Andragogy
Andragogy centers on adult learning principles such as self-directedness, leveraging prior experiences, and readiness to learn based on real-life needs. It emphasizes problem-centered learning rather than content-oriented instruction, promoting active participation and practical application. Core concepts also include intrinsic motivation and the necessity for learners to understand the relevance of material to their personal and professional lives.
Differences in Learner Characteristics
Pedagogy centers on teaching children who rely heavily on instructors for guidance, with learning driven by structured curricula and external motivation. Andragogy addresses adult learners characterized by self-direction, life experience, and a preference for practical, problem-centered learning. These distinct learner characteristics necessitate tailoring instructional strategies to optimize engagement and knowledge retention in each demographic.
Teacher-Centered vs Learner-Centered Approaches
Teacher-centered approaches emphasize structured lesson plans, direct instruction, and the teacher's role as the primary knowledge holder, focusing on content delivery and classroom management. Learner-centered approaches prioritize active student engagement, collaboration, and personalized learning experiences that develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Pedagogy typically aligns with teacher-centered models for young learners, while andragogy supports learner-centered strategies for adult education, fostering autonomy and self-directed learning.
Motivation in Child and Adult Learning
Motivation in child learning often depends on external rewards and structured guidance, aligning with pedagogical methods that emphasize teacher-led instruction and reinforcement. In contrast, adult learning motivation is primarily driven by intrinsic factors such as personal goals and self-direction, which are central to andragogical approaches that prioritize autonomy and experiential learning. Effective educational strategies must tailor motivational techniques to these differences, fostering engagement through age-appropriate stimuli and learning environments.
Practical Applications in the Classroom
Pedagogy emphasizes structured, teacher-directed learning suited for children, utilizing techniques such as direct instruction and repetitive practice to build foundational skills. Andragogy focuses on self-directed, experiential learning tailored to adult learners, encouraging collaboration, critical thinking, and real-world problem-solving. Implementing a blended approach in the classroom enhances engagement by combining clear guidance with opportunities for autonomous exploration and practical application of knowledge.
Challenges in Blending Pedagogy and Andragogy
Blending pedagogy and andragogy presents challenges such as addressing diverse learning needs across age groups and balancing structured guidance with self-directed learning. Educators often struggle to create curricula that engage both children's developmental stages and adults' life experiences effectively. Integrating assessment methods that accommodate varying cognitive and motivational differences remains a critical hurdle.
Future Trends in Educational Methodologies
Emerging future trends in educational methodologies emphasize a shift from traditional pedagogy, which focuses on structured learning for children, towards andragogy that prioritizes self-directed, experiential learning for adults. Adaptive learning technologies and AI-driven platforms tailor educational experiences to individual learners' needs, enhancing the andragogical approach. Blended learning environments integrate both pedagogical and andragogical strategies to foster lifelong learning and skill development across diverse age groups.
pedagogy vs andragogy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com