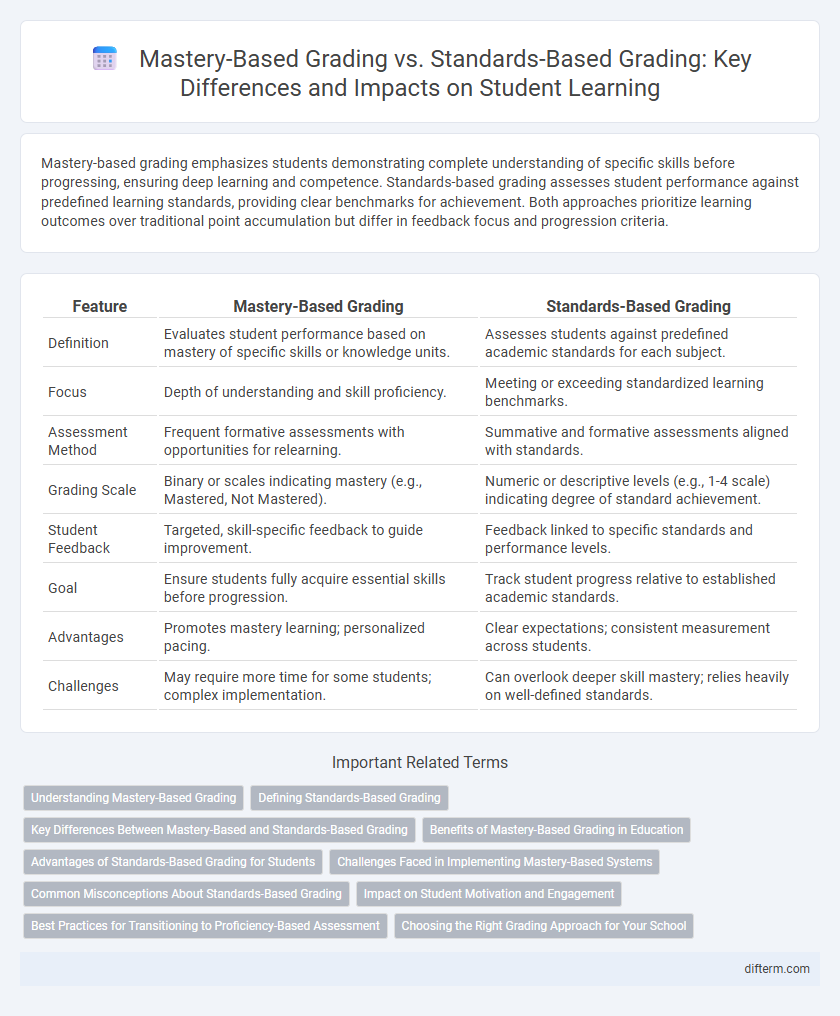
Mastery-based grading emphasizes students demonstrating complete understanding of specific skills before progressing, ensuring deep learning and competence. Standards-based grading assesses student performance against predefined learning standards, providing clear benchmarks for achievement. Both approaches prioritize learning outcomes over traditional point accumulation but differ in feedback focus and progression criteria.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mastery-Based Grading | Standards-Based Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates student performance based on mastery of specific skills or knowledge units. | Assesses students against predefined academic standards for each subject. |
| Focus | Depth of understanding and skill proficiency. | Meeting or exceeding standardized learning benchmarks. |
| Assessment Method | Frequent formative assessments with opportunities for relearning. | Summative and formative assessments aligned with standards. |
| Grading Scale | Binary or scales indicating mastery (e.g., Mastered, Not Mastered). | Numeric or descriptive levels (e.g., 1-4 scale) indicating degree of standard achievement. |
| Student Feedback | Targeted, skill-specific feedback to guide improvement. | Feedback linked to specific standards and performance levels. |
| Goal | Ensure students fully acquire essential skills before progression. | Track student progress relative to established academic standards. |
| Advantages | Promotes mastery learning; personalized pacing. | Clear expectations; consistent measurement across students. |
| Challenges | May require more time for some students; complex implementation. | Can overlook deeper skill mastery; relies heavily on well-defined standards. |
Understanding Mastery-Based Grading
Mastery-based grading emphasizes demonstrating a deep understanding of specific competencies rather than accumulating points over time. It allows students to progress at their own pace, ensuring they achieve proficiency before moving forward. This approach fosters personalized learning and accurately reflects individual student growth in mastery of learning objectives.
Defining Standards-Based Grading
Standards-Based Grading (SBG) focuses on evaluating students' mastery of specific learning objectives or standards rather than assigning traditional letter grades. This method provides detailed feedback on a student's progress toward clearly defined academic skills, promoting personalized learning paths and targeted interventions. Unlike Mastery-Based Grading, which often emphasizes overall proficiency, SBG breaks down performance into discrete standards to better track and support student growth.
Key Differences Between Mastery-Based and Standards-Based Grading
Mastery-based grading evaluates students on their proficiency in specific skills or concepts, allowing multiple reassessments until mastery is demonstrated. Standards-based grading measures progress against predefined educational standards, often using a scale to indicate levels of achievement rather than a single grade. Key differences include the focus on mastery thresholds in mastery-based grading versus performance relative to standards in standards-based grading, impacting assessment methods and reporting practices.
Benefits of Mastery-Based Grading in Education
Mastery-based grading improves student learning by emphasizing proficiency in specific skills and knowledge, ensuring that assessments reflect true understanding rather than cumulative point totals. This approach promotes personalized learning pathways, allowing students to progress at their own pace and focus on areas needing improvement. It enhances motivation and accountability by clearly defining learning targets and providing timely feedback aligned with mastery levels.
Advantages of Standards-Based Grading for Students
Standards-Based Grading (SBG) clearly communicates students' mastery of specific learning objectives, enabling targeted feedback and personalized learning paths that improve academic outcomes. It fosters a growth mindset by emphasizing progress toward standards rather than averaging scores, which motivates continuous improvement and reduces anxiety. Students benefit from increased transparency in expectations, better self-assessment skills, and enhanced readiness for college and careers through precise alignment with established educational standards.
Challenges Faced in Implementing Mastery-Based Systems
Implementing mastery-based grading faces challenges such as the significant shift in teacher mindset required to assess students continuously on skill mastery rather than on cumulative points. Schools encounter difficulties in developing clear, consistent rubrics that accurately reflect student progress without bias or ambiguity. Additionally, integrating mastery-based systems demands substantial professional development and time investment to ensure reliable, meaningful feedback aligned with learning objectives.
Common Misconceptions About Standards-Based Grading
Standards-based grading is often misunderstood as simply a numeric score or an average of test results, whereas it actually emphasizes students' proficiency in learning objectives over time. It does not ignore effort or improvement but incorporates these factors through clear, measurable standards tied to curriculum goals. Misconceptions also include the belief that standards-based grading reduces rigor, while it instead promotes targeted feedback and mastery by identifying specific areas needing support.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Mastery-based grading emphasizes students demonstrating complete understanding of specific skills before progressing, which tends to increase motivation by promoting a growth mindset and reducing anxiety over traditional letter grades. Standards-based grading breaks down academic expectations into clear, measurable learning targets, encouraging consistent engagement through transparent feedback and personalized learning paths. Both approaches shift focus from competition to individual progress, fostering deeper involvement and sustained motivation in the educational process.
Best Practices for Transitioning to Proficiency-Based Assessment
Mastery-based grading emphasizes continuous improvement and individualized pacing, while standards-based grading focuses on clear, specific skill mastery aligned with learning objectives. Effective transition to proficiency-based assessment involves clear communication of criteria, consistent teacher calibration sessions, and ongoing student feedback loops to guide learning progress. Implementing data-driven instructional adjustments and engaging stakeholders through professional development ensures alignment between assessment practices and desired educational outcomes.
Choosing the Right Grading Approach for Your School
Mastery-based grading emphasizes demonstrating complete understanding of specific skills, while standards-based grading assesses progress against predefined educational standards. Selecting the most effective grading approach depends on your school's academic goals, student population, and curriculum framework. Evaluating assessment consistency, feedback clarity, and alignment with learning objectives ensures the grading method supports student growth and instructional improvement.
Mastery-based grading vs standards-based grading Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com