Digital literacy involves the ability to use technology tools effectively for communication, research, and problem-solving, emphasizing skills such as navigating software and understanding online safety. Media literacy focuses on critically analyzing and evaluating the vast array of information across various media formats, promoting the discernment of bias, misinformation, and persuasive messaging. Both literacies are essential for students to become informed, responsible digital citizens capable of navigating and interpreting the modern information landscape.
Table of Comparison
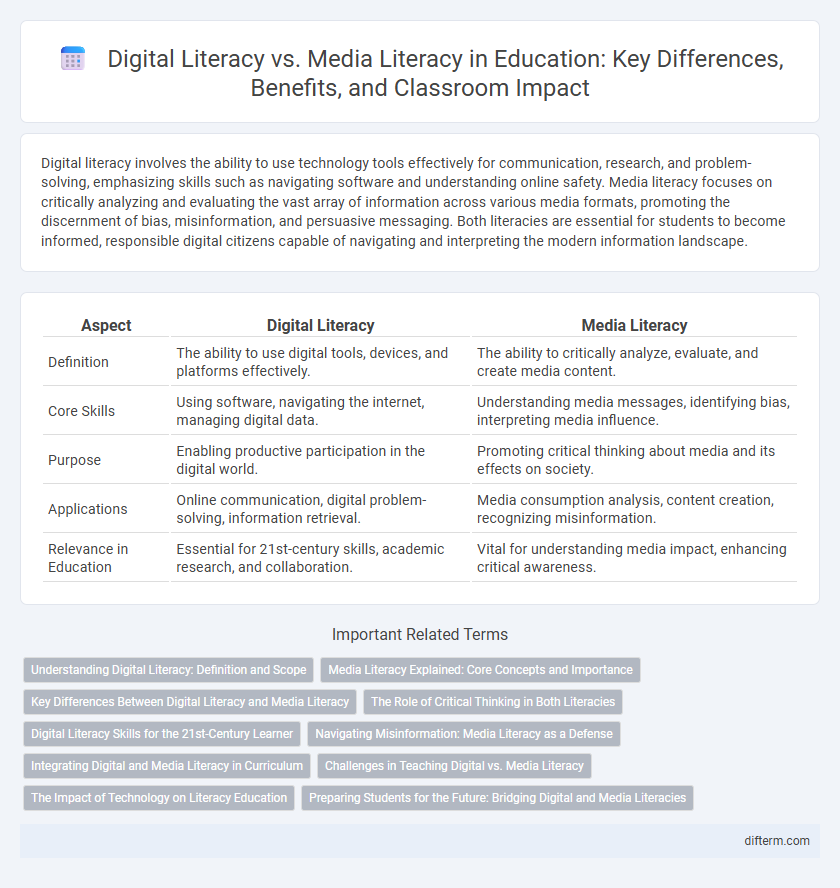
| Aspect | Digital Literacy | Media Literacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to use digital tools, devices, and platforms effectively. | The ability to critically analyze, evaluate, and create media content. |
| Core Skills | Using software, navigating the internet, managing digital data. | Understanding media messages, identifying bias, interpreting media influence. |
| Purpose | Enabling productive participation in the digital world. | Promoting critical thinking about media and its effects on society. |
| Applications | Online communication, digital problem-solving, information retrieval. | Media consumption analysis, content creation, recognizing misinformation. |
| Relevance in Education | Essential for 21st-century skills, academic research, and collaboration. | Vital for understanding media impact, enhancing critical awareness. |
Understanding Digital Literacy: Definition and Scope
Digital literacy encompasses the ability to effectively use digital tools, technologies, and platforms to access, evaluate, create, and communicate information. It involves skills such as navigating online environments, critical thinking about digital content, and understanding the ethical implications of technology use. Media literacy, while overlapping, specifically emphasizes analyzing and interpreting various media formats, making digital literacy a broader concept covering technical competence and responsible digital citizenship.
Media Literacy Explained: Core Concepts and Importance
Media literacy involves the ability to critically analyze, evaluate, and create content across various media platforms, emphasizing understanding bias, misinformation, and the intent behind messages. It encompasses skills to discern credible sources, recognize persuasive techniques, and navigate the complex digital information landscape effectively. Media literacy is essential for fostering informed citizenship and empowering individuals to participate responsibly in democratic societies.
Key Differences Between Digital Literacy and Media Literacy
Digital literacy emphasizes the ability to effectively use digital devices, software, and online tools for communication, information retrieval, and problem-solving, while media literacy focuses on critically analyzing, evaluating, and creating media content across various platforms. Digital literacy involves technical skills such as coding, navigating digital environments, and data management, whereas media literacy centers on understanding media messages, recognizing bias, and discerning sources. Both literacies converge in fostering informed digital citizenship, but their core competencies target distinct aspects of interaction with technology and media.
The Role of Critical Thinking in Both Literacies
Critical thinking is essential in both digital literacy and media literacy, enabling learners to analyze the credibility of online sources and the bias in media content. Digital literacy emphasizes evaluating technical accuracy and information security, while media literacy focuses on interpreting messages and understanding underlying agendas. Mastery of critical thinking skills enhances the ability to discern misinformation and make informed decisions in a digital and media-saturated environment.
Digital Literacy Skills for the 21st-Century Learner
Digital literacy skills encompass the ability to navigate, evaluate, and create information using digital technologies, essential for 21st-century learners to effectively participate in a technology-driven world. These competencies include critical thinking, online communication, cybersecurity awareness, and proficiency with digital tools that support collaboration and problem-solving. Developing robust digital literacy empowers students to adapt to evolving digital environments, enhances their career readiness, and fosters lifelong learning in various educational and professional contexts.
Navigating Misinformation: Media Literacy as a Defense
Media literacy equips individuals with critical thinking skills to identify and analyze misinformation across diverse digital platforms. It emphasizes understanding source credibility, recognizing biased content, and evaluating evidence to discern factual information from falsehoods. While digital literacy covers technical proficiency in using devices and software, media literacy specifically targets the interpretation and evaluation of media messages to combat misinformation effectively.
Integrating Digital and Media Literacy in Curriculum
Integrating digital and media literacy in curriculum enhances students' critical thinking and information evaluation skills, preparing them for a technology-driven society. Digital literacy emphasizes proficiency in using digital tools and platforms, while media literacy focuses on analyzing and understanding media messages and their impact. A combined approach fosters comprehensive competence, enabling learners to navigate, create, and critically assess digital and media content effectively.
Challenges in Teaching Digital vs. Media Literacy
Teaching digital literacy faces challenges such as rapidly evolving technologies and the need for continuous curriculum updates to keep pace with new digital tools. Media literacy instruction struggles with overcoming misinformation and bias while fostering critical thinking skills to evaluate diverse media sources effectively. Both require educators to balance technical proficiency with analytical abilities in a dynamic, information-rich environment.
The Impact of Technology on Literacy Education
Digital literacy enhances students' ability to navigate, evaluate, and create information using digital platforms, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential in modern education. Media literacy equips learners to critically analyze media messages, understand biases, and recognize persuasive techniques, promoting informed consumption and ethical sharing of content. The integration of technology in literacy education transforms traditional learning methods by combining digital and media literacy competencies, preparing students for effective communication and participation in a digitally interconnected world.
Preparing Students for the Future: Bridging Digital and Media Literacies
Preparing students for the future requires integrating both digital literacy and media literacy to develop critical analytical skills and technological proficiency. Digital literacy enables students to effectively navigate, evaluate, and create information using digital tools, while media literacy fosters the ability to critically assess and interpret diverse media messages. Bridging these literacies empowers learners to become informed, responsible citizens capable of thriving in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Digital literacy vs Media literacy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com