Literacy skills enable students to comprehend, analyze, and communicate effectively through written and spoken language, forming the foundation for critical thinking across subjects. Numeracy involves the ability to understand and work with numbers, essential for problem-solving and logical reasoning in everyday life and academic disciplines. Both literacy and numeracy are fundamental competencies that empower learners to navigate complex information and succeed in a knowledge-driven society.
Table of Comparison
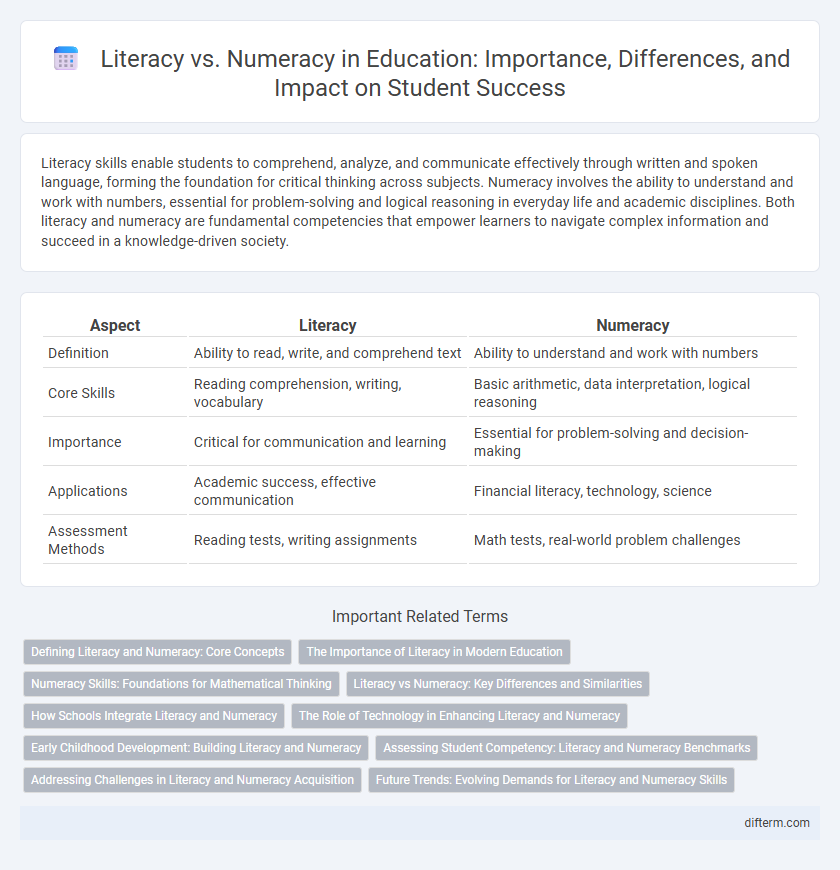
| Aspect | Literacy | Numeracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to read, write, and comprehend text | Ability to understand and work with numbers |
| Core Skills | Reading comprehension, writing, vocabulary | Basic arithmetic, data interpretation, logical reasoning |
| Importance | Critical for communication and learning | Essential for problem-solving and decision-making |
| Applications | Academic success, effective communication | Financial literacy, technology, science |
| Assessment Methods | Reading tests, writing assignments | Math tests, real-world problem challenges |
Defining Literacy and Numeracy: Core Concepts
Literacy encompasses the ability to read, write, and comprehend written texts, enabling effective communication and information processing. Numeracy involves understanding and applying basic mathematical concepts such as numbers, calculations, measurements, and data interpretation in practical contexts. Both literacy and numeracy are foundational skills critical for academic achievement, personal empowerment, and workforce readiness.
The Importance of Literacy in Modern Education
Literacy remains a foundational skill in modern education, essential for reading, writing, and effective communication across all disciplines. Mastery of literacy enhances critical thinking and comprehension, which supports learning in mathematics and science, thereby strengthening overall academic performance. Emphasizing literacy development fosters cognitive abilities and prepares students for complex problem-solving in both educational and real-world contexts.
Numeracy Skills: Foundations for Mathematical Thinking
Numeracy skills form the essential foundation for mathematical thinking by enabling individuals to understand and apply numerical concepts in everyday problem-solving. Developing strong numeracy promotes critical thinking, logical reasoning, and the ability to interpret quantitative information accurately. Mastery of these skills supports success in STEM subjects, financial literacy, and informed decision-making across various real-world contexts.
Literacy vs Numeracy: Key Differences and Similarities
Literacy primarily involves the ability to read, write, and comprehend language, enabling effective communication and critical thinking. Numeracy centers on understanding and applying mathematical concepts such as numbers, operations, and problem-solving skills in everyday contexts. Both literacy and numeracy are foundational skills essential for personal development, academic success, and informed decision-making, highlighting their complementary roles in education.
How Schools Integrate Literacy and Numeracy
Schools integrate literacy and numeracy by embedding reading, writing, and mathematical reasoning within cross-curricular lessons that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Educators use project-based learning and real-world scenarios to simultaneously develop students' abilities to interpret text and analyze numerical data. Technology tools such as interactive software and digital resources support differentiated instruction, enhancing literacy and numeracy proficiency for diverse learners.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Literacy and Numeracy
Technology plays a transformative role in enhancing both literacy and numeracy by providing interactive tools such as educational apps and digital platforms that adapt to individual learning paces. These technologies incorporate gamification, real-time feedback, and multimedia content, which improve student engagement and comprehension in reading, writing, and mathematical problem-solving. Data analytics integrated into learning management systems enable educators to track progress and tailor instruction, boosting educational outcomes in foundational skills.
Early Childhood Development: Building Literacy and Numeracy
Early childhood development programs that integrate literacy and numeracy skills promote cognitive growth and school readiness in young learners. Research shows that balanced emphasis on letter recognition, phonemic awareness, number sense, and counting enhances foundational abilities for academic success. Targeted interventions in preschool settings improve language acquisition and mathematical reasoning, supporting lifelong learning outcomes.
Assessing Student Competency: Literacy and Numeracy Benchmarks
Assessing student competency involves using established literacy and numeracy benchmarks to measure foundational skills in reading, writing, and mathematical reasoning. Literacy benchmarks focus on comprehension, vocabulary, and fluency, while numeracy benchmarks evaluate number sense, problem-solving, and computational skills. Accurate assessment data supports targeted instruction and helps educators identify areas for intervention to improve student outcomes.
Addressing Challenges in Literacy and Numeracy Acquisition
Addressing challenges in literacy and numeracy acquisition requires targeted interventions that incorporate evidence-based instructional strategies such as phonics for reading fluency and manipulatives for conceptual math understanding. Early assessments identifying learning gaps enable personalized support, leveraging technology tools like adaptive learning software to enhance engagement and skill mastery. Collaborations among educators, families, and communities foster supportive environments crucial for overcoming barriers and promoting sustained academic growth in foundational literacy and numeracy skills.
Future Trends: Evolving Demands for Literacy and Numeracy Skills
Emerging future trends indicate a growing demand for advanced literacy skills integrated with digital and data literacy, reflecting the increasing reliance on technology and information processing. Numeracy skills are evolving to encompass computational thinking, statistical analysis, and problem-solving abilities essential for careers in STEM fields and data-driven industries. Education systems must adapt curricula to develop critical thinking, quantitative reasoning, and multimodal communication to prepare learners for complex real-world challenges.
Literacy vs Numeracy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com