Flipped classrooms enhance student engagement by allowing learners to consume lecture material at their own pace outside of class, freeing up in-person sessions for interactive activities and personalized support. Traditional classrooms primarily rely on direct instruction during class time, which limits opportunities for active learning and individualized feedback. Studies show that flipped classrooms improve comprehension and critical thinking skills compared to traditional teaching methods.
Table of Comparison
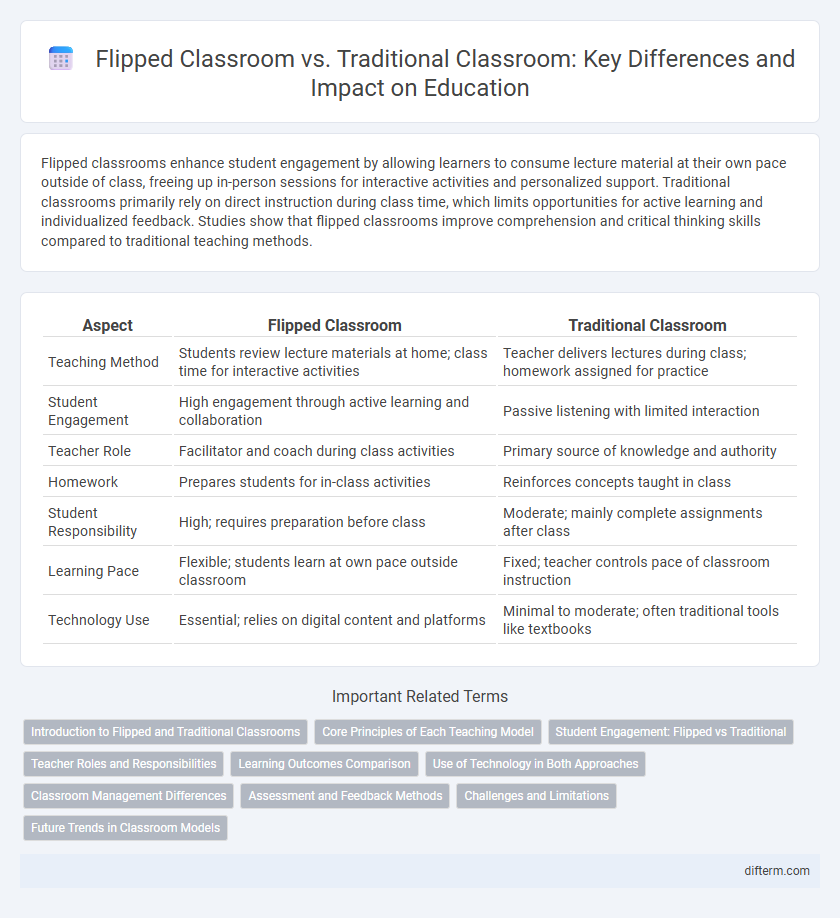
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Traditional Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Method | Students review lecture materials at home; class time for interactive activities | Teacher delivers lectures during class; homework assigned for practice |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through active learning and collaboration | Passive listening with limited interaction |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and coach during class activities | Primary source of knowledge and authority |
| Homework | Prepares students for in-class activities | Reinforces concepts taught in class |
| Student Responsibility | High; requires preparation before class | Moderate; mainly complete assignments after class |
| Learning Pace | Flexible; students learn at own pace outside classroom | Fixed; teacher controls pace of classroom instruction |
| Technology Use | Essential; relies on digital content and platforms | Minimal to moderate; often traditional tools like textbooks |
Introduction to Flipped and Traditional Classrooms
Flipped classrooms reverse the traditional learning environment by delivering instructional content online outside of class and moving homework into the classroom, enhancing student engagement and active learning. Traditional classrooms rely on in-person lectures during class time, with students completing assignments and practice independently at home. Studies show flipped models improve comprehension and retention through collaborative activities and immediate teacher feedback.
Core Principles of Each Teaching Model
The flipped classroom emphasizes student-centered learning by delivering instructional content outside of class, allowing classroom time to focus on active problem-solving and collaborative activities. In contrast, the traditional classroom relies on direct teacher-led instruction during class hours, with students completing homework independently to reinforce lessons. Core principles of the flipped model include increased student engagement and personalized learning, whereas the traditional model prioritizes structured content delivery and standardized pacing.
Student Engagement: Flipped vs Traditional
The flipped classroom model significantly enhances student engagement by fostering active participation through pre-class video lessons and in-class collaborative activities. In contrast, traditional classrooms often rely on passive learning, with students primarily listening to lectures and taking notes. Research shows that flipped classrooms increase student interaction, critical thinking, and motivation compared to conventional teaching methods.
Teacher Roles and Responsibilities
In a flipped classroom, teachers transition from traditional knowledge transmitters to facilitators and coaches, guiding students through active learning and personalized support. They design interactive pre-class materials such as videos and readings, then lead in-class discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative activities to deepen understanding. Conversely, in traditional classrooms, teachers primarily deliver lectures and control content pacing, with limited opportunities for student-centered engagement during class time.
Learning Outcomes Comparison
Flipped classrooms enhance learning outcomes by promoting active engagement and allowing students to absorb content at their own pace, resulting in higher retention and improved critical thinking skills. Traditional classrooms often rely on passive information delivery, which can limit student interaction and reduce comprehension. Studies indicate that learners in flipped settings achieve better academic performance and demonstrate greater mastery of course material compared to those in conventional lecture-based environments.
Use of Technology in Both Approaches
Flipped classrooms leverage digital platforms, video lectures, and interactive online tools to facilitate pre-class learning, allowing students to engage with materials at their own pace. Traditional classrooms primarily utilize in-person instruction with limited technological integration, often relying on textbooks and face-to-face lectures. The enhanced use of technology in flipped classrooms promotes active learning and instant feedback, contrasting with the more passive, teacher-centered approach found in conventional settings.
Classroom Management Differences
Flipped classrooms require educators to shift from direct instruction to facilitation, managing student-centered activities and collaboration more actively than traditional classrooms. Traditional classrooms emphasize teacher-led control with structured schedules and whole-group management, while flipped classrooms demand monitoring of diverse learning paces and individualized support. Effective classroom management in flipped settings hinges on clear guidelines, technology integration, and fostering student autonomy.
Assessment and Feedback Methods
Flipped classrooms utilize technology-driven assessments such as online quizzes and peer evaluations to provide immediate, personalized feedback, enhancing student learning outcomes compared to traditional classrooms. Traditional classrooms often rely on periodic summative assessments like midterms and finals with delayed feedback, limiting timely intervention opportunities. The interactive assessment methods in flipped models foster continuous feedback loops that support adaptive learning and skill mastery.
Challenges and Limitations
Flipped classrooms often face challenges such as unequal access to technology, increased preparation time for instructors, and potential student resistance to self-directed learning. Traditional classrooms may struggle with limited engagement and passive learning but benefit from structured environments and direct teacher supervision. Both models encounter limitations in addressing diverse learning styles and ensuring consistent student motivation.
Future Trends in Classroom Models
Future trends in classroom models emphasize the integration of flipped classrooms, leveraging technology to facilitate personalized and interactive learning experiences. Data indicates that flipped classrooms enhance student engagement and retention by allowing in-class time for collaborative problem-solving and critical thinking exercises. Traditional classrooms are evolving through hybrid models, combining face-to-face instruction with digital content delivery to accommodate diverse learning styles and improve accessibility.
flipped classroom vs traditional classroom Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com