Learning styles refer to individual preferences for acquiring information, such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic methods, while learning modalities are the various sensory channels through which learning occurs, including sight, sound, and touch. Understanding the distinction helps educators design more effective instructional strategies that address both preferred styles and multiple modalities to enhance comprehension and retention. Tailoring teaching approaches to encompass diverse modalities supports inclusive education, accommodating the varied learning needs of students.
Table of Comparison
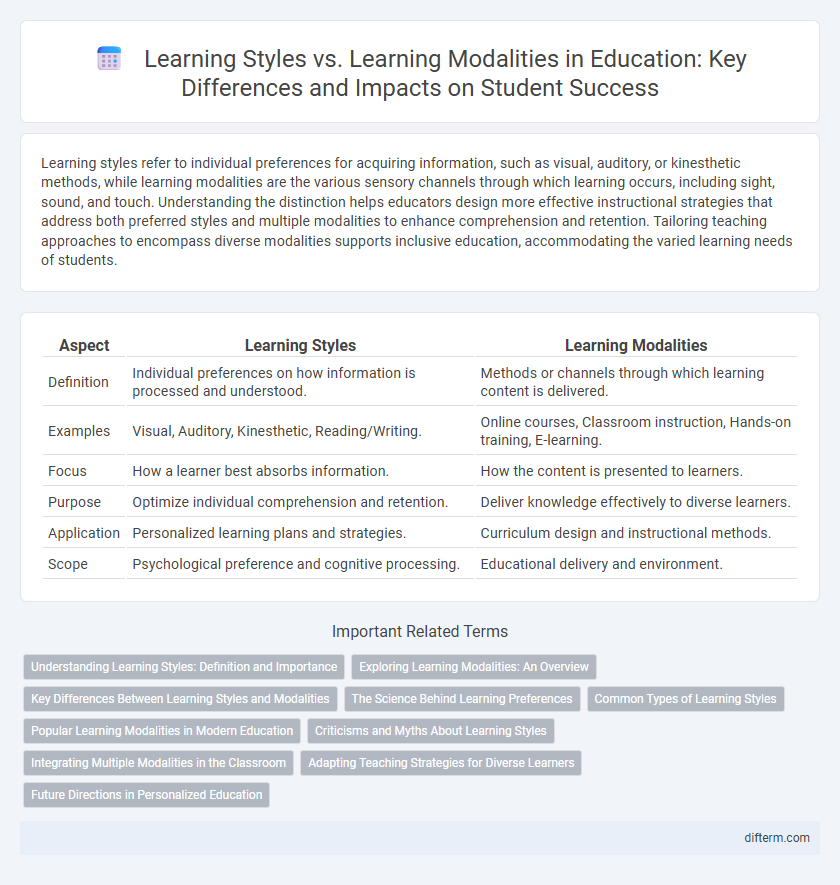
| Aspect | Learning Styles | Learning Modalities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual preferences on how information is processed and understood. | Methods or channels through which learning content is delivered. |
| Examples | Visual, Auditory, Kinesthetic, Reading/Writing. | Online courses, Classroom instruction, Hands-on training, E-learning. |
| Focus | How a learner best absorbs information. | How the content is presented to learners. |
| Purpose | Optimize individual comprehension and retention. | Deliver knowledge effectively to diverse learners. |
| Application | Personalized learning plans and strategies. | Curriculum design and instructional methods. |
| Scope | Psychological preference and cognitive processing. | Educational delivery and environment. |
Understanding Learning Styles: Definition and Importance
Understanding learning styles involves recognizing individual preferences in processing information, such as visual, auditory, and kinesthetic styles, which influence how students absorb and retain knowledge. Learning styles are crucial for tailoring educational strategies to enhance engagement and improve academic performance by addressing diverse cognitive needs. Differentiating learning styles from learning modalities helps educators implement more effective, personalized teaching methods that align with students' unique ways of learning.
Exploring Learning Modalities: An Overview
Learning modalities refer to the sensory channels through which learners absorb, process, and retain information, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic modes. Differentiating learning modalities from learning styles emphasizes how instructional methods can be adapted to engage multiple senses and optimize comprehension. Incorporating varied learning modalities in educational environments enhances student engagement and supports diverse cognitive processing preferences.
Key Differences Between Learning Styles and Modalities
Learning styles refer to individual preferences in processing information, such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic methods, while learning modalities denote the sensory channels through which information is delivered. Key differences lie in learning styles being about how students prefer to learn, whereas modalities focus on how content is presented by educators. Understanding these distinctions allows for tailored instructional strategies that enhance student engagement and retention.
The Science Behind Learning Preferences
Learning styles refer to an individual's preferred way of processing information, such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic, while learning modalities encompass the sensory channels through which learners receive information. Neuroscientific research highlights that although learners exhibit preferences, the brain's plasticity allows for adaptation across multiple modalities, suggesting no single style guarantees superior retention. Effective education leverages diverse modalities to engage multiple cognitive pathways, optimizing comprehension and long-term memory consolidation.
Common Types of Learning Styles
Common types of learning styles include visual, auditory, and kinesthetic, each emphasizing different sensory modalities for information absorption. Visual learners benefit from diagrams and charts, auditory learners excel with lectures and discussions, while kinesthetic learners require hands-on experiences to grasp concepts effectively. Understanding these distinct learning styles helps educators tailor instruction methods to maximize student engagement and retention.
Popular Learning Modalities in Modern Education
Popular learning modalities in modern education include visual, auditory, and kinesthetic approaches, each catering to different sensory preferences for information acquisition. Visual learners benefit from diagrams and videos, auditory learners excel through lectures and discussions, while kinesthetic learners grasp concepts better through hands-on activities and movement. Emphasizing diverse modalities enhances student engagement and accommodates varied learning needs in contemporary classrooms.
Criticisms and Myths About Learning Styles
The concept of learning styles, such as visual, auditory, and kinesthetic, faces significant criticism for lacking empirical evidence supporting improved educational outcomes through tailored instruction. Research indicates that categorizing students by learning styles may lead to oversimplification and misallocation of teaching resources, diverting attention from universally effective strategies. Promoting myths about learning styles risks reinforcing fixed mindsets and limits adaptability in diverse learning environments.
Integrating Multiple Modalities in the Classroom
Integrating multiple learning modalities in the classroom enhances student engagement and retention by addressing diverse sensory preferences such as visual, auditory, and kinesthetic. Employing multimodal strategies like interactive lectures, hands-on activities, and digital media supports differentiated instruction and fosters inclusive learning environments. Research indicates that combining modalities improves cognitive processing and accommodates varied learning styles, leading to higher academic achievement.
Adapting Teaching Strategies for Diverse Learners
Adapting teaching strategies to accommodate diverse learners requires understanding the distinction between learning styles, which refer to individual preferences such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic methods, and learning modalities, which involve the sensory channels through which information is perceived. Educators who integrate multimodal approaches and differentiate instruction based on these concepts can enhance engagement and retention among students with varied cognitive and sensory needs. Tailoring lesson plans to include varied instructional techniques supports inclusivity and improves academic outcomes across heterogeneous classroom environments.
Future Directions in Personalized Education
Future directions in personalized education emphasize leveraging advanced data analytics and adaptive technologies to align learning modalities--visual, auditory, kinesthetic--with individual learning styles, enhancing engagement and retention. Emerging AI-driven platforms are designed to tailor educational content dynamically based on real-time assessments of learner preferences and performance metrics. Integrating neuroscience insights with digital tools facilitates the development of customized learning pathways that optimize cognitive strengths and address diverse learner needs.
learning styles vs learning modalities Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com