Experiential learning immerses students in hands-on activities, fostering critical thinking and deeper retention of knowledge through direct experience. Observational learning relies on watching and imitating others, which helps develop skills and understanding but may lack the engagement and personal insight gained from active participation. Blending both methods enhances comprehension and application by leveraging observation to guide experience-based practice.
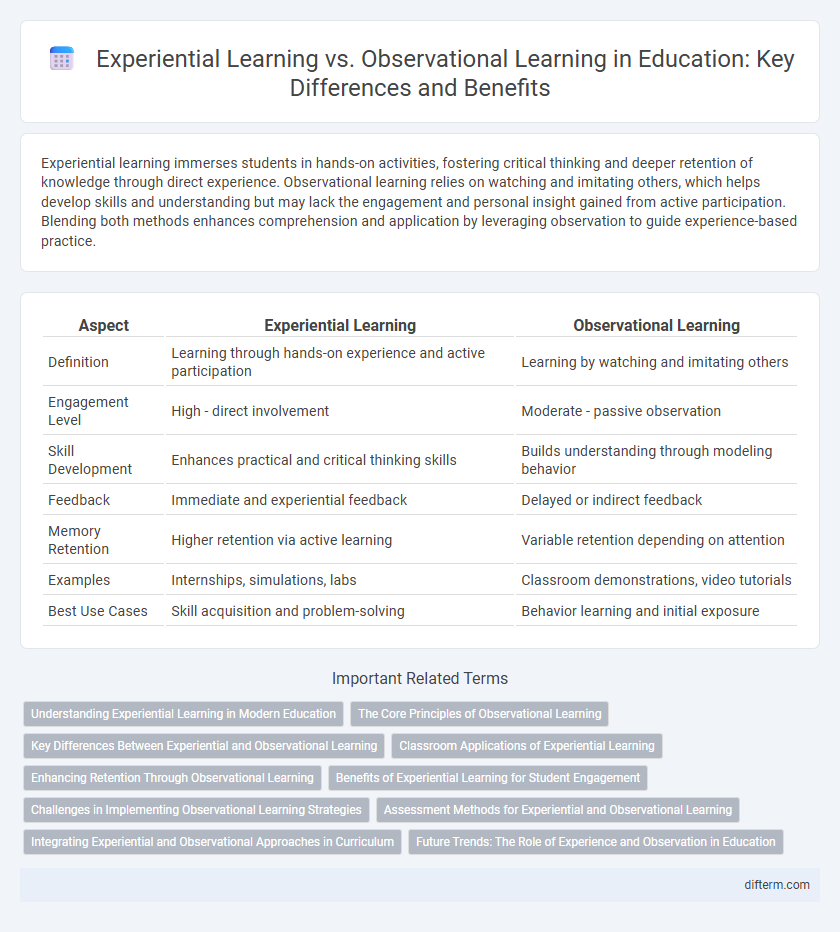
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Observational Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through hands-on experience and active participation | Learning by watching and imitating others |
| Engagement Level | High - direct involvement | Moderate - passive observation |
| Skill Development | Enhances practical and critical thinking skills | Builds understanding through modeling behavior |
| Feedback | Immediate and experiential feedback | Delayed or indirect feedback |
| Memory Retention | Higher retention via active learning | Variable retention depending on attention |
| Examples | Internships, simulations, labs | Classroom demonstrations, video tutorials |
| Best Use Cases | Skill acquisition and problem-solving | Behavior learning and initial exposure |
Understanding Experiential Learning in Modern Education
Experiential learning in modern education emphasizes hands-on experiences where students actively engage in problem-solving and critical thinking, leading to deeper retention and practical skill development. Unlike observational learning, which relies on watching and imitating others, experiential learning promotes direct involvement and reflection, fostering autonomous knowledge construction. Research shows that incorporating experiments, simulations, and real-world projects enhances student motivation and bridges theoretical concepts with tangible outcomes.
The Core Principles of Observational Learning
Observational learning is grounded in the core principles of attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation, which enable learners to acquire new behaviors by watching others. Attention ensures learners focus on significant behaviors, while retention involves encoding and storing the observed information for later recall. Reproduction allows learners to imitate the behavior accurately, and motivation drives the desire to replicate the observed actions, making observational learning a powerful tool in educational settings.
Key Differences Between Experiential and Observational Learning
Experiential learning involves active participation, where learners engage directly in tasks to acquire skills and knowledge through hands-on experience. Observational learning relies on watching and imitating others' behaviors or actions without direct involvement, emphasizing modeling and cognitive processing. The key differences lie in experience engagement, with experiential learning fostering deeper retention through practice, while observational learning depends on attention, retention, and reproduction of observed behaviors.
Classroom Applications of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning in the classroom engages students through hands-on activities, promoting deeper understanding and retention compared to observational learning, which relies on passive observation. Implementing project-based assignments, simulations, and role-playing enables learners to connect theory with real-world applications, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Research shows that experiential learning increases student motivation and fosters collaboration, making it a valuable approach for diverse educational settings.
Enhancing Retention Through Observational Learning
Observational learning enhances retention by allowing students to model behaviors and cognitive strategies demonstrated by experts, thereby reinforcing neural pathways associated with the skill. Video modeling and peer demonstrations create immersive environments that promote active engagement and deeper understanding, leading to longer-lasting memory retention compared to passive, experiential methods. Research shows that incorporating observational techniques can increase knowledge retention by up to 40% in educational settings.
Benefits of Experiential Learning for Student Engagement
Experiential learning enhances student engagement by actively involving learners in hands-on activities, fostering deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. This approach promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and real-world application, which observational learning alone may not achieve. Studies show that learners participating in experiential methods demonstrate higher motivation, improved collaboration, and increased academic performance compared to those relying solely on passive observation.
Challenges in Implementing Observational Learning Strategies
Implementing observational learning strategies faces challenges such as ensuring learners have access to skilled models who demonstrate accurate behaviors in diverse contexts. Another difficulty lies in maintaining learner engagement and attention during observation sessions, which can impact knowledge retention and skill acquisition. Furthermore, assessing the effectiveness of observational learning is complex due to individual differences in interpretation and internalization of observed behaviors.
Assessment Methods for Experiential and Observational Learning
Assessment methods for experiential learning emphasize practical demonstrations, portfolio reviews, and reflective journals to measure skill acquisition and real-world application. Observational learning assessments typically utilize quizzes, verbal explanations, and performance tasks to evaluate comprehension and imitation accuracy. Both approaches align assessment techniques with their learning objectives, ensuring effective measurement of knowledge transfer and behavioral change.
Integrating Experiential and Observational Approaches in Curriculum
Integrating experiential and observational learning in curriculum design enhances student engagement by combining hands-on activities with critical analysis of modeled behaviors. This approach promotes deeper cognitive processing and skill retention by allowing learners to apply concepts in real-world contexts while reflecting on observed examples. Research indicates that curricula incorporating both methodologies improve problem-solving abilities and foster adaptive expertise.
Future Trends: The Role of Experience and Observation in Education
Future trends in education emphasize the integration of experiential learning and observational learning to enhance student engagement and skill retention. Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies enable immersive experiential learning environments, while AI-powered analytics optimize observational learning by tailoring feedback based on student behaviors. Blending these approaches fosters personalized education that prepares learners for complex, real-world challenges.
experiential learning vs observational learning Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com