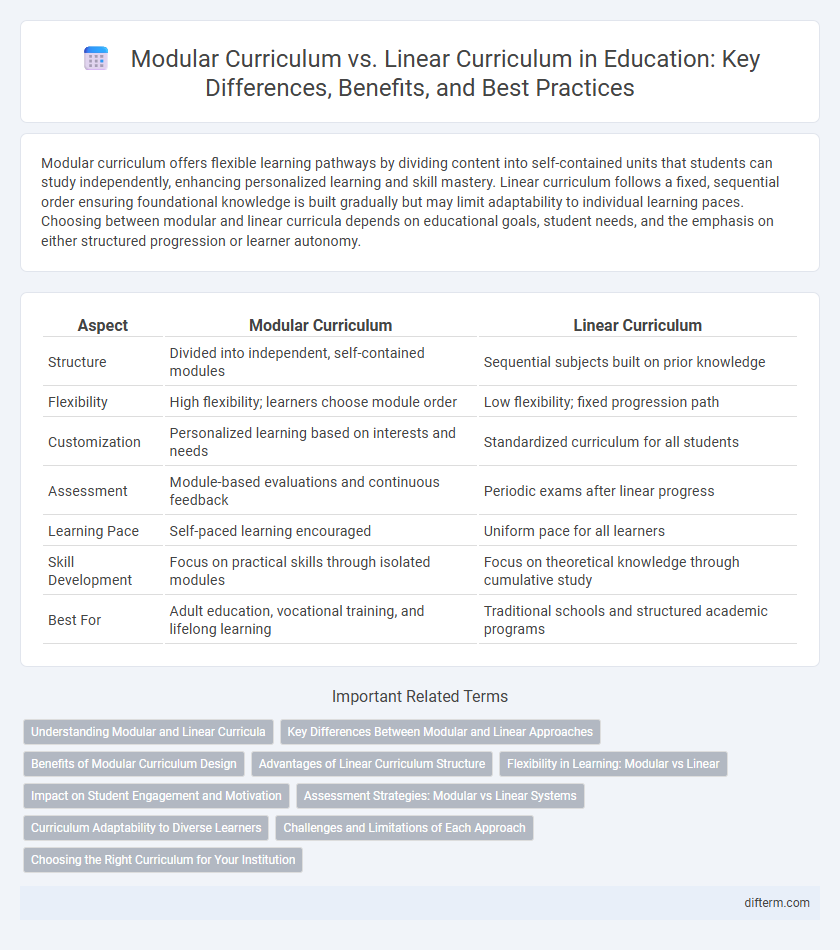
Modular curriculum offers flexible learning pathways by dividing content into self-contained units that students can study independently, enhancing personalized learning and skill mastery. Linear curriculum follows a fixed, sequential order ensuring foundational knowledge is built gradually but may limit adaptability to individual learning paces. Choosing between modular and linear curricula depends on educational goals, student needs, and the emphasis on either structured progression or learner autonomy.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Modular Curriculum | Linear Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Divided into independent, self-contained modules | Sequential subjects built on prior knowledge |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; learners choose module order | Low flexibility; fixed progression path |
| Customization | Personalized learning based on interests and needs | Standardized curriculum for all students |
| Assessment | Module-based evaluations and continuous feedback | Periodic exams after linear progress |
| Learning Pace | Self-paced learning encouraged | Uniform pace for all learners |
| Skill Development | Focus on practical skills through isolated modules | Focus on theoretical knowledge through cumulative study |
| Best For | Adult education, vocational training, and lifelong learning | Traditional schools and structured academic programs |
Understanding Modular and Linear Curricula
Modular curricula divide learning content into self-contained units, allowing flexible pacing and focused mastery of specific topics, enhancing personalized education paths. Linear curricula follow a sequential structure, where concepts build progressively to develop foundational knowledge methodically, benefiting coherent skill acquisition. Understanding these curriculum designs helps educators tailor instruction to diverse learner needs and optimize educational outcomes.
Key Differences Between Modular and Linear Approaches
Modular curricula divide subjects into independent, self-contained units that allow flexible learning paths, contrasting with linear curricula, which follow a sequential structure where each topic builds on the previous one. The modular approach promotes personalized pace and mastery of individual modules, while linear curricula emphasize a fixed progression ensuring foundational knowledge before advancing. Assessment in modular systems often targets discrete units, whereas linear systems assess cumulative understanding over time.
Benefits of Modular Curriculum Design
Modular curriculum design enhances personalized learning by allowing students to progress at their own pace and select modules that match their interests and career goals. This flexibility improves knowledge retention and engagement through diverse, focused content units tailored to individual learning styles. It also facilitates easier curriculum updates, ensuring educational programs remain relevant to industry demands and emerging trends.
Advantages of Linear Curriculum Structure
Linear curriculum structure offers a clear, sequential progression of topics that enhances student comprehension and retention by building foundational knowledge step-by-step. This approach simplifies assessment and instructional planning by providing a standardized framework aligned with educational standards. Students benefit from predictable learning paths that reduce cognitive overload and promote mastery of essential concepts before advancing.
Flexibility in Learning: Modular vs Linear
Modular curriculum offers significant flexibility, allowing learners to choose specific modules tailored to their interests and pace, enhancing personalized education. Linear curriculum follows a fixed sequence, limiting options and often requiring students to complete courses in a predetermined order. This structured progression may hinder adaptability to diverse learning needs and styles.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Modular curricula enhance student engagement by allowing learners to focus on smaller, manageable units, fostering a sense of achievement and autonomy that boosts motivation. Linear curricula often impose a fixed sequence, which can limit flexibility and reduce personalized pacing, sometimes leading to disengagement. Research shows modular designs increase active participation and intrinsic motivation by accommodating diverse learning styles and interests.
Assessment Strategies: Modular vs Linear Systems
Modular curriculum assessment strategies emphasize formative evaluations tailored to individual modules, enabling targeted feedback and mastery of discrete topics before progression. Linear curriculum assessments often rely on cumulative exams that measure knowledge retention over an extended sequence of content, emphasizing chronological learning. Modular systems facilitate flexible, adaptive testing environments, whereas linear systems promote a standardized, summative evaluation approach.
Curriculum Adaptability to Diverse Learners
Modular curriculum enhances adaptability by allowing learners to engage with discrete, self-contained units tailored to diverse learning styles and paces, promoting personalized education. In contrast, linear curriculum follows a fixed, sequential structure that may limit flexibility and not accommodate individual learner differences effectively. Schools implementing modular curricula report increased student engagement and improved mastery of concepts due to customizable learning pathways.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Modular curriculum challenges include potential gaps in knowledge due to fragmented learning and the need for strong self-discipline, while linear curriculum limitations involve reduced flexibility and slower adaptation to diverse student needs. Students in modular systems may struggle with integrating concepts across modules, whereas linear curricula often fail to accommodate different learning paces and styles. Both approaches require carefully designed assessment methods to accurately measure student understanding and progression.
Choosing the Right Curriculum for Your Institution
Modular curriculum offers flexible learning paths tailored to diverse student needs, enabling institutions to update content rapidly in response to industry trends. In contrast, linear curriculum provides a structured sequence of courses that ensure foundational knowledge is systematically built over time. Selecting the right curriculum depends on institutional goals, student demographics, and resource availability to maximize educational outcomes and workforce preparedness.
modular curriculum vs linear curriculum Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com