Implicit learning occurs unconsciously through exposure and experience, allowing individuals to acquire knowledge without direct instruction, while explicit learning involves conscious awareness and deliberate effort to understand and memorize information. In educational settings, balancing implicit and explicit learning strategies enhances comprehension and retention by catering to different cognitive processes. Combining storytelling, hands-on activities, and clear explanations fosters a more dynamic and effective learning environment.
Table of Comparison
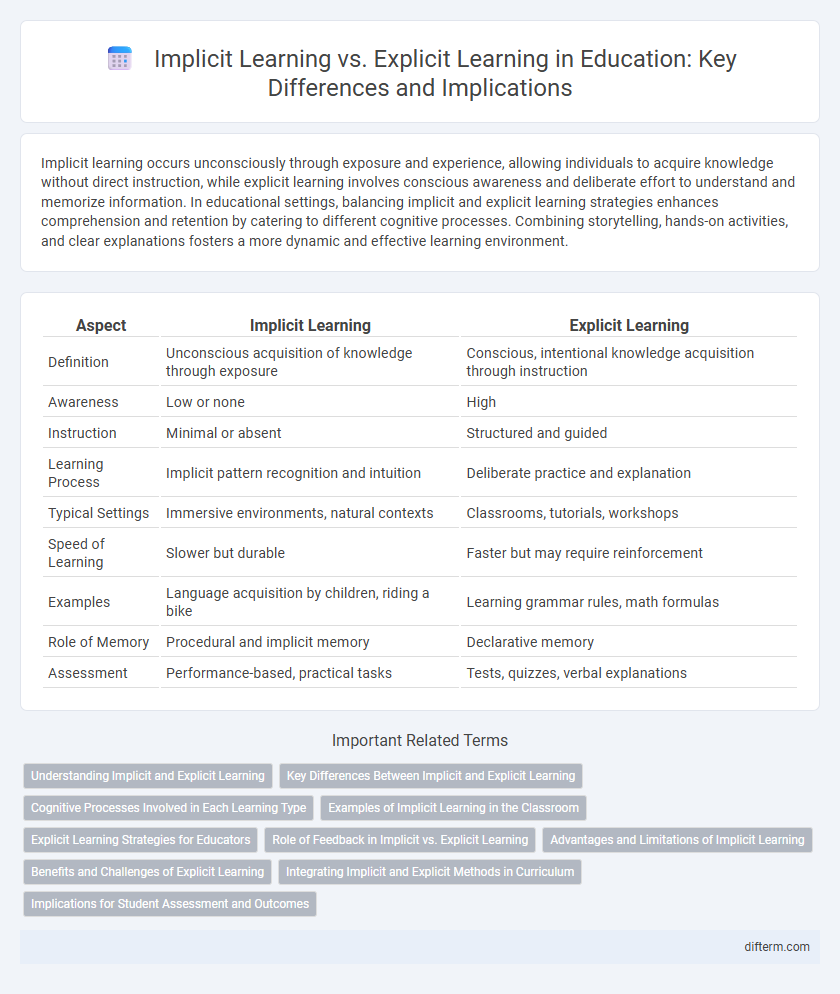
| Aspect | Implicit Learning | Explicit Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unconscious acquisition of knowledge through exposure | Conscious, intentional knowledge acquisition through instruction |
| Awareness | Low or none | High |
| Instruction | Minimal or absent | Structured and guided |
| Learning Process | Implicit pattern recognition and intuition | Deliberate practice and explanation |
| Typical Settings | Immersive environments, natural contexts | Classrooms, tutorials, workshops |
| Speed of Learning | Slower but durable | Faster but may require reinforcement |
| Examples | Language acquisition by children, riding a bike | Learning grammar rules, math formulas |
| Role of Memory | Procedural and implicit memory | Declarative memory |
| Assessment | Performance-based, practical tasks | Tests, quizzes, verbal explanations |
Understanding Implicit and Explicit Learning
Implicit learning involves acquiring knowledge unconsciously through exposure and experience, enabling individuals to grasp patterns without deliberate effort. Explicit learning requires focused attention and conscious awareness, where learners actively process information and apply strategies to understand and remember content. Understanding the differences supports tailored educational approaches, optimizing skill acquisition by leveraging both subconscious pattern recognition and intentional instruction.
Key Differences Between Implicit and Explicit Learning
Implicit learning occurs unconsciously through exposure and practice, allowing learners to acquire skills and knowledge without direct instruction. Explicit learning involves conscious awareness and deliberate effort to understand concepts, often through formal teaching and structured environments. Key differences include the learner's awareness, the role of feedback, and the types of memory systems engaged, with implicit learning relying on procedural memory and explicit learning engaging declarative memory.
Cognitive Processes Involved in Each Learning Type
Implicit learning involves unconscious acquisition of knowledge through exposure and pattern recognition, primarily engaging the basal ganglia and cerebellum for procedural memory. Explicit learning requires conscious effort and awareness, activating the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus to encode and retrieve declarative knowledge. These distinct cognitive processes highlight the brain's ability to adapt learning strategies based on task demands and informational context.
Examples of Implicit Learning in the Classroom
Implicit learning in the classroom occurs when students acquire knowledge unconsciously through exposure and practice, such as picking up grammatical rules by reading extensively or developing problem-solving skills during interactive group activities. For example, language learners often internalize syntax and vocabulary without formal instruction, while math students may intuitively grasp patterns and relationships through hands-on experiments or exploratory tasks. These naturalistic learning experiences enhance cognitive development by embedding skills in meaningful contexts without explicit teaching.
Explicit Learning Strategies for Educators
Explicit learning strategies for educators involve clear instruction, structured lessons, and direct feedback to enhance student understanding and skill acquisition. Techniques such as guided practice, modeling, and systematic scaffolding help learners consciously grasp concepts and apply knowledge effectively. Implementing these strategies improves academic performance by promoting deliberate focus on specific learning objectives and mastery of material.
Role of Feedback in Implicit vs. Explicit Learning
Feedback plays a critical role in distinguishing implicit from explicit learning processes, where explicit learning relies heavily on direct, corrective feedback for conscious knowledge acquisition. In implicit learning, feedback tends to be indirect or minimal, supporting subconscious pattern recognition without explicit awareness. Research shows that timely, clear feedback enhances explicit learning outcomes, while implicit learning benefits more from practice and environmental cues rather than overt feedback.
Advantages and Limitations of Implicit Learning
Implicit learning enables the acquisition of skills and knowledge unconsciously, enhancing adaptability and reducing cognitive load during complex tasks. This form of learning fosters intuitive problem-solving and long-term retention but may limit the learner's ability to verbalize or consciously control the acquired knowledge. Challenges include slower initial learning rates and difficulties in transferring skills across different contexts compared to explicit learning methods.
Benefits and Challenges of Explicit Learning
Explicit learning offers clear advantages by providing structured and intentional instruction that facilitates faster acquisition of complex concepts and skills. Its benefits include precise feedback, measurable progress, and easier curriculum design tailored to specific educational goals. Challenges involve potential cognitive overload for learners and reduced natural retention compared to implicit learning, requiring ongoing motivation and reinforcement for long-term mastery.
Integrating Implicit and Explicit Methods in Curriculum
Integrating implicit and explicit learning methods in curriculum design enhances student comprehension by combining unconscious skill acquisition with conscious knowledge development. Incorporating embedding language patterns and deliberate practice tasks facilitates a balanced approach that supports deeper understanding and long-term retention. Curriculum frameworks that blend storytelling, contextual clues, and direct instruction optimize cognitive engagement and promote versatile learning outcomes.
Implications for Student Assessment and Outcomes
Implicit learning facilitates unconscious skill acquisition, leading to improved problem-solving and adaptability without explicit instruction, which benefits student assessment by highlighting practical competence beyond standard testing. Explicit learning drives conscious knowledge retention and understanding of concepts, supporting traditional assessment methods like exams and quizzes that measure factual recall and procedural knowledge. Incorporating both learning types in educational strategies can enhance student outcomes by balancing deep comprehension with applied skills, fostering holistic academic development.
implicit learning vs explicit learning Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com