Vertical alignment in education ensures that curriculum, skills, and assessments progressively build from one grade level to the next, promoting continuity and deeper understanding over time. Horizontal alignment involves coordinating content and teaching methods across subjects or classrooms within the same grade to provide a consistent and coherent learning experience. Effective integration of both alignments enhances student achievement by creating a structured and unified educational framework.
Table of Comparison
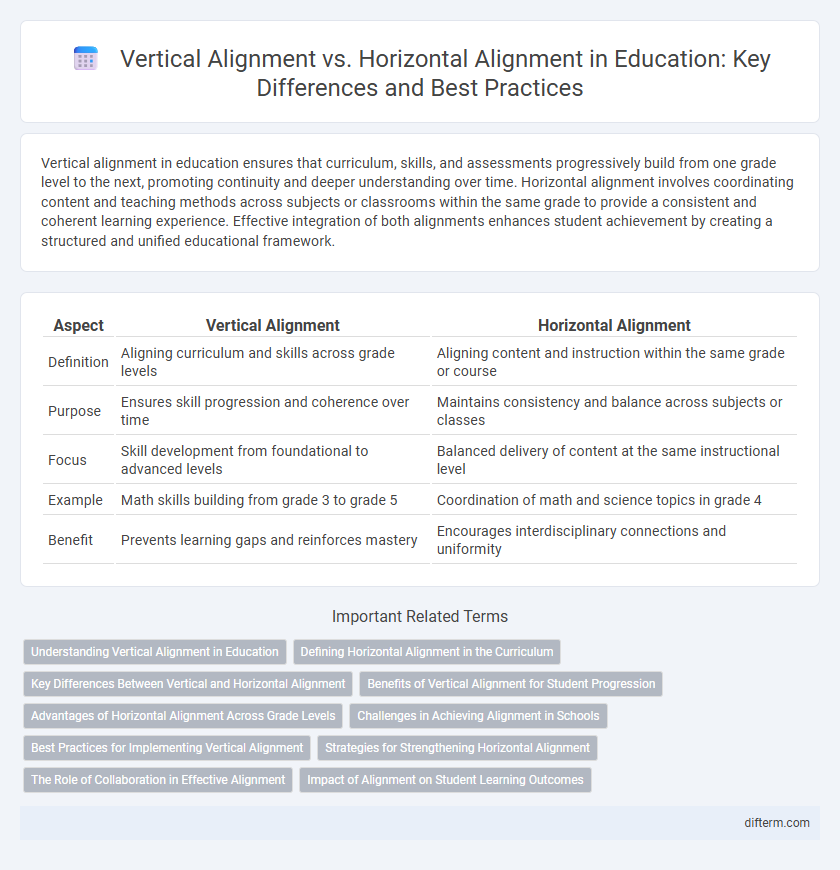
| Aspect | Vertical Alignment | Horizontal Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Aligning curriculum and skills across grade levels | Aligning content and instruction within the same grade or course |
| Purpose | Ensures skill progression and coherence over time | Maintains consistency and balance across subjects or classes |
| Focus | Skill development from foundational to advanced levels | Balanced delivery of content at the same instructional level |
| Example | Math skills building from grade 3 to grade 5 | Coordination of math and science topics in grade 4 |
| Benefit | Prevents learning gaps and reinforces mastery | Encourages interdisciplinary connections and uniformity |
Understanding Vertical Alignment in Education
Vertical alignment in education ensures that curriculum, instruction, and assessments are systematically organized across grade levels to promote continuous skill development and knowledge acquisition. This alignment facilitates coherent progression from foundational concepts in early grades to more complex topics in higher grades, enhancing student learning outcomes. Effective vertical alignment supports teachers in scaffolding instruction and closing learning gaps, thereby preparing students for success in subsequent educational stages.
Defining Horizontal Alignment in the Curriculum
Horizontal alignment in the curriculum refers to the consistency and coherence of learning objectives, instructional strategies, and assessments across different subjects or grade levels taught simultaneously. It ensures that students receive a balanced and integrated learning experience, promoting interdisciplinary connections and avoiding content overlap. Effective horizontal alignment enhances collaboration among educators and supports the development of comprehensive skill sets within a single academic year.
Key Differences Between Vertical and Horizontal Alignment
Vertical alignment in education ensures curriculum continuity across grade levels, focusing on sequential skill development and mastery as students progress. Horizontal alignment emphasizes consistency in content and instructional strategies within the same grade, promoting uniform learning experiences across different classrooms or schools. Key differences include vertical alignment's role in long-term academic progression versus horizontal alignment's focus on standardizing teaching practices at a single educational stage.
Benefits of Vertical Alignment for Student Progression
Vertical alignment in education ensures a coherent progression of skills and knowledge across grade levels, enabling students to build on prior learning systematically. It reduces gaps and redundancies in curriculum delivery, promoting smoother transitions between educational stages. This alignment enhances long-term academic achievement by fostering cumulative understanding and consistent skill development throughout a student's educational journey.
Advantages of Horizontal Alignment Across Grade Levels
Horizontal alignment across grade levels promotes consistency in curriculum delivery by ensuring that students receive a uniform educational experience regardless of the teacher or classroom. This alignment facilitates collaboration among educators, allowing for the sharing of best practices and resources that enhance instructional quality. Students benefit from a more cohesive learning environment that reduces content overlap and gaps, supporting smoother academic progression and skill development.
Challenges in Achieving Alignment in Schools
Challenges in achieving vertical and horizontal alignment in schools often stem from inconsistent curriculum expectations across grade levels and subject areas, leading to fragmented student learning experiences. Vertical alignment requires coordinated progression of skills and knowledge from one grade to the next, while horizontal alignment demands uniformity of instruction among teachers of the same grade or subject, both of which can be hindered by varying teacher expertise and limited collaboration time. Addressing these challenges involves establishing clear communication channels, ongoing professional development, and unified curriculum frameworks to ensure cohesive educational outcomes.
Best Practices for Implementing Vertical Alignment
Best practices for implementing vertical alignment in education include clearly mapping learning objectives and standards across grade levels to ensure seamless skill progression. Collaboration among educators from different grades promotes consistency in curriculum delivery and assessment methods, enhancing student readiness for subsequent academic challenges. Regular data analysis and adjustments based on student performance support continuous improvement and effective vertical progression.
Strategies for Strengthening Horizontal Alignment
Horizontal alignment strategies focus on ensuring consistency across grade levels and subject areas by collaboratively developing common learning objectives, assessment practices, and instructional materials. Teachers engage in professional learning communities to share best practices and align curriculum pacing, fostering coherence and equity in student learning experiences. Utilizing data-driven decision-making and regular cross-grade meetings further strengthens horizontal alignment by addressing gaps and promoting uniform standards.
The Role of Collaboration in Effective Alignment
Collaboration plays a critical role in achieving both vertical and horizontal alignment in education by fostering open communication among educators at different levels and across various subjects. Vertical alignment ensures curriculum coherence from grade to grade, while horizontal alignment promotes consistency among teachers within the same grade or subject area. Effective collaboration empowers teachers to share goals, instructional strategies, and assessment practices, leading to a more integrated and student-centered learning experience.
Impact of Alignment on Student Learning Outcomes
Vertical alignment ensures curriculum coherence across grade levels, enabling students to build on prior knowledge systematically, which significantly enhances mastery and retention of concepts. Horizontal alignment promotes consistency in teaching methods and assessment within the same grade, fostering equitable learning experiences and minimizing achievement gaps. Together, effective alignment drives improved student learning outcomes by creating a structured and collaborative educational environment.
vertical alignment vs horizontal alignment Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com