Brake fade occurs when the braking system loses effectiveness due to overheating, often caused by prolonged or intense braking, resulting in a spongy brake pedal and reduced stopping power. Brake judder manifests as a vibrating or pulsating sensation in the brake pedal or steering wheel, typically caused by uneven brake rotor surfaces or worn components. Understanding the distinction between brake fade and brake judder is essential for diagnosing and addressing brake system issues to ensure optimal vehicle safety and performance.
Table of Comparison
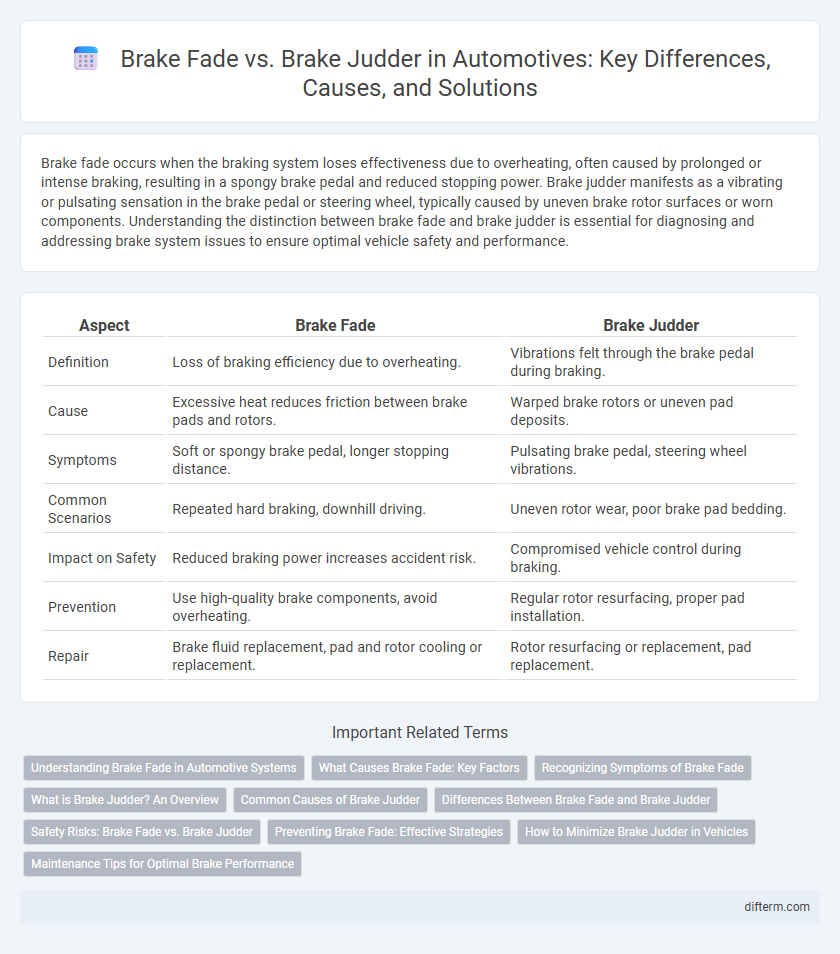
| Aspect | Brake Fade | Brake Judder |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss of braking efficiency due to overheating. | Vibrations felt through the brake pedal during braking. |
| Cause | Excessive heat reduces friction between brake pads and rotors. | Warped brake rotors or uneven pad deposits. |
| Symptoms | Soft or spongy brake pedal, longer stopping distance. | Pulsating brake pedal, steering wheel vibrations. |
| Common Scenarios | Repeated hard braking, downhill driving. | Uneven rotor wear, poor brake pad bedding. |
| Impact on Safety | Reduced braking power increases accident risk. | Compromised vehicle control during braking. |
| Prevention | Use high-quality brake components, avoid overheating. | Regular rotor resurfacing, proper pad installation. |
| Repair | Brake fluid replacement, pad and rotor cooling or replacement. | Rotor resurfacing or replacement, pad replacement. |
Understanding Brake Fade in Automotive Systems
Brake fade in automotive systems occurs when excessive heat reduces the friction between brake pads and rotors, leading to diminished braking performance. It primarily results from prolonged or intense braking, causing the brake components to overheat and lose effectiveness. Understanding brake fade is essential for optimizing brake system design and ensuring driver safety under high-stress conditions.
What Causes Brake Fade: Key Factors
Brake fade primarily occurs due to excessive heat generated during prolonged braking, causing the brake pads and rotors to lose friction efficiency. Key factors contributing to brake fade include overheating of brake components, glazing of brake pads, and brake fluid boiling, which reduce braking performance and increase stopping distances. Effective thermal management and regular brake system maintenance are critical to preventing brake fade and ensuring consistent brake response.
Recognizing Symptoms of Brake Fade
Brake fade is characterized by a gradual loss of braking power due to overheating of brake components, commonly experienced during prolonged or aggressive braking. Symptoms include a spongy brake pedal, increased stopping distances, and a noticeable reduction in braking efficiency. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and preventing brake system failure.
What is Brake Judder? An Overview
Brake judder is a vibration or pulsation felt through the brake pedal or steering wheel during braking, often caused by uneven brake rotor surfaces or warped discs. This phenomenon leads to inconsistent braking performance and can compromise vehicle safety by reducing stopping efficiency. Recognizing brake judder early helps prevent further damage to braking components and ensures optimal vehicle control.
Common Causes of Brake Judder
Brake judder commonly results from uneven rotor wear, often caused by excessive heat buildup during repeated heavy braking, leading to warped or contaminated rotors. Misaligned or improperly installed brake components and worn suspension parts can also contribute to vibrations felt through the brake pedal. Regular inspection of rotor surface condition and brake system alignment helps prevent brake judder and maintains optimal braking performance.
Differences Between Brake Fade and Brake Judder
Brake fade occurs when the braking system overheats, causing a reduction in stopping power due to the loss of friction between brake pads and rotors. Brake judder, on the other hand, is characterized by a vibrating or pulsing sensation during braking, often caused by warped brake rotors or uneven wear. Understanding these differences is essential for diagnosing braking issues and ensuring vehicle safety in automotive maintenance.
Safety Risks: Brake Fade vs. Brake Judder
Brake fade occurs when the braking system overheats, significantly reducing stopping power and increasing the risk of accidents during prolonged or intense braking, particularly on steep descents. Brake judder causes intermittent vibrations and uneven brake application, leading to compromised vehicle control and potential loss of stability during braking. Both conditions severely impact safety by diminishing the driver's ability to maintain consistent and reliable braking performance.
Preventing Brake Fade: Effective Strategies
Preventing brake fade involves maintaining proper brake fluid levels, using high-quality brake pads designed for heat resistance, and ensuring adequate cooling through vented rotors or upgraded calipers. Regular inspection and replacement of worn components reduce the risk of overheating and loss of braking efficiency during prolonged or intense use. Implementing these strategies enhances vehicle safety by maintaining consistent braking performance under various driving conditions.
How to Minimize Brake Judder in Vehicles
Brake judder in vehicles can be minimized by ensuring brake rotors are properly balanced and free from warping through regular maintenance and timely resurfacing. Using high-quality brake pads with appropriate friction materials reduces uneven wear and vibration during braking. Proper wheel alignment and torque settings further prevent brake judder by maintaining even pressure distribution across the braking components.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Brake Performance
Regularly inspect brake pads and rotors for wear to prevent brake fade, ensuring consistent friction and proper heat dissipation. Address brake judder by checking for warped rotors and uneven pad wear, which can cause vibrations during braking. Properly maintaining brake fluid levels and timely replacement also enhances overall brake system reliability and performance.
brake fade vs brake judder Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com