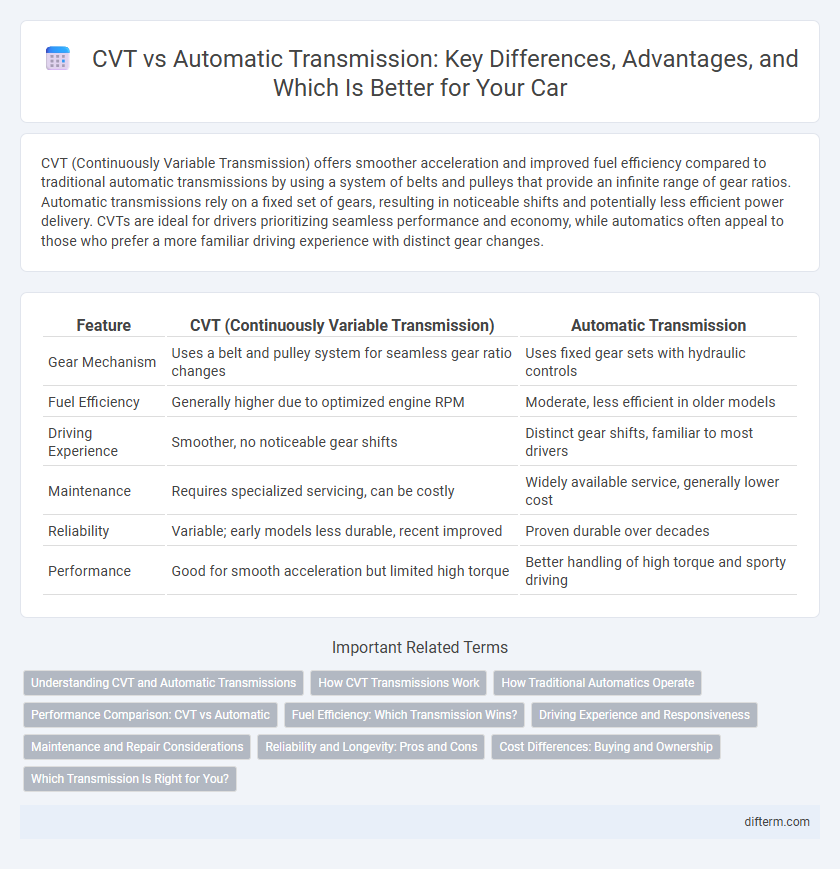
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) offers smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency compared to traditional automatic transmissions by using a system of belts and pulleys that provide an infinite range of gear ratios. Automatic transmissions rely on a fixed set of gears, resulting in noticeable shifts and potentially less efficient power delivery. CVTs are ideal for drivers prioritizing seamless performance and economy, while automatics often appeal to those who prefer a more familiar driving experience with distinct gear changes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) | Automatic Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Gear Mechanism | Uses a belt and pulley system for seamless gear ratio changes | Uses fixed gear sets with hydraulic controls |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally higher due to optimized engine RPM | Moderate, less efficient in older models |
| Driving Experience | Smoother, no noticeable gear shifts | Distinct gear shifts, familiar to most drivers |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized servicing, can be costly | Widely available service, generally lower cost |
| Reliability | Variable; early models less durable, recent improved | Proven durable over decades |
| Performance | Good for smooth acceleration but limited high torque | Better handling of high torque and sporty driving |
Understanding CVT and Automatic Transmissions
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) use a belt and pulley mechanism to provide seamless gear ratio changes, enhancing fuel efficiency and delivering smoother acceleration compared to traditional automatic transmissions. Automatic transmissions rely on a set number of fixed gears and hydraulics to shift between those gears, offering reliable performance and widespread compatibility across vehicle models. Understanding the mechanical differences helps consumers choose between the fuel-saving benefits of CVTs and the robust durability of traditional automatic transmissions.
How CVT Transmissions Work
CVT transmissions use a system of pulleys and a flexible belt to provide an infinite range of gear ratios, enabling smooth and efficient power delivery. Unlike traditional automatic transmissions with fixed gear sets, CVTs adjust continuously to the optimal engine speed, improving fuel efficiency and driving comfort. This seamless variation in gear ratios reduces engine strain and enhances performance in varying driving conditions.
How Traditional Automatics Operate
Traditional automatic transmissions operate using a complex arrangement of planetary gearsets, hydraulic controls, and a torque converter to seamlessly change gear ratios without driver input. The hydraulic system manages fluid pressure to engage clutches and bands, enabling smooth shifting and power transfer from the engine to the drivetrain. This system's mechanical efficiency and durability have made it a longstanding choice in automotive engineering despite the emergence of alternative transmission technologies like Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT).
Performance Comparison: CVT vs Automatic
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) deliver smoother acceleration by eliminating traditional gear shifts, improving fuel efficiency and providing a more consistent power band compared to conventional automatic transmissions. Automatic transmissions with fixed gear ratios typically offer better performance during high-torque applications and provide a more engaging driving experience due to defined shift points. While CVTs excel in optimizing engine output for fuel economy, automatics often outperform in responsiveness and durability under strenuous driving conditions.
Fuel Efficiency: Which Transmission Wins?
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) typically offer superior fuel efficiency compared to traditional automatic transmissions due to their ability to maintain optimal engine speeds without fixed gear ratios. CVTs adjust seamlessly to driving conditions, reducing fuel consumption by keeping the engine in its most efficient RPM range. In contrast, conventional automatic transmissions often experience energy losses through gear shifts, resulting in slightly lower fuel economy.
Driving Experience and Responsiveness
CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) offers seamless acceleration with a smooth, stepless gear ratio adjustment that enhances fuel efficiency and reduces engine noise, resulting in a refined driving experience. Traditional automatic transmissions provide distinct gear shifts that deliver more responsive and predictable power delivery, especially during aggressive acceleration or towing. Drivers seeking smooth city driving often prefer CVTs, while those valuing prompt throttle response and sporty performance tend to favor automatic transmissions.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
CVT transmissions require specialized maintenance such as regular fluid changes with manufacturer-specific CVT fluid to prevent belt and pulley wear, while traditional automatic transmissions use more common ATF that is less sensitive to change intervals. Repair costs for CVTs tend to be higher due to their complex design and fewer repair shops equipped to handle them, whereas automatic transmissions have well-established service networks reducing overall repair expenses. Proper maintenance significantly extends the lifespan of both systems, but improper servicing of CVTs often leads to costly failures compared to the generally more robust automatic transmissions.
Reliability and Longevity: Pros and Cons
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) offer smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency but often face concerns regarding long-term reliability due to belt or chain wear and higher maintenance costs. Traditional automatic transmissions, with their fixed gear sets and proven hydraulic systems, generally provide greater durability and lower repair frequency, making them a preferred choice for longevity in heavy-duty or high-mileage vehicles. However, advancements in CVT technology are gradually improving their robustness, narrowing the gap in lifespan compared to conventional automatics.
Cost Differences: Buying and Ownership
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) typically have a lower initial purchase price compared to traditional automatic transmissions due to fewer mechanical components and simpler design. However, CVTs may incur higher maintenance and repair costs over time because of their specialized belts and pulleys, which can wear out faster than conventional automatic transmission parts. Owners should also consider fuel efficiency advantages of CVTs, which can offset some ownership costs despite potentially higher service expenses.
Which Transmission Is Right for You?
Choosing between a CVT and an automatic transmission depends on your driving preferences and vehicle requirements. CVTs offer smoother acceleration and improved fuel efficiency by providing seamless gear ratios, ideal for city driving and hybrid vehicles. Traditional automatic transmissions deliver a more familiar shifting feel and better performance during high-torque applications, making them suitable for towing and sporty driving.
CVT vs automatic transmission Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com