Analog photography captures images on film, creating a tangible, vintage aesthetic with unique grain and color depth that many artists value for its authenticity. Digital photography offers greater flexibility with instant image review, extensive editing capabilities, and cost efficiency, appealing to photographers seeking convenience and creative control. Both mediums provide distinct artistic expressions, allowing photographers to choose based on their desired style and workflow.
Table of Comparison
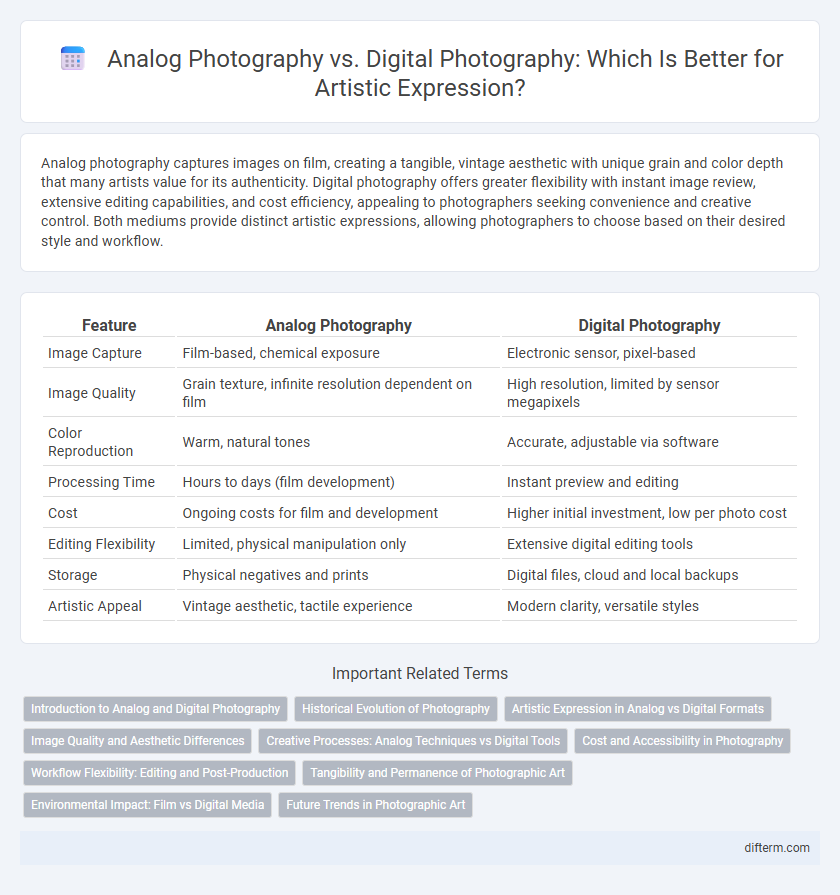
| Feature | Analog Photography | Digital Photography |
|---|---|---|
| Image Capture | Film-based, chemical exposure | Electronic sensor, pixel-based |
| Image Quality | Grain texture, infinite resolution dependent on film | High resolution, limited by sensor megapixels |
| Color Reproduction | Warm, natural tones | Accurate, adjustable via software |
| Processing Time | Hours to days (film development) | Instant preview and editing |
| Cost | Ongoing costs for film and development | Higher initial investment, low per photo cost |
| Editing Flexibility | Limited, physical manipulation only | Extensive digital editing tools |
| Storage | Physical negatives and prints | Digital files, cloud and local backups |
| Artistic Appeal | Vintage aesthetic, tactile experience | Modern clarity, versatile styles |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Photography
Analog photography captures images on film through chemical processes, offering a tactile experience and rich, organic tones prized by many artists. Digital photography records images using electronic sensors, enabling instant review, extensive editing options, and efficient storage, favored for versatility and convenience. Both mediums require distinct technical skills and creative approaches, influencing artistic expression and workflow in unique ways.
Historical Evolution of Photography
The historical evolution of photography highlights the transition from analog to digital formats, beginning with early 19th-century chemical processes like daguerreotypes and evolving into modern digital sensors by the late 20th century. Analog photography relies on light-sensitive film to capture images, preserving a tangible, artisanal quality prized by traditionalists. Digital photography revolutionized image capture with instant processing and editing, drastically expanding creative possibilities and accessibility for photographers worldwide.
Artistic Expression in Analog vs Digital Formats
Analog photography offers a unique tactile experience with film grain and chemical processing that enhances artistic expression through texture and depth. Digital photography provides immediate feedback and extensive editing capabilities, enabling artists to manipulate images with precision and creative flexibility. Both formats contribute distinct aesthetic qualities that shape the visual narrative and emotional impact of photographic art.
Image Quality and Aesthetic Differences
Analog photography delivers unique image quality through its organic grain structure and wide dynamic range, often resulting in richer color depth and nuanced shadow detail. Digital photography offers higher resolution, precise color accuracy, and instant editing capabilities, making it versatile for various styles and conditions. The aesthetic differences lie in analog's tangible, textured feel contrasted with digital's clean, crisp images, appealing to distinct artistic preferences and creative intentions.
Creative Processes: Analog Techniques vs Digital Tools
Analog photography emphasizes tactile engagement with light and chemicals, fostering a deliberate creative process that often results in unique textures and imperfections. Digital photography leverages advanced software and editing tools, enabling precise manipulation and experimentation with color, exposure, and composition. Both methods shape artistic expression differently, with analog promoting organic unpredictability and digital offering customizable control.
Cost and Accessibility in Photography
Analog photography involves higher costs due to film purchase, development, and printing, making it less accessible for casual photographers. Digital photography offers lower ongoing expenses since images can be stored and edited digitally without extra material costs. The affordability and immediate access to digital cameras and smartphones have significantly democratized photography, expanding creative possibilities for artists worldwide.
Workflow Flexibility: Editing and Post-Production
Analog photography requires a meticulous darkroom process for editing and post-production, offering limited flexibility compared to digital methods. Digital photography enables instant image review and non-destructive editing using software like Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom, significantly enhancing workflow efficiency. The ability to adjust exposure, color, and composition at any stage allows photographers to experiment freely and achieve precise creative outcomes.
Tangibility and Permanence of Photographic Art
Analog photography offers a tangible, physical artifact through negatives and prints, providing a sense of permanence and authenticity often absent in digital images. Darkroom techniques allow artists to manipulate the chemical process, creating unique textures and depth that digital files cannot replicate. Digital photography, while easily shareable and editable, relies on technology that risks data loss or format obsolescence, challenging the long-term preservation of photographic art.
Environmental Impact: Film vs Digital Media
Analog photography relies on chemical processing of film, which involves toxic substances such as silver halide, lead, and other heavy metals that can harm the environment if improperly disposed. Digital photography, while energy-intensive during manufacturing and use of electronic devices, eliminates chemical waste and reduces the need for physical materials like film and photo paper. Considering the lifecycle emissions, analog photography generally has a higher environmental impact due to chemical pollutants and resource-intensive production processes associated with film development.
Future Trends in Photographic Art
Emerging AI-enhanced digital cameras and deep learning algorithms are shaping the future trends in photographic art, enabling unprecedented creativity and precision that surpass analog limitations. Innovation in hybrid workflows combines analog film aesthetics with digital post-processing, preserving traditional textures while expanding artistic possibilities. Market demand for sustainable and experimental methods fuels investment in eco-friendly analog materials and cutting-edge computational photography techniques.
analog photography vs digital photography Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com