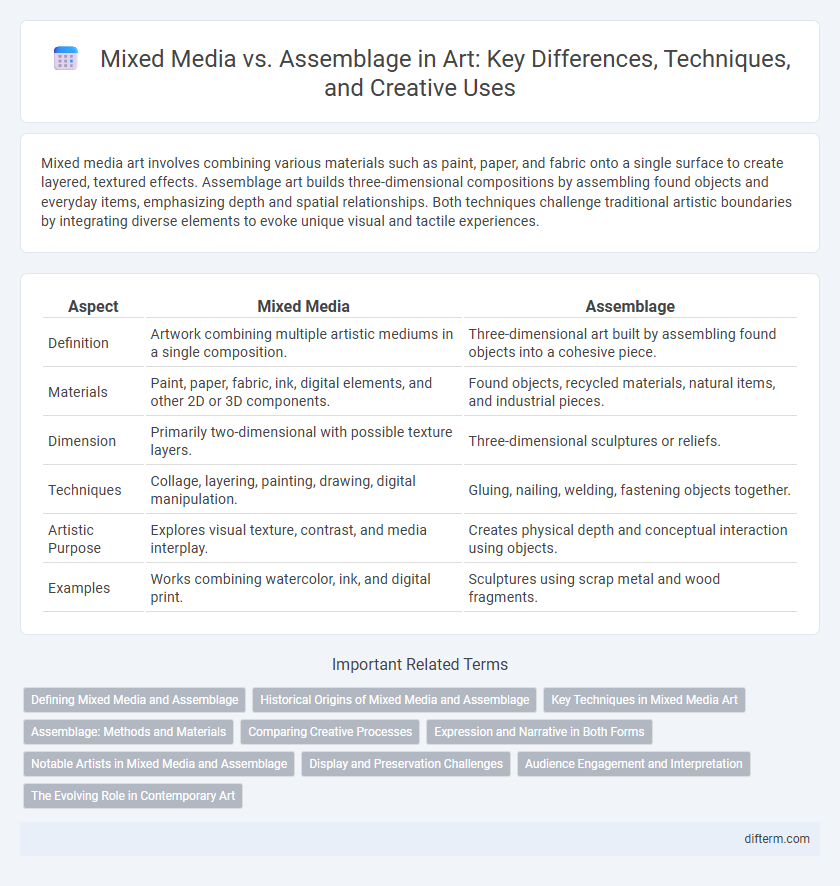
Mixed media art involves combining various materials such as paint, paper, and fabric onto a single surface to create layered, textured effects. Assemblage art builds three-dimensional compositions by assembling found objects and everyday items, emphasizing depth and spatial relationships. Both techniques challenge traditional artistic boundaries by integrating diverse elements to evoke unique visual and tactile experiences.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mixed Media | Assemblage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artwork combining multiple artistic mediums in a single composition. | Three-dimensional art built by assembling found objects into a cohesive piece. |
| Materials | Paint, paper, fabric, ink, digital elements, and other 2D or 3D components. | Found objects, recycled materials, natural items, and industrial pieces. |
| Dimension | Primarily two-dimensional with possible texture layers. | Three-dimensional sculptures or reliefs. |
| Techniques | Collage, layering, painting, drawing, digital manipulation. | Gluing, nailing, welding, fastening objects together. |
| Artistic Purpose | Explores visual texture, contrast, and media interplay. | Creates physical depth and conceptual interaction using objects. |
| Examples | Works combining watercolor, ink, and digital print. | Sculptures using scrap metal and wood fragments. |
Defining Mixed Media and Assemblage
Mixed media art combines various artistic materials such as paint, ink, fabric, and paper on a single surface, emphasizing texture and layered composition. Assemblage involves creating three-dimensional works by assembling found objects and non-traditional materials into sculptural forms. Both techniques blur traditional boundaries, but mixed media remains two-dimensional while assemblage occupies physical space.
Historical Origins of Mixed Media and Assemblage
Mixed media art originated in the early 20th century with Cubist artists like Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, who integrated collage elements into traditional painting to challenge conventional forms. Assemblage emerged slightly later, gaining prominence in the 1950s through artists such as Joseph Cornell and Robert Rauschenberg, who constructed three-dimensional works by combining found objects. Both movements reflect a shift towards experimentation and the breaking of boundaries between artistic disciplines during modernism.
Key Techniques in Mixed Media Art
Key techniques in mixed media art include layering diverse materials such as paint, fabric, paper, and found objects to create textured, multidimensional surfaces. Artists utilize collage methods, combining both two-dimensional and three-dimensional elements, often incorporating unconventional tools like stencils, stamps, and digital prints to enhance visual depth. Experimentation with adhesives, varnishes, and mediums allows seamless integration of disparate components, producing dynamic compositions that challenge traditional boundaries.
Assemblage: Methods and Materials
Assemblage art involves creating three-dimensional compositions by combining found objects and materials, such as wood, metal, fabric, and paper, into a unified artwork. This method emphasizes the tactile manipulation and spatial arrangement of disparate elements, often incorporating techniques like welding, gluing, and nailing to secure components firmly. The choice of materials ranges from everyday items to recycled industrial parts, allowing artists to explore texture, form, and narrative through physical layering and juxtaposition.
Comparing Creative Processes
Mixed media combines various artistic materials like paint, ink, and collage elements on a single surface, fostering spontaneous layering and textural exploration. Assemblage involves constructing three-dimensional artworks by assembling found objects, emphasizing spatial relationships and physical composition. Both techniques encourage experimentation, but mixed media prioritizes surface interaction while assemblage focuses on volumetric arrangement.
Expression and Narrative in Both Forms
Mixed media combines diverse materials and techniques, allowing artists to layer textures and colors that evoke complex emotions and multifaceted narratives. Assemblage, defined by the physical assembly of found objects, creates tangible storytelling through spatial relationships and symbolic juxtaposition. Both forms amplify expression by transforming ordinary elements into immersive visual dialogues that engage viewers in interpreting layered meanings.
Notable Artists in Mixed Media and Assemblage
Notable artists in mixed media include Robert Rauschenberg, known for his "Combines" that integrate painting and sculpture, and Pablo Picasso, who pioneered collages incorporating diverse materials. Assemblage artists like Louise Nevelson and Joseph Cornell gained acclaim for creating intricate three-dimensional compositions from found objects. Both art forms emphasize combining various materials, but mixed media often involves layering different artistic techniques, while assemblage focuses on constructing with physical objects.
Display and Preservation Challenges
Mixed media artworks, combining various materials like paint, fabric, and found objects, require careful display to avoid damage from light, humidity, and physical stress due to their diverse textures and fragility. Assemblage art, constructed from three-dimensional objects, faces preservation challenges including structural stability and material degradation, necessitating tailored supports and controlled environments. Both mediums demand specialized conservation techniques to maintain their integrity and visual impact over time.
Audience Engagement and Interpretation
Mixed media art combines diverse materials and techniques, encouraging audiences to explore layered textures and meanings, which stimulates deeper interpretative engagement. Assemblage art uses found objects arranged in three-dimensional compositions, prompting viewers to connect disparate elements and uncover symbolic narratives. Both forms foster active participation by challenging traditional art boundaries and inviting personal interpretation through tactile and visual complexity.
The Evolving Role in Contemporary Art
Mixed media integrates diverse materials and techniques to expand artistic expression, blending painting, collage, and digital elements into cohesive narratives. Assemblage, rooted in the tradition of found objects and three-dimensional construction, challenges spatial perceptions and material hierarchies by recontextualizing everyday items. Contemporary art increasingly blurs boundaries between mixed media and assemblage, fostering innovation and critical dialogue on materiality and cultural identity.
Mixed media vs Assemblage Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com