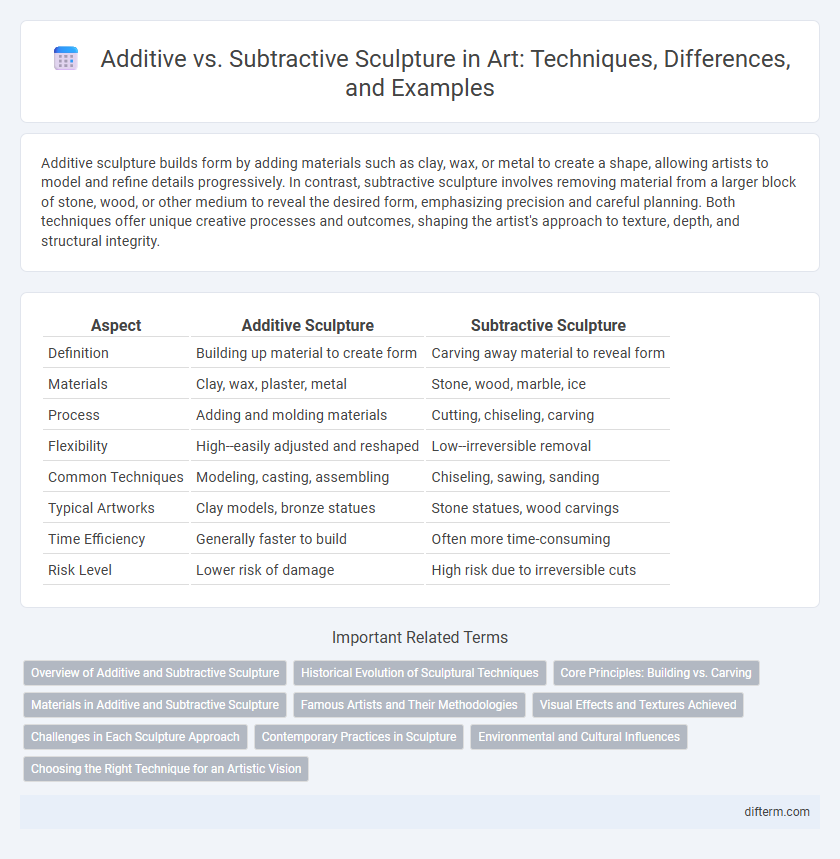
Additive sculpture builds form by adding materials such as clay, wax, or metal to create a shape, allowing artists to model and refine details progressively. In contrast, subtractive sculpture involves removing material from a larger block of stone, wood, or other medium to reveal the desired form, emphasizing precision and careful planning. Both techniques offer unique creative processes and outcomes, shaping the artist's approach to texture, depth, and structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Additive Sculpture | Subtractive Sculpture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building up material to create form | Carving away material to reveal form |
| Materials | Clay, wax, plaster, metal | Stone, wood, marble, ice |
| Process | Adding and molding materials | Cutting, chiseling, carving |
| Flexibility | High--easily adjusted and reshaped | Low--irreversible removal |
| Common Techniques | Modeling, casting, assembling | Chiseling, sawing, sanding |
| Typical Artworks | Clay models, bronze statues | Stone statues, wood carvings |
| Time Efficiency | Generally faster to build | Often more time-consuming |
| Risk Level | Lower risk of damage | High risk due to irreversible cuts |
Overview of Additive and Subtractive Sculpture
Additive sculpture involves building up material, such as clay, wax, or plaster, to create a form by adding elements gradually. Subtractive sculpture requires removing material from a solid block, typically stone or wood, by carving or chiseling to reveal the desired shape. Both techniques emphasize different creative processes, with additive allowing more flexibility and subtractive demanding precision and planning.
Historical Evolution of Sculptural Techniques
The historical evolution of sculptural techniques highlights a clear distinction between additive and subtractive methods, with additive sculpture emerging prominently in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt through clay modeling and metal casting. Subtractive sculpture, notably developed during the Classical Greek and Renaissance periods, involves carving materials like marble and wood to reveal form by removal. These contrasting techniques reflect cultural priorities and technological advancements that shaped artistic expression across eras.
Core Principles: Building vs. Carving
Additive sculpture involves constructing a form by assembling materials such as clay, metal, or plaster, emphasizing the creation of volume through layering and joining. Subtractive sculpture relies on carving away material from a solid mass like stone, wood, or marble, highlighting precision and material removal to reveal the desired shape. Understanding these core principles of building versus carving guides artists in selecting techniques based on the intended texture, form, and expressive qualities of the sculpture.
Materials in Additive and Subtractive Sculpture
Additive sculpture primarily uses malleable materials such as clay, wax, and plaster, allowing artists to build form by layering and shaping. Subtractive sculpture involves carving or chiseling away from solid blocks of stone, wood, or marble, demanding precision to reveal the final form. The choice of material directly influences the sculpting process and durability of the artwork.
Famous Artists and Their Methodologies
Auguste Rodin revolutionized additive sculpture by building forms through modeling clay and wax, allowing dynamic, expressive detail. In contrast, Michelangelo's subtractive approach involved meticulously carving marble, revealing intricate figures through removal of material. Contemporary artist Anish Kapoor combines both methods, layering materials additively before refining details subtractively to achieve his signature smooth, reflective surfaces.
Visual Effects and Textures Achieved
Additive sculpture techniques, such as clay modeling or wax building, allow artists to build up material layer by layer, creating smooth and intricate textures with a high level of detail and dynamic surface variations. Subtractive sculpture, often involving carving marble or wood, produces sharp, controlled edges and textures defined by the material's inherent grain and natural striations, resulting in a more tactile and raw visual effect. The interplay of light and shadow in additive works tends to emphasize volume and fluidity, whereas subtractive sculptures highlight structural form and surface contrasts.
Challenges in Each Sculpture Approach
Additive sculpture faces challenges in maintaining structural stability when building up materials like clay or wax, requiring careful layering and support to prevent collapse. Subtractive sculpture demands precision and skill in removing material from mediums such as marble or wood, where mistakes are irreversible and can compromise the entire piece. Both approaches require mastery over different tools and techniques to achieve the desired artistic expression without damaging the work.
Contemporary Practices in Sculpture
Contemporary practices in sculpture explore additive techniques such as welding, 3D printing, and assemblage, allowing artists to build complex forms from various materials like metal, plastic, and found objects. Subtractive methods involving carving and chiseling remain vital, offering tactile engagement with traditional materials like stone and wood to reveal inner structures. These approaches often merge, with artists employing hybrid processes to push conceptual boundaries and material innovation in modern sculpture.
Environmental and Cultural Influences
Additive sculpture, which involves building up materials like clay or metal, reflects cultures valuing creation and growth, often influenced by environmental availability of malleable resources. Subtractive sculpture, carved from stone or wood, is tied to societies with abundant natural stone or timber, emphasizing permanence and tradition shaped by landscape and climate. Environmental factors such as resource accessibility and cultural narratives directly shape the choice of sculptural method and artistic expression.
Choosing the Right Technique for an Artistic Vision
Additive sculpture involves building up material such as clay or wax to create form, allowing artists to experiment and modify shapes easily. Subtractive sculpture requires carving or chiseling materials like stone or wood, emphasizing precision and planning to reveal the desired figure from a solid block. Selecting the ideal technique depends on the artist's vision, material availability, and the intended texture or detail level in the artwork.
additive vs subtractive sculpture Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com