Additive sculpture involves building up a form by adding materials such as clay, wax, or metal, which allows for greater flexibility and detail throughout the creative process. Subtractive sculpture, on the other hand, requires removing material from a solid block, like stone or wood, demanding precision and planning to reveal the final shape. Both techniques offer unique artistic challenges and outcomes, influencing texture, form, and the overall expression of the artwork.
Table of Comparison
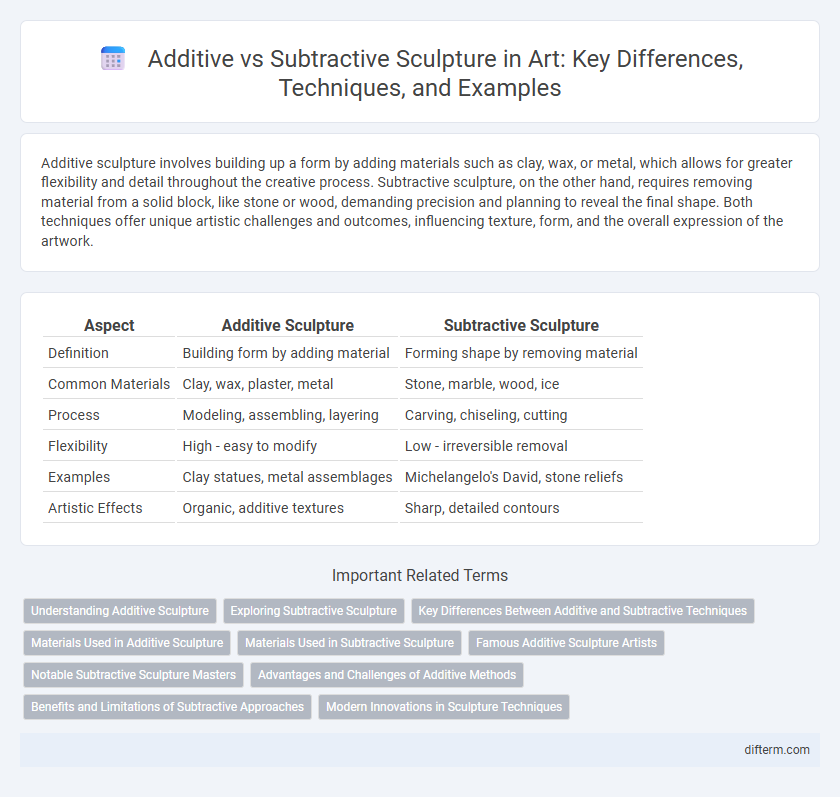
| Aspect | Additive Sculpture | Subtractive Sculpture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building form by adding material | Forming shape by removing material |
| Common Materials | Clay, wax, plaster, metal | Stone, marble, wood, ice |
| Process | Modeling, assembling, layering | Carving, chiseling, cutting |
| Flexibility | High - easy to modify | Low - irreversible removal |
| Examples | Clay statues, metal assemblages | Michelangelo's David, stone reliefs |
| Artistic Effects | Organic, additive textures | Sharp, detailed contours |
Understanding Additive Sculpture
Additive sculpture involves creating forms by assembling materials such as clay, metal, or wood, layer by layer, allowing for greater flexibility and experimentation in shapes and textures. This process contrasts with subtractive sculpture, which requires carving away from a solid block, often limiting modifications once material is removed. Understanding additive sculpture highlights its capacity for intricate, complex designs and its adaptability in contemporary art practices.
Exploring Subtractive Sculpture
Subtractive sculpture involves the meticulous process of removing material from a solid block, commonly using tools such as chisels, hammers, and rasps to reveal the desired form. This technique emphasizes precision and planning, typically employed with materials like marble, wood, or stone, where every removed fragment shapes the final artwork. Artists exploring subtractive sculpture must carefully navigate the permanence of material removal, fostering a deep understanding of texture, depth, and dimensionality in their creative process.
Key Differences Between Additive and Subtractive Techniques
Additive sculpture involves building up material, such as clay or wax, to create form, allowing for flexibility and continuous modification during the creative process. Subtractive sculpture requires removing material from a solid block, like marble or wood, demanding precision and planning to reveal the final shape. These fundamental differences influence both the artist's approach and the tactile qualities of the resulting artwork.
Materials Used in Additive Sculpture
Additive sculpture primarily utilizes materials such as clay, wax, plaster, and metal that can be easily molded and combined to build forms layer by layer. Common materials include polymers and resin, which offer flexibility and durability for intricate details and large-scale works. These substances enable artists to create volumetric and textured sculptures through the process of adding material instead of removing it.
Materials Used in Subtractive Sculpture
Subtractive sculpture primarily involves materials such as marble, limestone, wood, and alabaster, chosen for their ability to be carefully carved and shaped. These materials must possess sufficient hardness to allow detailed chipping or cutting while maintaining structural integrity. Artists often select stone or hardwood for subtractive works due to their durability and capacity to hold fine details during the removal process.
Famous Additive Sculpture Artists
Famous additive sculpture artists like Auguste Rodin, Alexander Calder, and Claes Oldenburg revolutionized the art world by building forms through assembling materials such as metal, clay, and found objects. Their work contrasts with subtractive sculpture, which involves carving away material from stone or wood. These pioneers expanded creative possibilities by layering, welding, and modeling, emphasizing construction over removal in three-dimensional art.
Notable Subtractive Sculpture Masters
Notable subtractive sculpture masters include Michelangelo, renowned for his detailed marble works such as "David," where form emerges through the removal of material. Auguste Rodin also excelled in subtractive techniques, creating dynamic figures from stone with expressive surface textures. These artists highlight the precision and vision required to reveal form by carving away from a solid block.
Advantages and Challenges of Additive Methods
Additive sculpture techniques enable artists to build forms layer by layer, allowing for greater flexibility in modifying shapes and incorporating intricate details not easily achieved through subtractive methods. These processes often utilize materials such as clay, wax, or 3D-printed polymers, broadening creative possibilities and reducing waste compared to carving methods. However, challenges include ensuring structural integrity during construction and the potential for longer completion times due to the layering process.
Benefits and Limitations of Subtractive Approaches
Subtractive sculpture, involving the removal of material to reveal form, offers precise control and the ability to work with dense, durable materials like stone or wood, resulting in timeless, textured artworks. Limitations include the irreversible nature of the process, which restricts flexibility and increases the risk of material waste or structural weaknesses if errors occur. Despite these challenges, subtractive techniques excel in producing detailed, monumental sculptures with a tangible connection to traditional craftsmanship.
Modern Innovations in Sculpture Techniques
Additive sculpture techniques, which involve building forms by adding materials like clay, metal, or resin, have advanced with the introduction of 3D printing and digital modeling, enabling unprecedented precision and complexity. Subtractive sculpture, traditionally reliant on carving materials such as stone or wood, now incorporates CNC machines and laser cutting technologies, allowing artists to achieve detailed and intricate designs more efficiently. Modern innovations blend these approaches, fostering hybrid techniques that expand creative possibilities within contemporary sculpture.
additive sculpture vs subtractive sculpture Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com