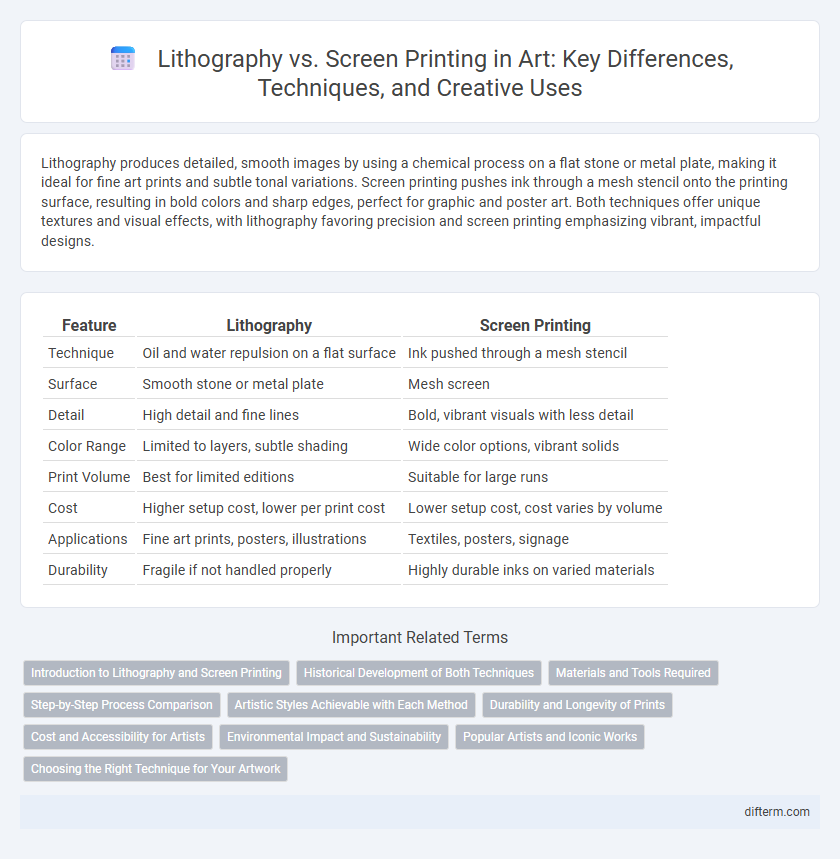
Lithography produces detailed, smooth images by using a chemical process on a flat stone or metal plate, making it ideal for fine art prints and subtle tonal variations. Screen printing pushes ink through a mesh stencil onto the printing surface, resulting in bold colors and sharp edges, perfect for graphic and poster art. Both techniques offer unique textures and visual effects, with lithography favoring precision and screen printing emphasizing vibrant, impactful designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lithography | Screen Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Oil and water repulsion on a flat surface | Ink pushed through a mesh stencil |
| Surface | Smooth stone or metal plate | Mesh screen |
| Detail | High detail and fine lines | Bold, vibrant visuals with less detail |
| Color Range | Limited to layers, subtle shading | Wide color options, vibrant solids |
| Print Volume | Best for limited editions | Suitable for large runs |
| Cost | Higher setup cost, lower per print cost | Lower setup cost, cost varies by volume |
| Applications | Fine art prints, posters, illustrations | Textiles, posters, signage |
| Durability | Fragile if not handled properly | Highly durable inks on varied materials |
Introduction to Lithography and Screen Printing
Lithography is a printmaking technique that relies on the immiscibility of oil and water to transfer ink from a flat stone or metal plate to paper, enabling detailed and precise images. Screen printing, also known as serigraphy, involves pushing ink through a stenciled mesh screen onto various surfaces, producing vibrant and bold prints ideal for textiles and posters. Both methods offer unique artistic effects, with lithography favored for fine lines and gradients, while screen printing excels in color saturation and texture.
Historical Development of Both Techniques
Lithography, invented by Alois Senefelder in 1796, revolutionized printmaking by using a flat stone surface and grease-based inks to create detailed images. Screen printing, with origins tracing back to ancient China but modernized in the early 20th century by artists like Andy Warhol, employs a stencil and mesh screen to transfer ink onto various surfaces. Both techniques evolved significantly through technological advancements, enabling diverse artistic expressions and commercial applications.
Materials and Tools Required
Lithography requires materials such as limestone or aluminum plates, greasy pencils or crayons, and chemical solutions for etching and fixing images, while screen printing involves mesh screens, squeegees, photo emulsion, and various inks. The precision of lithography depends on the quality of the limestone or plate surface and the grease application, whereas screen printing's effectiveness relies on tensioned mesh screens and stencil creation. Both techniques demand specialized tools tailored to their unique processes, with lithography emphasizing chemical preparation and screen printing focusing on stencil and ink application.
Step-by-Step Process Comparison
Lithography involves preparing a flat stone or metal plate with a greasy substance, then treating it chemically to retain ink only on the drawn areas, followed by pressing paper onto the inked surface to create the print. Screen printing requires creating a stencil on a fine mesh screen, forcing ink through the open areas with a squeegee onto the printing surface, allowing for vibrant color layering. While lithography relies on chemical repulsion between oil and water for image transfer, screen printing uses physical stenciling to achieve bold, opaque prints ideal for fabric and posters.
Artistic Styles Achievable with Each Method
Lithography enables artists to achieve fine, detailed textures and gradients due to its capacity for subtle tonal variations, ideal for realistic and delicate artistic styles. Screen printing is suited for bold, vibrant colors and sharp, graphic designs, making it popular for pop art and contemporary visual expressions. Each technique offers distinct advantages, influencing the aesthetic outcome according to the desired artistic style and medium characteristics.
Durability and Longevity of Prints
Lithography offers exceptional durability due to its ability to produce fine, stable images that resist fading over time, making it ideal for archival prints. Screen printing uses thicker layers of ink which create robust, vibrant prints with superior resistance to wear and environmental factors such as UV exposure and moisture. Both techniques ensure longevity, but screen printing's ink density often results in longer-lasting color retention for outdoor and functional art applications.
Cost and Accessibility for Artists
Lithography typically involves higher initial setup costs due to specialized materials and equipment, making it less accessible for emerging artists compared to screen printing. Screen printing offers more affordable tools and quicker production, enabling artists to create multiple copies at lower cost. This affordability and ease of use make screen printing a popular choice for artists seeking budget-friendly and scalable printmaking techniques.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lithography and screen printing differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability; lithography uses chemical solvents and metal plates that can generate hazardous waste, while screen printing often involves water-based inks and reusable mesh screens, reducing toxic emissions. Screen printing tends to be more eco-friendly due to its lower energy consumption and the recyclability of materials, whereas lithography's reliance on petroleum-based inks and cleaning agents poses greater environmental risks. Choosing sustainable art practices favors screen printing for minimizing pollution and promoting resource conservation.
Popular Artists and Iconic Works
Andy Warhol revolutionized screen printing with his vibrant, repetitive images like the Marilyn Monroe series, making it a hallmark of pop art. Meanwhile, lithography was favored by artists such as Pablo Picasso and Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec for its ability to capture fine detail and subtle gradations, exemplified in Toulouse-Lautrec's Moulin Rouge posters. Both techniques have deeply influenced modern art, with screen printing emphasizing bold color contrasts and lithography showcasing intricate line work and texture.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Artwork
Choosing between lithography and screen printing depends on the desired texture and detail of the artwork. Lithography excels in capturing fine gradients and subtle shading, making it ideal for detailed, photo-realistic images, while screen printing is favored for bold, vibrant colors and graphic designs with sharp edges. Consider the production scale and material compatibility, as lithography suits paper-based projects and smaller editions, whereas screen printing accommodates various surfaces and larger print runs.
Lithography vs Screen printing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com