Traditional art emphasizes skillful craftsmanship and realistic representation using established techniques such as painting and sculpture. Conceptual art prioritizes ideas and meaning over aesthetic form, often challenging conventional perceptions and encouraging intellectual engagement. The contrast between these approaches highlights evolving definitions of artistic value and expression in contemporary culture.
Table of Comparison
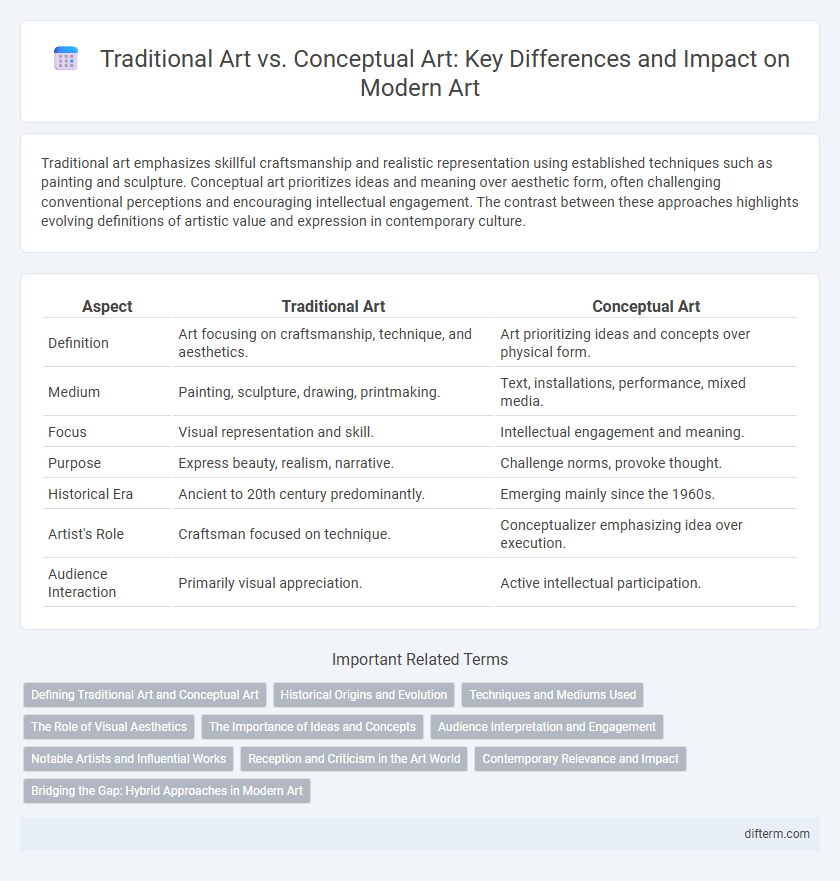
| Aspect | Traditional Art | Conceptual Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art focusing on craftsmanship, technique, and aesthetics. | Art prioritizing ideas and concepts over physical form. |
| Medium | Painting, sculpture, drawing, printmaking. | Text, installations, performance, mixed media. |
| Focus | Visual representation and skill. | Intellectual engagement and meaning. |
| Purpose | Express beauty, realism, narrative. | Challenge norms, provoke thought. |
| Historical Era | Ancient to 20th century predominantly. | Emerging mainly since the 1960s. |
| Artist's Role | Craftsman focused on technique. | Conceptualizer emphasizing idea over execution. |
| Audience Interaction | Primarily visual appreciation. | Active intellectual participation. |
Defining Traditional Art and Conceptual Art
Traditional art emphasizes skillful craftsmanship and the use of established techniques to create visually appealing works such as paintings, sculptures, and drawings. Conceptual art prioritizes ideas and intellectual engagement over aesthetic form, often challenging conventional notions of art by focusing on meaning and concept rather than visual representation. Understanding these distinctions highlights how traditional art values tangible creation while conceptual art centers around the artist's message and innovation.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Traditional art, rooted in ancient civilizations, emphasizes realistic representation and skilled craftsmanship, evolving through periods like the Renaissance and Baroque that prioritized form and technique. Conceptual art emerged in the 20th century, challenging these conventions by prioritizing ideas over aesthetics, influenced by movements such as Dada, Surrealism, and Fluxus. The evolution highlights a shift from tangible artistry to intellectual engagement, reflecting broader cultural changes in the understanding of art's purpose.
Techniques and Mediums Used
Traditional art employs established techniques such as oil painting, watercolor, sculpture, and drawing, often emphasizing mastery of form, color, and composition using physical mediums like canvas, clay, and paper. Conceptual art prioritizes ideas over aesthetics, frequently utilizing non-traditional mediums including installations, performance, text, and digital media to convey meaning beyond conventional craftsmanship. The contrast in techniques and mediums highlights traditional art's reliance on tangible artistic skills, whereas conceptual art explores innovation and intellectual engagement through diverse and experimental formats.
The Role of Visual Aesthetics
Traditional art emphasizes visual aesthetics through techniques like symmetry, color harmony, and realistic representation, prioritizing sensory appeal and craftsmanship. Conceptual art shifts focus from visual aesthetics to ideas and meanings, often using minimal or unconventional forms to challenge perceptions. The role of visual aesthetics in conceptual art serves as a vehicle to support the underlying concept rather than being the central element.
The Importance of Ideas and Concepts
Traditional art emphasizes mastery of techniques, form, and aesthetics, often reflecting cultural heritage and historical context. Conceptual art prioritizes the underlying ideas and concepts, challenging viewers to engage intellectually rather than solely visually. The importance of ideas in conceptual art expands artistic expression beyond physical representation, fostering critical thinking and redefinition of what art can be.
Audience Interpretation and Engagement
Traditional art often emphasizes visual craftsmanship and recognizable subjects, inviting audiences to appreciate technical skill and aesthetic beauty. Conceptual art prioritizes ideas and challenges viewers to actively interpret meaning, fostering deeper intellectual engagement and personal reflection. Audience interaction shifts from passive observation in traditional art to an active dialogue in conceptual art, enhancing interpretive diversity.
Notable Artists and Influential Works
Notable artists in traditional art include Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Rembrandt, whose works such as the Mona Lisa, the Sistine Chapel ceiling, and The Night Watch remain iconic. In contrast, conceptual art features pioneers like Marcel Duchamp, Joseph Kosuth, and Yoko Ono, known for pieces like Fountain, One and Three Chairs, and Grapefruit, which challenge conventional aesthetics and emphasize ideas over form. These influential works highlight the evolution of artistic expression from skill-based craftsmanship to idea-centered creation, shaping contemporary art discourse.
Reception and Criticism in the Art World
Traditional art, rooted in techniques like painting and sculpture, often garners appreciation for its craftsmanship and aesthetic qualities, appealing to both critics and general audiences. Conceptual art, emphasizing ideas over visual form, frequently sparks polarized reception, with some critics valuing its intellectual engagement while others question its artistic legitimacy. The art world continues to debate the impact of these differing approaches on cultural value and artistic innovation.
Contemporary Relevance and Impact
Traditional art, characterized by classical techniques and representational forms, continues to influence contemporary culture through its emphasis on craftsmanship and aesthetic beauty, often serving as a foundation for emerging artists. Conceptual art prioritizes ideas over aesthetics, challenging viewers to engage intellectually and question societal norms, which drives much of today's critical discourse and innovation in galleries and museums. Both forms shape contemporary relevance by balancing historical continuity with progressive explorations, impacting art markets, exhibitions, and cultural conversations worldwide.
Bridging the Gap: Hybrid Approaches in Modern Art
Hybrid approaches in modern art merge traditional techniques such as painting and sculpture with conceptual frameworks that emphasize idea over form, creating innovative expressions. Artists integrate tangible craftsmanship with abstract concepts to challenge viewers' perceptions and expand the boundaries of artistic practice. This fusion fosters a dynamic dialogue between materiality and meaning, reshaping contemporary art's landscape.
Traditional Art vs Conceptual Art Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com