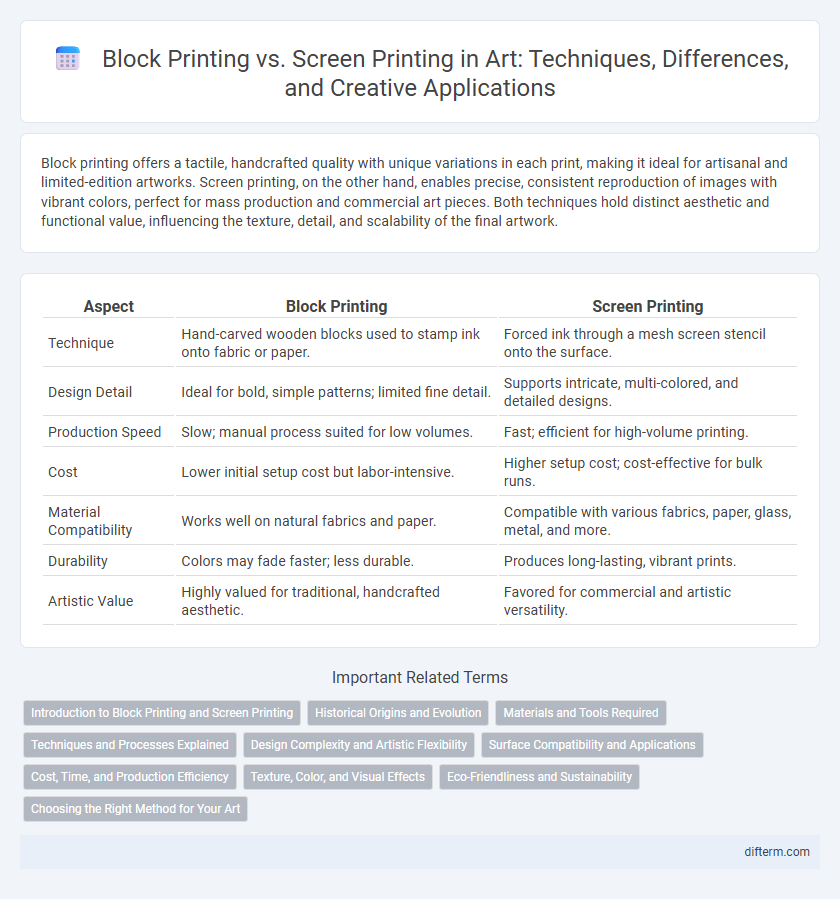
Block printing offers a tactile, handcrafted quality with unique variations in each print, making it ideal for artisanal and limited-edition artworks. Screen printing, on the other hand, enables precise, consistent reproduction of images with vibrant colors, perfect for mass production and commercial art pieces. Both techniques hold distinct aesthetic and functional value, influencing the texture, detail, and scalability of the final artwork.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Block Printing | Screen Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Hand-carved wooden blocks used to stamp ink onto fabric or paper. | Forced ink through a mesh screen stencil onto the surface. |
| Design Detail | Ideal for bold, simple patterns; limited fine detail. | Supports intricate, multi-colored, and detailed designs. |
| Production Speed | Slow; manual process suited for low volumes. | Fast; efficient for high-volume printing. |
| Cost | Lower initial setup cost but labor-intensive. | Higher setup cost; cost-effective for bulk runs. |
| Material Compatibility | Works well on natural fabrics and paper. | Compatible with various fabrics, paper, glass, metal, and more. |
| Durability | Colors may fade faster; less durable. | Produces long-lasting, vibrant prints. |
| Artistic Value | Highly valued for traditional, handcrafted aesthetic. | Favored for commercial and artistic versatility. |
Introduction to Block Printing and Screen Printing
Block printing involves carving a design into a wooden or linoleum block, applying ink to the raised surface, and pressing it onto fabric or paper to create repeated patterns with rich textures. Screen printing uses a mesh screen to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas blocked by a stencil, enabling precise, vibrant, and multi-colored designs ideal for textiles and posters. Both techniques offer unique tactile qualities and artistic versatility, but block printing is often valued for its handcrafted, organic feel while screen printing excels in speed and color consistency.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Block printing originated in ancient China around the Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD), where artisans carved designs onto wooden blocks to transfer ink onto fabric or paper. Screen printing emerged much later in early 20th-century Japan and the United States, evolving with the development of stencils and mesh screens to produce sharper, more versatile images. Both techniques have significantly influenced textile and art production, adapting over centuries with technological advancements to meet contemporary artistic demands.
Materials and Tools Required
Block printing requires carving tools, wooden or linoleum blocks, and oil-based or water-based inks that adhere well to the block surface, while screen printing utilizes a mesh screen, squeegee, stencil, and screen printing ink designed for fabric or paper. The durability of materials in block printing depends on the hardness of the block and quality of carving tools, whereas screen printing demands precise stencils and tensioned mesh screens to achieve clean prints. Ink consistency and drying time vary, with block printing inks being thicker, while screen printing inks are more fluid for even application through the screen mesh.
Techniques and Processes Explained
Block printing involves carving a design into a wooden or linoleum block, applying ink, and pressing it onto fabric or paper, creating textured, hand-crafted patterns with slight variations in each print. Screen printing uses a mesh stencil to transfer ink onto a surface, allowing for bold, consistent, and multi-colored designs through layering, ideal for mass production. Both techniques require precise alignment and multiple steps, but block printing emphasizes manual craftsmanship while screen printing leverages mechanical precision.
Design Complexity and Artistic Flexibility
Block printing offers limited design complexity due to its reliance on hand-carved wooden blocks, making intricate patterns difficult to achieve. Screen printing enables higher artistic flexibility by using stencils and mesh screens, which allow detailed and multi-colored designs with precision. The choice between the two methods significantly impacts the level of detail and color variation possible in the final artwork.
Surface Compatibility and Applications
Block printing excels on textured and uneven surfaces such as fabric and handmade paper, providing distinct, bold impressions ideal for artisanal crafts and textiles. Screen printing offers greater versatility, effectively adhering to smooth surfaces like glass, metal, and plastic, making it a preferred choice for commercial applications including posters, apparel, and industrial labeling. Each technique's compatibility with specific surfaces directly influences its practical use, with block printing favoring organic materials and screen printing catering to a broader range of substrates.
Cost, Time, and Production Efficiency
Block printing involves manually carving and stamping designs onto fabric, resulting in higher labor costs and longer production time compared to screen printing. Screen printing uses stencils and mesh screens to quickly produce large quantities, offering greater production efficiency and lower overall cost per unit. For extensive runs, screen printing is more cost-effective and faster, while block printing suits small-batch or artisanal projects due to its detailed and unique finish.
Texture, Color, and Visual Effects
Block printing produces unique texture through hand-carved wooden blocks, creating raised, tactile patterns with slight variances in ink application that add depth and character. Screen printing offers vibrant, consistent color saturation by forcing ink through a mesh screen, enabling smooth gradients and sharp edges suited for precise designs. The visual effects of block printing are organic and rustic, while screen printing achieves bold, clean lines and layered color effects ideal for modern, graphic artwork.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Block printing uses hand-carved wooden blocks and natural dyes, producing minimal waste and relying on renewable materials, making it highly eco-friendly and sustainable. Screen printing often involves synthetic inks and water-heavy processes, resulting in more chemical runoff and higher environmental impact. Choosing block printing supports sustainable art practices by reducing pollution and promoting resource conservation.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Art
Block printing offers tactile texture and unique, handcrafted qualities ideal for limited editions or intricate patterns, while screen printing excels in producing vibrant, consistent colors suitable for large-scale runs and detailed designs. Consider the complexity of your artwork, desired color richness, and production volume when choosing between these methods. Evaluating factors such as material compatibility, time investment, and budget will help determine the best printing technique for your artistic vision.
Block printing vs Screen printing Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com